Benfluralin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
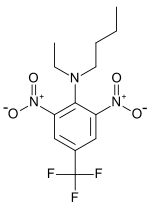
| IUPAC name
N-Butyl-N-ethyl-2,6-dinitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)aniline | |
| Other names
Benefin; Benfluraline; α,α,α-Trifluoro-2,6-dinitro-N,N-ethylbutyl-p-toluidine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1861-40-1 | |
| ChemSpider | 2229 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 2319 |
| |
| UNII | 28224BUY6R |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C13H16F3N3O4 |
| Molar mass | 335.28 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange crystalline solid[1] |
| Density | 1.338 g/mL |
| Melting point | 65.0 °C (149.0 °F; 338.1 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 121 °C (250 °F; 394 K)[1] at 0.6 mbar |
| 1 mg/L[1] | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Benfluralin is an herbicide of the dinitroaniline class.[2] It is used to control grasses and other weeds. Annual use in the United States was approximately 700,000 pounds in 2004.[3]
The mechanism of action of benfluralin involves inhibition of root and shoot development.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the IFA
- ↑ Benfluralin, alanwood.net
- ↑ R.E.D. FACTS: Benfluralin, United States Environmental Protection Agency
- ↑ Agrochemicals, Globachem
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||