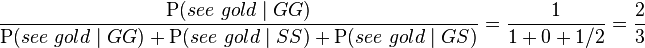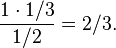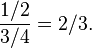Bertrand's box paradox
Bertrand's box paradox is a classic paradox of elementary probability theory. It was first posed by Joseph Bertrand in his Calcul des probabilités, published in 1889.
There are three boxes:
- a box containing two gold coins,
- a box containing two silver coins,
- a box containing one gold coin and one silver coin.
After choosing a box at random and withdrawing one coin at random, if that happens to be a gold coin, it may seem that the probability that the remaining coin is gold is 1⁄2; in fact, the probability is actually 2⁄3. Two problems that are very similar are the Monty Hall problem and the Three Prisoners problem.
These simple but counterintuitive puzzles are used as a standard example in teaching probability theory. Their solution illustrates some basic principles, including the Kolmogorov axioms.
Box version
There are three boxes, each with one drawer on each of two sides. Each drawer contains a coin. One box has a gold coin on each side (GG), one a silver coin on each side (SS), and the other a gold coin on one side and a silver coin on the other (GS). A box is chosen at random, a random drawer is opened, and a gold coin is found inside it. What is the chance of the coin on the other side being gold?
The following reasoning appears to give a probability of 1⁄2:
- Originally, all three boxes were equally likely to be chosen.
- The chosen box cannot be box SS.
- So it must be box GG or GS.
- The two remaining possibilities are equally likely. So the probability that the box is GG, and the other coin is also gold, is 1⁄2.
The flaw is in the last step. While those two cases were originally equally likely, the fact that you are certain to find a gold coin if you had chosen the GG box, but are only 50% sure of finding a gold coin if you had chosen the GS box, means they are no longer equally likely given that you have found a gold coin. Specifically:
- The probability that GG would produce a gold coin is 1.
- The probability that SS would produce a gold coin is 0.
- The probability that GS would produce a gold coin is 1⁄2.
Initially GG, SS and GS are equally likely. Therefore by Bayes rule the conditional probability that the chosen box is GG, given we have observed a gold coin, is:
The correct answer of 2⁄3 can also be obtained as follows:
- Originally, all six coins were equally likely to be chosen.
- The chosen coin cannot be from drawer S of box GS, or from either drawer of box SS.
- So it must come from the G drawer of box GS, or either drawer of box GG.
- The three remaining possibilities are equally likely, so the probability that the drawer is from box GG is 2⁄3.
Alternatively, one can simply note that the chosen box has two coins of the same type 2⁄3 of the time. So, regardless of what kind of coin is in the chosen drawer, the box has two coins of that type 2⁄3 of the time. In other words, the problem is equivalent to asking the question "What is the probability that I will pick a box with two coins of the same color?".
Bertrand's point in constructing this example was to show that merely counting cases is not always proper. Instead, one should sum the probabilities that the cases would produce the observed result; and the two methods are equivalent only if this probability is either 1 or 0 in every case. This condition is correctly applied in the second solution method, but not in the first.
The paradox as stated by Bertrand
It can be easier to understand the correct answer if you consider the paradox as Bertrand originally described it. After a box has been chosen, but before a box is opened to let you observe a coin, the probability is 2/3 that the box has two of the same kind of coin. If the probability of "observing a gold coin" in combination with "the box has two of the same kind of coin" is 1/2, then the probability of "observing a silver coin" in combination with "the box has two of the same kind of coin" must also be 1/2. And if the probability that the box has two like coins changes to 1/2 no matter what kind of coin is shown, the probability would have to be 1/2 even if you hadn't observed a coin this way. Since we know his probability is 2/3, not 1/2, we have an apparent paradox. It can be resolved only by recognizing how the combination of "observing a gold coin" with each possible box can only affect the probability that the box was GS or SS, but not GG.
Card version
Suppose there are three cards:
- A black card that is black on both sides,
- A white card that is white on both sides, and
- A mixed card that is black on one side and white on the other.
All the cards are placed into a hat and one is pulled at random and placed on a table. The side facing up is black. What are the odds that the other side is also black?
The answer is that the other side is black with probability 2⁄3. However, common intuition suggests a probability of 1⁄2 either because there are two cards with black on them that this card could be, or because there are 3 white and 3 black sides and many people forget to eliminate the possibility of the "white card" in this situation (i.e. the card they flipped CANNOT be the "white card" because a black side was turned over).
In a survey of 53 Psychology freshmen taking an introductory probability course, 35 incorrectly responded 1⁄2; only 3 students correctly responded 2⁄3.
Another presentation of the problem is to say : pick a random card out of the three, what are the odds that it has the same color on the other side? Since only one card is mixed and two have the same color on their sides, it is easier to understand that the probability is 2⁄3. Also note that saying that the color is black (or the coin is gold) instead of white doesn't matter since it is symmetric: the answer is the same for white. So is the answer for the generic question 'same color on both sides'.
Preliminaries
To solve the problem, either formally or informally, one must assign probabilities to the events of drawing each of the six faces of the three cards. These probabilities could conceivably be very different; perhaps the white card is larger than the black card, or the black side of the mixed card is heavier than the white side. The statement of the question does not explicitly address these concerns. The only constraints implied by the Kolmogorov axioms are that the probabilities are all non-negative, and they sum to 1.
The custom in problems when one literally pulls objects from a hat is to assume that all the drawing probabilities are equal. This forces the probability of drawing each side to be 1⁄6, and so the probability of drawing a given card is 1⁄3. In particular, the probability of drawing the double-white card is 1⁄3, and the probability of drawing a different card is 2⁄3.
