Batam
| Batam باتم | ||
|---|---|---|
| City | ||
 | ||
| ||
|
Motto: "Batam, Menuju Bandar Dunia yang Modern dan Sebagai Pusat Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Nasional " (Batam, towards a civil modern city and as the centre of national economy development) | ||
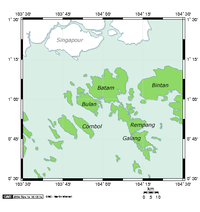 | ||
 Batam Location in Indonesia. | ||
| Coordinates: 1°05′N 104°02′E / 1.083°N 104.033°ECoordinates: 1°05′N 104°02′E / 1.083°N 104.033°E | ||
| Country | Indonesia | |
| Province | Riau Islands | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Drs. H. Ahmad Dahlan MH, Ph.D | |
| • Deputy | Datuk H.M. Rudi SE, MM | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 715 km2 (276 sq mi) | |
| Population | ||
| • Total | 1,578,054 | |
| • Density | 2,200/km2 (5,700/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | WIB (UTC+7) | |
| Postal code | 29453 | |
| Area code(s) | +62 778 | |
| Vehicle registration | BP | |
| Website |
www | |
Batam (Jawi: باتم) is an island, municipality (an Indonesian kotamadya), the largest city in the Riau Islands Province of Indonesia and the third largest city in Sumatra area. Batam is a free trade zone, part of the Indonesia–Malaysia–Singapore Growth Triangle, located 20 km (12 mi) off Singapore's south coast. The 715 km² (276 miles²) island, almost identical in size to Singapore, is the core part of the municipality. The municipality (2,200 km²) has a population of 1,578,054 (Prediction in April 2015).[1] As per the 2010 Census it was the fastest growing municipality in the nation, with a growth rate of 11% per year.[2] Though the municipality covers adjacent islands, nearly all the people reside on Batam island.
Geography
Batam is located west of Bintan Island, south of Singapore, north of Rempang and east of Bulan Island. The Riau Strait separates Batam and Bintan.
Batam has a tropical climate with average temperatures between 26-32 °C. Humidity in the region ranges from 73% to 96%. The region has a wet season from November to April and a dry season from May to October. Average annual rainfall is around 2,600 mm.
Population
Tribes Society Batam is a heterogeneous society consisting of diverse ethnic and class. The dominant tribe among other Malays, Javanese, Batak, Minangkabau, and Chinese. With have smth. As an umbrella and uphold Malay Unity in Diversity, Batam be conducive to moving economic activity, socio-political and cultural society. Until April 2012, Batam has a population of 1.15386 million inhabitants and has a population growth rate is very high. In the period 2001 to April 2012 had a population growth rate averaging more than 8 percent per year.
Religion Islam is the majority religion in Batam, the number of adherents as much as 76.69% of the entire population of the city. Followed by Christians (17.02%), Buddhists (5.79%), and Hinduism (0.40%). [3] Mosque Batam, located in the city center, adjacent to the main square, the mayor's office and the office Parliament became a symbol of the religious people of Batam. Christianity and Catholicism are also widely embraced by people of Batam, especially those from the Batak tribe and Flores. Buddhism is mostly held by Chinese citizens. Batam has Vihara which reputedly the largest in Southeast Asia, namely Vihara Duta Maitreya.
Language Indonesian is used as the language of instruction daily. Language is also used by the people who come from abroad such as English, German and other parts of Indonesia, such as Malay, Minang, Batak, Sundanese, and Javanese and Chinese ethnic dialects. It so happens because Batam is where various tribes met.
Administration
The local governmental offices are in Batam Centre. The largest community on the island is Lubuk Baja (formerly known as Nagoya). Other residential areas include Baloi Garden, Sekupang, Nongsapura (Nongsa), Waterfront City (Teluk Senimba), Batu Ampar and Jodoh.
Batam City (Kotamadya Batam) is divided into 12 districts (kecamatan) - which include several adjacent islands such as Bulan, Rempang and Galang as well as Batam Island itself.The districts are tabulated below with their 2010 Census population:[3]
| Name | Population Census 2010[3] |
|---|---|
| Belakang Padang | 18,508 |
| Bulang | 9,531 |
| Galang | 14,983 |
| Sei Beduk | 80,349 |
| Sagulung | 149,727 |
| Nongsa | 49,828 |
| Batam Kota (central city) | 162,238 |
| Sekupang | 100,108 |
| Batu Aji | 127,455 |
| Lubuk Baja | 80,780 |
| Batu Ampar | 58,745 |
| Bengkong | 92,033 |
Economy
Beginning in the 1970s, the island underwent a significant transformation from a largely forested area into a major harbour and industrial zone. Shipbuilding and electronics manufacturing are important industries on the island. Being close to the ports of Singapore increases the speed for goods shipping and product distribution which benefits the island's economy. With lower labour costs and special government incentives, it is the site of many factories operated by foreign companies.[4]
Under a framework signed in June 2006, Batam, along with parts of neighbouring Bintan and Karimun, are a part of a Special Economic Zone with Singapore; this zone eliminates tariffs and value-added taxes for goods shipped between Batam and Singapore.[5]
In 2010, approximately 58 percent of foreign tourists came from Singapore, and 13 percent from Malaysia.[6] The island is the location of International University of Batam.
Batam has recently been exposed as a major facilitator of the controversial ivory trade.[7]
Demographics
The population of Batam consists of a mixture of races, religions and languages. With a population of more than 1.3 million, Islam is the majority religion at 74.25%, followed by Christianity, Buddhism, Confucianism and others.
As in other regions of Indonesia, Bahasa Indonesia is the primary language, with several other languages and dialects such as Malay and Chinese (mainly Hokkien and Teochew) as well as Mandarin and English due to the close proximity of Singapore and Malaysia.
Transport
Ferry

