Beach Abort
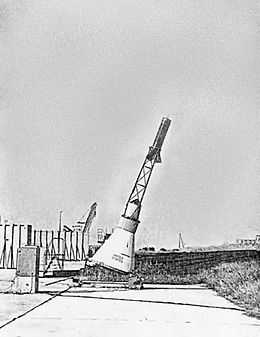 Spacecraft with launch escape system on the ground | |||||
| Mission type | Abort test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operator | NASA | ||||
| Mission duration | 1 minutes, 16 secondsec | ||||
| Distance travelled | 1.6 kilometres (1 mi) | ||||
| Apogee | 0.80 kilometres (0.5 mi) | ||||
| Spacecraft properties | |||||
| Spacecraft | Mercury No.1 | ||||
| Manufacturer | McDonnell Aircraft | ||||
| Launch mass | 1,007 kilograms (2,220 lb) | ||||
| Start of mission | |||||
| Launch date | May 9, 1960 | ||||
| Rocket | Mercury LES | ||||
| Launch site | Wallops | ||||
| End of mission | |||||
| Landing date | May 9, 1960 | ||||

| |||||
The Beach Abort was an unmanned test in NASA's Project Mercury, of the Mercury spacecraft Launch Escape System. Objectives of the test were a performance evaluation of the escape system, the parachute and landing system, and recovery operations in an off-the-pad abort situation. The test took place at NASA's Wallops Island, Virginia, test facility on May 9, 1960. In the test, the Mercury spacecraft and its Launch Escape System were fired from the ground level. The flight lasted 1 minute, 16 seconds and reached an apogee of 0.751 kilometres (2,465 ft) and a range of 0.97 kilometres (0.6 mi). A Marine Corps helicopter recovered the spacecraft 17 minutes after launch. Top speed was a velocity of 436 metres per second (976 mph). The test was considered a success, although there was insufficient separation distance when the tower jettisoned. Mercury Spacecraft #1, the first spacecraft off McDonnell's production line was used in this test. Total payload weight was 1,154 kg.
Mercury Spacecraft #1 is displayed at the New York Hall of Science, Corona Park, NY. It is displayed indoors, suspended from the ceiling, with an escape tower of unknown provenance attached.[1]

See also
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
External links
- This New Ocean: A History of Project Mercury - NASA SP-4201
- NASA NSSDC Master Catalog
- Video of Mercury Beach Abort Test
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
