Bicipital groove
| Intertubercular groove | |
|---|---|
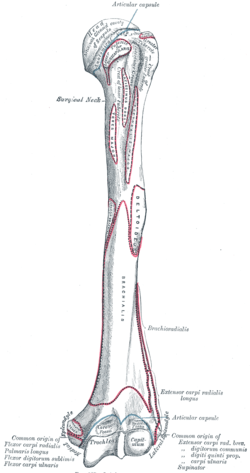 Left humerus. Anterior view. (Intertubercular groove visible at top.) | |
| Details | |
| Latin | sulcus intertubercularis humeri |
| Identifiers | |
| Gray's | p.209 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | s_28/12768832 |
| TA | A02.4.04.007 |
| FMA | 74573 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus are separated from each other by a deep groove, the intertubercular groove (bicipital groove, sulcus intertubercular), which lodges the long tendon of the Biceps Brachii muscle between the tendons of Pectoralis Major on the lateral lip and Teres Major on the medial lip. It also transmits a branch of the anterior humeral circumflex artery to the shoulder-joint.
The insertion of Latissimus Dorsi is found along the floor of the intertubercular sulcus.
It runs obliquely downward, and ends near the junction of the upper with the middle third of the bone.
It is the lateral wall of the axilla.[1]
See also
- radial groove
- medial bicipital groove
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ "Dissector Answers - Axilla and Arm". Archived from the original on 2007-12-10. Retrieved 2007-12-23.
External links
- Anatomy photo:03:st-0204 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||