The local ferry terminal ports connect to nearby Singapore and Bintan, and provides routes to Johor Bahru (Malaysia). There are five ferry terminals on the island: Harbourbay, Nongsapura Ferry Terminal, Sekupang, Waterfront City and Batam Centre International Ferry Terminal.
- Remain silent
Signs showing a picture of a raised finger over a pair of lips have been raised in August 2014 at the Batam Centre International Ferry Terminal means you have to silent while queing for immigration to hear your names being called and clearly hear immigration officer instructions or you will be sent back to Singapore, if you are too noisy. Some visitors have been sent back immediately use the first ferry available. The signs are also apply at other ferry terminals, but they are not strictly enforced.[8][9]
Trans Batam

Batam's city bus is named "Trans Batam". Before, the bus was named "Bis Kota Batam" (Batam City Bus). With more than 20 units of buses, this bus operates the Sekupang-Batam Centre route and Batu Aji-Sekupang route.
Taxi

Taxi services are available in Batam. There are more than 3.000 units of taxies in Batam. The taxies are equipped with meters, driver's identity, air conditioner and a non-smoking taxi.
Airport
Hang Nadim International Airport is the island's main airport, and has the longest runway in Indonesia. The airport is the largest in Sumatra in 1995-2012 with a capacity of 6 million passengers per year, and now the second largest in Sumatra after Kuala Namu International Airport in Medan with a capacity of 8 million passengers. The airport has 4 pairs of jetbridges in 1985-2011 and there were 2 jetbridges added on 2012. So there are 6 jetbridges in total. BP Batam also plans to build a new terminal with a capacity of 8 million passengers each terminal (16 million passengers in total for two terminals) . BP Batam targets to build 12 pairs of jetbridges in each terminal.[10] Domestic destinations include Pekanbaru, Palembang, Medan Jakarta, and many more. International flights currently include Kuala Lumpur (operated by Firefly and Malindo Air), and in 2015, Malindo Air will open two international routes to Bangkok-Don Mueang and Hong Kong.
Monorail
Monorail will be built in Batam in 2016 by Batam Authority, BP Batam and investors from South Korea. Batam will be the first city in Indonesia to have a monorail.
Batam Botanical Gardens
On 28 August 2014, a groundbreaking of international standard Batam Botanical Garden has been done by Public Utility Works Minister. The Batam Botanical Garden with 86 hectares will be the second largest botanical garden after Bogor Botanical Gardens and will also have a dam.[11]
Gallery
-

One of Batam's top leading resorts, Turi Beach
-

The 2014 National MTQ Building in Dataran Engku Putri, Batam Centre
-

Batam's Great Mosque
-

Hang Nadim International Airport in the early 2015
-

Pacific Palace, the cruise-shaped hotel in Jodoh
-

Batam Centre Area, Batam's office complex centre
-

Barelang Bridge, the icon of Batam
-

Nagoya and Jodoh Area, Batam's business centre
-

Baloi Area, Batam's business centre
-
Kwan Im statue in Sekupang
References
- ↑ http://globalfmlombok.com/content/soal-mandalika-resort-dprd-ntb-studi-komparatif-dengan-pemkot-batam
- ↑ http://www.thejakartapost.com/news/2012/05/12/urbanization-and-urban-development-patterns.html
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ↑ "Indonesia President inaugurates Batam free trade zone". Xinhua General News Service. 19 January 2009.
- ↑ Teo, Laurel (19 May 2007). "Indon SEZ rules ready by end-May; Setting of a deadline likely to please potential investors". The Business Times Singapore.
- ↑ Singaporeans constitute 57 pct of tourists in Batam
- ↑ http://www.thejakartapost.com/news/2013/03/10/batam-alleged-transshipment-point-ivory-africa.html
- ↑ "Shhh! Be silent at Batam immigration queue or be sent back home". 17 August 2014.
- ↑ Chris Kitching (19 August 2014). "'Keep quiet or you'll be kicked out of the country!': Ferry terminal's noisy visitors could be DEPORTED if they even whisper while standing in immigration queues".
- ↑ Airports in Indonesia
- ↑ "Kebun Raya Batam Bertaraf Internasional". 29 August 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Batam. |
-
 Batam travel guide from Wikivoyage
Batam travel guide from Wikivoyage - Official website
- Batam Free and Easy Package Tour
- An independent and complete travel guide to Batam from JoTravelGuide.com
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||

.jpg)
