Basic beryllium acetate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Hexakis(μ-acetato)-μ(sup 4)-oxotetraberyllium | |
| Other names
Beryllium oxyacetate Beryllium oxide acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 19049-40-2 | |
| ChemSpider | 2299653 |
| EC number | 242-785-4 |
| PubChem | 3035396 |
| Properties | |
| C 12H 18Be 4O 13 | |
| Molar mass | 406.3122 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless |
| Melting point | 285 °C (545 °F; 558 K) |
| Boiling point | 330 °C (626 °F; 603 K) |
| Solubility in chloroform | soluble |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Basic beryllium acetate is the chemical compound with the formula Be4O(O2CCH3)6. Although this compound has no applications and has been only lightly studied, it adopts a distinctive structure. The compound is a colourless solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
Preparation
It can be prepared by treating basic beryllium carbonate with hot acetic acid.
- 2 Be
2CO
3(OH)
2 + 6 AcOH → Be
4O(AcO)
6 + 5 H
2O + 2 CO
2
Basic beryllium acetate is insoluble in water but soluble in chloroform, consistent with it being nonpolar. It melts and sublimes in a vacuum without decomposition.[1]
Structure
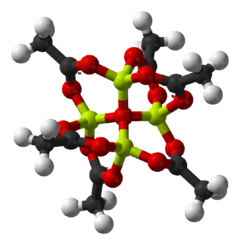
"Basic acetates" consist of an ensemble of metal centres bound to a central oxide ion, and an collection of acetate ligands. Basic beryllium acetate has a tetrahedral Be4O6+ core with acetates (CH3CO2−) spanning each of the pairs of Be2+ centres.[2][3] It is diamondoid, consisting of interlocking six-membered Be2O3C rings. The structure is relevant to its considerable stability (the compound is distillable at 330 °C).

See Also
- Basic zinc acetate - isostructural
References
- ↑ Moeller, T. (1950). "Basic Beryllium Derivatives of Organic Acids". In Audrieth, L. F. Inorganic Syntheses, Volume 3. John Wiley & Sons. p. 4. doi:10.1002/9780470132340.ch2. ISBN 978-0-470-13234-0.
- ↑ Bragg, W. H. (1923). "Crystal Structure of Basic Beryllium Acetate". Nature 111 (2790): 532. Bibcode:1923Natur.111..532B. doi:10.1038/111532a0.
- ↑ Pauling, L.; Sherman, J. (1934). "The Structure of the Carboxyl Group. II. The Crystal Structure of Basic Beryllium Acetate". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 20 (6): 340. Bibcode:1934PNAS...20..340P. doi:10.1073/pnas.20.6.340.