Barium ferrate
| | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Barium ferrate(VI) | |||
| Other names
Barium ferrate(2-) | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 13773-23-4 | |||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Molecular formula |
BaFeO4 | ||
| Molar mass | 257.17 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Dark red, opaque crystals | ||
| insoluble | |||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
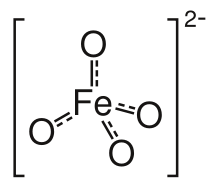
Barium ferrate is the chemical compound of formula BaFeO4. This compound contains iron in the +6 oxidation state.[1] It is isostructural with BaSO4, and contains the tetrahedral [FeO4]2− anion.[2]
Preparation and chemistry
Anhydrous barium ferrate can be prepared by precipitation from a solution containing potassium ferrate and barium chloride.[3] Barium ferrate is an oxidising agent and has been proposed as an oxidising reagent for use in organic syntheses.[4]
References
- ↑ J. G. R. Briggs (2005). Longman A-level course in chemistry (4th ed.). Pearson Education South Asia. p. 536. ISBN 981-4105-08-2.
- ↑ Wells, A.F. (1986). Structural inorganic chemistry (5th ed. ed.). Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- ↑ Gump, J. R.; Wagner, W. F.; schreyer, J. M. (1 December 1954). Analytical Chemistry 26 (12): 1957–1957. doi:10.1021/ac60096a027. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Firouzabadi, H.; Mohajer, D.; Entezari-moghaddam, M. "Barium Ferrate Monohydrate BaFeO4·H2O, A Versatile Reagent for the Oxidation of Organic Compounds under Aprotic Condiiton". Synthetic Communications 16 (6): 723–731. doi:10.1080/00397918608057745.
| ||||||