Bayburt
| Bayburt | |
|---|---|
| Municipality | |
 Bayburt | |
| Coordinates: 40°15′35″N 40°13′40″E / 40.25972°N 40.22778°ECoordinates: 40°15′35″N 40°13′40″E / 40.25972°N 40.22778°E | |
| Country | Turkey |
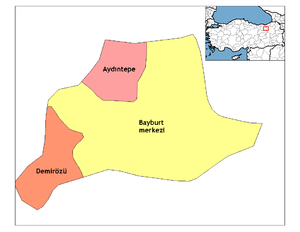
| Province | Bayburt |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Mete Memiş (AKP) |
| Area[1] | |
| • District | 2,655.41 km2 (1,025.26 sq mi) |
| Population (2012)[2] | |
| • Urban | 35,947 |
| • District | 61,354 |
| • District density | 23/km2 (60/sq mi) |
| Website |
www |
Bayburt (pronounced [ˈbajbuɾt]) is a city in northeast Turkey lying on the Çoruh River, and is the provincial capital of Bayburt Province.
Bayburt was once an important center on the ancient Silk Road and it was visited by Marco Polo and Turkish excursionist Evliya Celebi. Remains of its medieval castle still exist. There are several historical mosques, Turkish baths (Hamams) and tombstones in the city and ancient historical cites such as the Çatalçeşme Underground Complex and the natural wonders like Sirakayalar Waterfall in the other parts of the province.
History
Bayburt (From the Armenian: Բայտբերդ "Baydbert" (Bagratuni era) which in turn derives from Ամբատավան "Ambatavan" (Arsacid era)) was originally founded by the Azzi people. Groups who subsequently either settled in the area or dominated it include the Cimmerians in the 8th century BC, then in the 7th century BC the Medes, followed by the Persians, the Pontic Empire, the Roman, the Byzantines (who called it Paipert), the Bagratuni Armenian Kingdom, the Seljuk, Aq Qoyunlu, briefly Safavid and eventually under Ottoman.[3][4]
The town prospered in the late 13th and early 14th century because of the commerce between Trebizond and Iran.[5] It contained a Seljuk and Ilkhanid mint.[5] Under Ottoman rule the town was the center of the Bayburt sanjak. It served for some time in the early 16th century as the de facto capital of the Erzurum Eyalet before Erzurum town was rebuild.[5] The area was raided by the Safavids in 1553. Bayburt was captured by a Russian army in 1828/1829 and the town and citadel were largely damaged by them. The British traveller William John Hamilton commented on the ruins in the 1840s.[6]
Sights and activities
Parks and nature
Bayburt has many delightful parks and open spaces like "Gençlik Parkı" (Youth Park), "Şehit Nusret Bahçesi" (Martyr Nusret Gardens) and "Genç Osman Parkı" (Young Osman Park). The city has 535.780m² of nursery areas, where young plants are raised for the forests of Bayburt. Also there are two caves that visitors can see the interesting natural shapes of the stones. These caves are, "Çimağıl Mağarası" and "Helva Köyü Buz Mağarası".[7]
Universities
Bayburt University is located at the center of the city, university has several faculties such as Engineering, Arts and Sciences and Administrative Sciences. There are also several vocational schools.
Transportation
"Bayburt Otobus Terminali", located in the south of the city, is the main port to Bayburt.
Sports
The city has one football club currently competing in the Turkish Amateur Football Championship, struggling for promotion to the Turkish Third League, called Bayburtspor.Şalcilarspor played in the Second League between 1986-1988.
Bayburt Castle

This castle stands on the steep rocks north of Bayburt. When the It was held by the Bagratuni Dynasty (885-1044), who gave the castle the name it and the city is known for today. It was completely rebuilt by the Saltuk ruler Mugis-al-Din Tugrul Sah between 1200 and 1230, as attested by an inscription in the walls of the castle. The massive size of its walls and the quality of its masonry place it amongst the finest of all the castles in Anatolia but for its destruction by the Russians[5] during the early nineteenth century.[8] Rebuilding was done during the Ottoman period.[5] The castle was inhabited till the destruction of 1828.[5]
Çinimaçin among the people in the so-called Castle Castle, Dede Korkut stories "declares the length Beyrek BAMS Cam Buren Son" with the name of the story Beyrek'in (Mr. Böyrek or BAMS Beyrek) sets out to conquer the fortress to gain a reputation.
