Belastok Region
| Belastok Voblast Беластоцкая вобласць (Belarusian) Белостокская Область (Russian) Obwód białostocki (Polish) | |||||
| Voblast of the Byelorussian SSR | |||||
| |||||
|
Flag | |||||
| of which Belastok Voblast (left) was a part. | |||||
| Capital | Belastok (now Białystok) 53°08′N 23°09′E / 53.133°N 23.150°ECoordinates: 53°08′N 23°09′E / 53.133°N 23.150°E | ||||
| Historical era | World War II | ||||
| - | Established | November 1939 | |||
| - | Bezirk Bialystok established | 17 July 1941 | |||
| - | Red Army re-occupation | January 1945 | |||
| - | Disestablished | August 1945 | |||
| Political subdivisions | 24 raions (districts) | ||||
| Today part of | | ||||
Belastok Voblast or Belostok Oblast (Belarusian: Беластоцкая вобласць, Biełastockaja vobłasć, Russian: Белостокская Область, Polish: Obwód białostocki) was a short-lived territorial unit in the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR) during World War II from September 1939 until Operation Barbarossa of 22 June 1941. The administrative center of the newly created voblast was the Polish: Białystok renamed Belastok (Belarusian: Беласток).
Administrative units
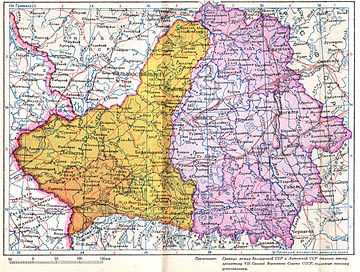
Belastok Voblast was created immediately following the Soviet invasion of Poland on 17 September 1939. It comprised part of the Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union assigned by Joseph Stalin to BSSR in November 1939 (part of the modern-day West Belarus).[1][2]
The Voblast consisted of 24 raions: Augustow, Bialystok, Belsky, Bryansk, Volkovysk, Grodno, Grajewo, Dombrowski, Zabludavski, Zambravski, Kolnavski, Krynkovsky, Lapski, Lomzhinsky, Monkavski (in the same year was renamed to Knyshynski), Porechsky ( in the same year transferred to the Lithuanian SSR ), Sakolkavski, Sapotskinsky, Skidelsky, Svislochsky, Snyadovski, Tsehanovetsky, Chyzhavski and Yadvabnavski .

According to Soviet statistical data, in the middle of 1940, the oblast had a population of 1,322,260, of whom 60.7% (802,770) were Poles, 22.7% (300,782) were Belarusians, 14.6% (193,510) were Jews, 0.63% (8,639) were Lithuanians, 0.09% (1,246) were Russians, and 1.15% (15,313) were "locals".[3]
In the aftermath of the German attack on the Soviet Union in June 1941, this western portion of then-Belarus, which until 1939 belonged to the Polish state was placed under German Civil Administration (Zivilverwaltungsgebiet). As Bezirk Bialystok, the area was under German rule from 1941 to 1944/45, without ever formally being incorporated into the German Reich.
After the Soviet liberation of the whole territory of Belarus in September 1944, the territory was administered by the BSSR, but according to the Border Agreement between Poland and the USSR of 16 August 1945, 17 raions, together with 3 raions of the Brest Voblast were passed on to the Białystok Voivodeship of Poland. The remaining raions were annexed into the Hrodna Voblast of the BSSR.
See also
- Polish population transfers (1944–1946)
- Curzon Line
Notes
- ↑ (Polish) Podział Polski między ZSRR i Trzecią Rzeszę według Paktu Ribbentrop-Mołotow
- ↑ Mapa podziału Polski. Podpisy: Stalin, Ribbentrop (German)
- ↑ (Polish) D. Boćkowski. Na zawsze razem. Białostocczyzna i Łomżyńskie w polityce radzieckiej w czasie II wojny światowej (IX 1939 – VIII 1944). Neriton, Instytut Historii PAN. 2005. pp. 115-116.
References
| ||||||||||
.svg.png)