In question, however, one has already selected a card from the hat and it shows a black face. At first glance it appears that there is a 50/50 chance (i.e. probability 1⁄2) that the other side of the card is black, since there are two cards it might be: the black and the mixed. However, this reasoning fails to exploit all of the information; one knows not only that the card on the table has at least one black face, but also that in the population it was selected from, only 1 of the 3 black faces was on the mixed card.
An easy explanation is that to name the black sides as x, y and z where x and y are on the same card while z is on the mixed card, then the probability is divided on the 3 black sides with 1⁄3 each. thus the probability that we chose either x or y is the sum of their probabilities thus 2⁄3.
Solutions
Intuition
Intuition tells one that one is choosing a card at random. However, one is actually choosing a face at random. There are 6 faces, of which 3 faces are white and 3 faces are black. Two of the 3 black faces belong to the same card. The chance of choosing one of those 2 faces is 2⁄3. Therefore, the chance of flipping the card over and finding another black face is also 2⁄3. Another way of thinking about it is that the problem is not about the chance that the other side is black, it's about the chance that you drew the all black card. If you drew a black face, then it's twice as likely that that face belongs to the black card than the mixed card.
Alternately, it can be seen as a bet not on a particular color, but a bet that the sides match. Betting on a particular color regardless of the face shown, will always have a chance of 1⁄2. However, betting that the sides match is 2⁄3, because 2 cards match and 1 does not.
Labels
One solution method is to label the card faces, for example numbers 1 through 6. Label the faces of the black card 1 and 2; label the faces of the mixed card 3 (black) and 4 (white); and label the faces of the white card 5 and 6. The observed black face could be 1, 2, or 3, all equally likely; if it is 1 or 2, the other side is black, and if it is 3, the other side is white. The probability that the other side is black is 2⁄3. This probability can be derived in the following manner: Let random variable B equal the a black face (i.e. the probability of a success since the black face is what we are looking for). Using Kolmogrov's Axiom of all probabilities having to equal 1, we can conclude that the probability of drawing a white face is 1-P(B). Since P(B)=P(1)+P(2) therefore P(B)=1⁄3+1⁄3=2⁄3. Likewise we can do this P(white face)=1-2⁄3=1⁄3.
Bayes' theorem
Given that the shown face is black, the other face is black if and only if the card is the black card. If the black card is drawn, a black face is shown with probability 1. The total probability of seeing a black face is 1⁄2; the total probability of drawing the black card is 1⁄3. By Bayes' theorem, the conditional probability of having drawn the black card, given that a black face is showing, is
It can be more intuitive to present this argument using Bayes' rule rather than Bayes' theorem. Having seen a black face we can rule out the white card. We are interested in the probability that the card is black given a black face is showing. Initially it is equally likely that the card is black and that it is mixed: the prior odds are 1:1. Given that it is black we are certain to see a black face, but given that it is mixed we are only 50% certain to see a black face. The ratio of these probabilities, called the likelihood ratio or Bayes factor, is 2:1. Bayes' rule says "posterior odds equals prior odds times likelihood ratio". Since the prior odds are 1:1 the posterior odds equals the likelihood ratio, 2:1. It is now twice as likely that the card is black than that it is mixed.
Eliminating the white card
Although the incorrect solution reasons that the white card is eliminated, one can also use that information in a correct solution. Modifying the previous method, given that the white card is not drawn, the probability of seeing a black face is 3⁄4, and the probability of drawing the black card is 1⁄2. The conditional probability of having drawn the black card, given that a black face is showing, is
Symmetry
The probability (without considering the individual colors) that the hidden color is the same as the displayed color is clearly 2⁄3, as this holds if and only if the chosen card is black or white, which chooses 2 of the 3 cards. Symmetry suggests that the probability is independent of the color chosen, so that the information about which color is shown does not affect the odds that both sides have the same color.
This argument is correct and can be formalized as follows. By the law of total probability, the probability that the hidden color is the same as the displayed color equals the weighted average of the probabilities that the hidden color is the same as the displayed color, given that the displayed color is black or white respectively (the weights are the probabilities of seeing black and white respectively). By symmetry, the two conditional probabilities that the colours are the same given we see black and given we see white are the same. Since they moreover average out to 2/3 they must both be equal to 2/3.
Experiment
Using specially constructed cards, the choice can be tested a number of times. Let "B" denote the colour Black. By constructing a fraction with the denominator being the number of times "B" is on top, and the numerator being the number of times both sides are "B", the experimenter will probably find the ratio to be near 2⁄3.
Note the logical fact that the B/B card contributes significantly more (in fact twice) to the number of times "B" is on top. With the card B/W there is always a 50% chance W being on top, thus in 50% of the cases card B/W is drawn, the draw affects neither numerator nor denominator and effectively does not count (this is also true for all times W/W is drawn, so that card might as well be removed from the set altogether). Conclusively, the cards B/B and B/W are not of equal chances, because in the 50% of the cases B/W is drawn, this card is simply "disqualified".
Related problems
Notes and references
- ^ Bar-Hillel and Falk (page 119)
- ^ Nickerson (page 158) advocates this solution as "less confusing" than other methods.
- ^ Bar-Hillel and Falk (page 120) advocate using Bayes' Rule.
- Bar-Hillel, Maya; Falk, Ruma (1982). "Some teasers concerning conditional probabilities". Cognition 11 (2): 109–22. doi:10.1016/0010-0277(82)90021-X. PMID 7198956.
- Nickerson, Raymond (2004). Cognition and Chance: The psychology of probabilistic reasoning, Lawrence Erlbaum. Ch. 5, "Some instructive problems: Three cards", pp. 157–160. ISBN 0-8058-4898-3
- Michael Clark, Paradoxes from A to Z, p. 16;
- Howard Margolis, Wason, Monty Hall, and Adverse Defaults.