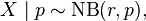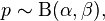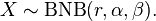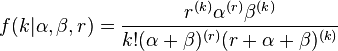Beta negative binomial distribution
| Parameters |
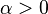 shape (real) shape (real)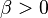 shape (real) shape (real) 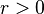 — number of failures until the experiment is stopped (integer but can be extended to real) — number of failures until the experiment is stopped (integer but can be extended to real) |
|---|---|
| Support | k ∈ { 0, 1, 2, 3, ... } |
| pmf |
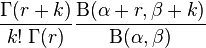 |
| Mean |
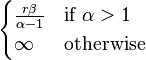 |
| Variance |
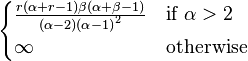 |
| Skewness |
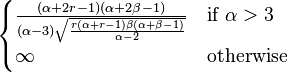 |
| MGF | undefined |
| CF |
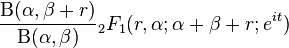 |
In probability theory, a beta negative binomial distribution is the probability distribution of a discrete random variable X equal to the number of failures needed to get r successes in a sequence of independent Bernoulli trials where the probability p of success on each trial is constant within any given experiment but is itself a random variable following a beta distribution, varying between different experiments. Thus the distribution is a compound probability distribution.
This distribution has also been called both the inverse Markov-Pólya distribution and the generalized Waring distribution.[1] A shifted form of the distribution has been called the beta-Pascal distribution.[1]
If parameters of the beta distribution are α and β, and if
where
then the marginal distribution of X is a beta negative binomial distribution:
In the above, NB(r, p) is the negative binomial distribution and B(α, β) is the beta distribution.
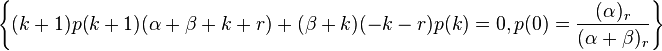
Definition
If  is an integer, then the PMF can be written in terms of the beta function,:
is an integer, then the PMF can be written in terms of the beta function,:
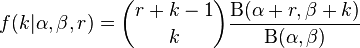 .
.
More generally the PMF can be written
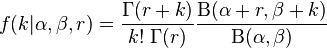 .
.
PMF expressed with Gamma
Using the properties of the Beta function, the PMF with integer  can be rewritten as:
can be rewritten as:
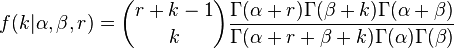 .
.
More generally, the PMF can be written as
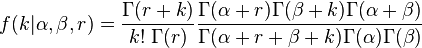 .
.
PMF expressed with the rising Pochammer symbol
The PMF is often also presented in terms of the Pochammer symbol for integer 
Properties
The beta negative binomial distribution contains the beta geometric distribution as a special case when 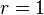 . It can therefore approximate the geometric distribution arbitrarily well. It also approximates the negative binomial distribution arbitrary well for large
. It can therefore approximate the geometric distribution arbitrarily well. It also approximates the negative binomial distribution arbitrary well for large 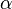 and
and 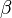 . It can therefore approximate the Poisson distribution arbitrarily well for large
. It can therefore approximate the Poisson distribution arbitrarily well for large 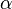 ,
, 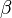 and
and  .
.
Notes
References
- Jonhnson, N.L.; Kotz, S.; Kemp, A.W. (1993) Univariate Discrete Distributions, 2nd edition, Wiley ISBN 0-471-54897-9 (Section 6.2.3)
- Kemp, C.D.; Kemp, A.W. (1956) "Generalized hypergeometric distributions, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 18, 202–211
- Wang, Zhaoliang (2011) "One mixed negative binomial distribution with application", Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 141 (3), 1153-1160 doi:10.1016/j.jspi.2010.09.020
External links
- Interactive graphic: Univariate Distribution Relationships