Climate
Bayburt has a continental climate with freezing cold winters, the majority of the time snowing heavily. Summers are warm with cool nights. The climate is best described as humid continental by the Köppen Climate System Dfb, on the border of Dsb.[9] Most of the precipitation occurs in late spring and early summer.
| Climate data for Bayburt (1960-2012) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.3 (50.5) |
13.9 (57) |
21.2 (70.2) |
25.3 (77.5) |
29.6 (85.3) |
32.4 (90.3) |
36.2 (97.2) |
37.1 (98.8) |
33.3 (91.9) |
28.8 (83.8) |
20.0 (68) |
18.2 (64.8) |
37.1 (98.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −1.3 (29.7) |
0.2 (32.4) |
5.4 (41.7) |
12.7 (54.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
22.4 (72.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
27.3 (81.1) |
23.3 (73.9) |
16.7 (62.1) |
8.6 (47.5) |
1.7 (35.1) |
13.49 (56.29) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −6.5 (20.3) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
0.0 (32) |
7.0 (44.6) |
11.7 (53.1) |
15.4 (59.7) |
19.0 (66.2) |
18.8 (65.8) |
14.7 (58.5) |
9.2 (48.6) |
2.6 (36.7) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
6.95 (44.52) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −10.9 (12.4) |
−9.8 (14.4) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
1.7 (35.1) |
5.5 (41.9) |
8.2 (46.8) |
11.0 (51.8) |
10.8 (51.4) |
7.1 (44.8) |
3.4 (38.1) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
−7.1 (19.2) |
1.12 (34.03) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −31.3 (−24.3) |
−27.6 (−17.7) |
−28.3 (−18.9) |
−12.7 (9.1) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
0.2 (32.4) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−23.6 (−10.5) |
−29.0 (−20.2) |
−31.3 (−24.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 26.5 (1.043) |
28.2 (1.11) |
39.7 (1.563) |
62.8 (2.472) |
68.6 (2.701) |
52.0 (2.047) |
20.6 (0.811) |
14.2 (0.559) |
20.7 (0.815) |
44.4 (1.748) |
34.2 (1.346) |
28.8 (1.134) |
440.7 (17.349) |
| Avg. precipitation days | 11.2 | 10.9 | 12.4 | 13.9 | 15.4 | 10.5 | 5.1 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 8.7 | 9.1 | 10.7 | 116.9 |
| Source: Devlet Meteoroloji İşleri Genel Müdürlüğü [10] | |||||||||||||
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Bayburt is twinned with:
-
 Ali Sabieh, Djibouti
Ali Sabieh, Djibouti -
 Domo, Ethiopia
Domo, Ethiopia -
 Mekele, Ethiopia
Mekele, Ethiopia -
 Safi, Morocco
Safi, Morocco -
 Mohammedia, Morocco
Mohammedia, Morocco -
 Magdeburg, Germany
Magdeburg, Germany -
.svg.png) Roeselare, Belgium
Roeselare, Belgium -
 Schaan, Liechtenstein
Schaan, Liechtenstein -
 Limerick, Ireland
Limerick, Ireland -
 Zaragoza, Spain
Zaragoza, Spain -
 Ipoh, Malaysia
Ipoh, Malaysia  Varna, Bulgaria
Varna, Bulgaria
Gallery
Notable people from Bayburt
- Irsadi Baba
- Aglar Baba
- Suat Türker
- Dede Korkut
See also
- Bayburt Museum of Modern Arts
- Şehit Osman Hill
- Arpalı Kasabası
References
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Baiburt. |
- ↑ "Area of regions (including lakes), km²". Regional Statistics Database. Turkish Statistical Institute. 2002. Retrieved 2013-03-05.
- ↑ "Population of province/district centers and towns/villages by districts - 2012". Address Based Population Registration System (ABPRS) Database. Turkish Statistical Institute. Retrieved 2013-02-27.
- ↑ Bayburt Guide (en)
- ↑ Bayburt (tr)
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Sinclair, T.A. (1989). Eastern Turkey: An Architectural & Archaeological Survey, Volume I. Pindar Press. pp. 284–289. ISBN 9780907132325.
- ↑ Hamilton, William John (1842). Researches in Asia Minor, Pontus and Armenia. Murray. pp. 231–233.
- ↑
- ↑ David Winfield, "A Note on the South-Eastern Borders of the Empire of Trebizond in the Thirteenth Century", Anatolian Studies, 12 (1962), p. 166
- ↑ Climate Summary for Bayburt
- ↑ "İl ve İlçelerimize Ait İstatistiki Veriler- Meteoroloji Genel Müdürlüğü". Dmi.gov.tr. 1996-10-25. Archived from the original on 30 April 2011. Retrieved 2011-03-20.