Benzothiophene
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
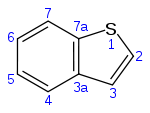
| IUPAC name
Benzo[b]thiophene | |
| Other names
1-Benzothiophene Thianaphthene Benzothiofuran | |
| Identifiers | |
| 95-15-8 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:35858 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL87112 |
| ChemSpider | 6951 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| RTECS number | 202-395-7 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C8H6S |
| Molar mass | 134.20 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.15 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 32 °C (90 °F; 305 K) |
| Boiling point | 221 °C (430 °F; 494 K) |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R22 |
| S-phrases | S22 S24/25 |
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Thiophene Indole Benzofuran |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Benzothiophene is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C8H6S and an odor similar to naphthalene (mothballs). It occurs naturally as a constituent of petroleum-related deposits such as lignite tar. Benzothiophene has no household use. It is used primarily in industry and research.
Being a heterocyclic compound, benzothiophene finds use in research as a starting material for the synthesis of larger, usually bioactive structures. It is found within the chemical structures of pharmaceutical drugs such as raloxifene, zileuton, and sertaconazole, and also BTCP. It is also used in the manufacturing of dyes such as thioindigo.
Its aromaticity makes it relatively stable, although as a heterocycle, it has reactive sites which allow for functionalization.
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9232
- ↑ 1-Benzothiophene at Sigma-Aldrich