Banach–Mazur game
In general topology, set theory and game theory, a Banach–Mazur game is a topological game played by two players, trying to pin down elements in a set (space). The concept of a Banach–Mazur game is closely related to the concept of Baire spaces. This game was the first infinite positional game of perfect information to be studied. It was introduced by Mazur as problem 43 in the Scottish book, and Mazur's questions about it were answered by Banach.
Definition and properties
In what follows we will make use of the formalism defined in Topological game. A general Banach–Mazur game is defined as follows: we have a topological space 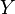 , a fixed subset
, a fixed subset 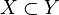 , and a family
, and a family 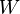 of subsets of
of subsets of 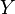 that satisfy the following properties.
that satisfy the following properties.
- Each member of
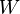 has non-empty interior.
has non-empty interior. - Each non-empty open subset of
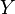 contains a member of
contains a member of 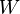 .
.
We will call this game 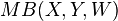 . Two players,
. Two players, 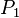 and
and 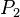 , choose alternatively elements
, choose alternatively elements 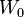 ,
, 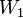 ,
, 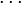 of
of 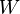 such that
such that 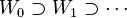 . The player
. The player 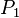 wins if and only if
wins if and only if 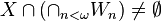 .
.
The following properties hold.
-
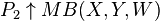 if and only if
if and only if  is of the first category in
is of the first category in  (a set is of the first category or meagre if it is the countable union of nowhere-dense sets).
(a set is of the first category or meagre if it is the countable union of nowhere-dense sets). - Assuming that
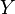 is a complete metric space,
is a complete metric space, 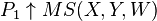 if and only if
if and only if 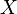 is comeager in some nonempty open subset of
is comeager in some nonempty open subset of 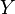 .
. - If
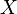 has the Baire property in
has the Baire property in 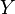 , then
, then 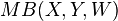 is determined.
is determined. - Any winning strategy of
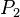 can be reduced to a stationary winning strategy.
can be reduced to a stationary winning strategy. - The siftable and strongly-siftable spaces introduced by Choquet can be defined in terms of stationary strategies in suitable modifications of the game. Let
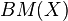 denote a modification of
denote a modification of 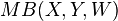 where
where  ,
, 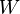 is the family of all nonempty open sets in
is the family of all nonempty open sets in 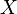 , and
, and 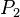 wins a play
wins a play 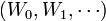 if and only if
if and only if 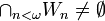 . Then
. Then 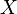 is siftable if and only if
is siftable if and only if 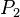 has a stationary winning strategy in
has a stationary winning strategy in 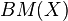 .
. - A Markov winning strategy for
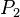 in
in 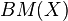 can be reduced to a stationary winning strategy. Furthermore, if
can be reduced to a stationary winning strategy. Furthermore, if 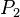 has a winning strategy in
has a winning strategy in 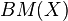 , then she has a winning strategy depending only on two preceding moves. It is still an unsettled question whether a winning strategy for
, then she has a winning strategy depending only on two preceding moves. It is still an unsettled question whether a winning strategy for 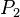 can be reduced to a winning strategy that depends only on the last two moves of
can be reduced to a winning strategy that depends only on the last two moves of 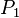 .
. -
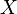 is called weakly
is called weakly 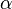 -favorable if
-favorable if 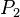 has a winning strategy in
has a winning strategy in 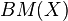 . Then,
. Then, 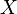 is a Baire space if and only if
is a Baire space if and only if 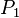 has no winning strategy in
has no winning strategy in 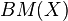 . It follows that each weakly
. It follows that each weakly 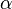 -favorable space is a Baire space.
-favorable space is a Baire space.
Many other modifications and specializations of the basic game have been proposed: for a thorough account of these, refer to [1987]. The most common special case, called 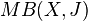 , consists in letting
, consists in letting 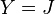 , i.e. the unit interval
, i.e. the unit interval ![[0,1]](../I/m/ccfcd347d0bf65dc77afe01a3306a96b.png) , and in letting
, and in letting 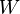 consist of all closed intervals
consist of all closed intervals ![[a,b]](../I/m/2c3d331bc98b44e71cb2aae9edadca7e.png) contained in
contained in ![[0,1]](../I/m/ccfcd347d0bf65dc77afe01a3306a96b.png) . The players choose alternatively subintervals
. The players choose alternatively subintervals 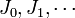 of
of 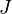 such that
such that 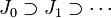 , and
, and 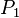 wins if and only if
wins if and only if 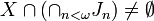 .
. 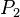 wins if and only if
wins if and only if 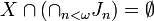 .
.
A simple proof: winning strategies
It is natural to ask for what sets 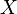 does
does 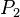 have a winning strategy. Clearly, if
have a winning strategy. Clearly, if 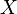 is empty,
is empty, 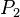 has a winning strategy, therefore the question can be informally rephrased as how "small" (respectively, "big") does
has a winning strategy, therefore the question can be informally rephrased as how "small" (respectively, "big") does 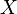 (respectively, the complement of
(respectively, the complement of 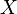 in
in 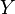 ) have to be to ensure that
) have to be to ensure that 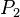 has a winning strategy. To give a flavor of how the proofs used to derive the properties in the previous section work, let us show the following fact.
has a winning strategy. To give a flavor of how the proofs used to derive the properties in the previous section work, let us show the following fact.
Fact: 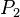 has a winning strategy if
has a winning strategy if 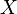 is countable,
is countable, 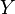 is T1, and
is T1, and 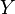 has no isolated points.
has no isolated points.
Proof: Let the elements of 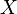 be
be 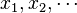 . Suppose that
. Suppose that 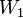 has been chosen by
has been chosen by 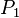 , and let
, and let 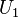 be the (non-empty) interior of
be the (non-empty) interior of 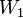 . Then
. Then 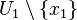 is a non-empty open set in
is a non-empty open set in 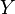 , so
, so 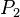 can choose a member
can choose a member 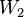 of
of 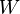 contained in this set. Then
contained in this set. Then 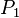 chooses a subset
chooses a subset 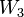 of
of 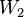 and, in a similar fashion,
and, in a similar fashion, 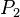 can choose a member
can choose a member 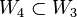 that excludes
that excludes 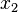 . Continuing in this way, each point
. Continuing in this way, each point 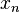 will be excluded by the set
will be excluded by the set 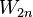 , so that the intersection of all the
, so that the intersection of all the 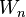 will have empty intersection with
will have empty intersection with 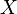 . Q.E.D
. Q.E.D
The assumptions on 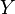 are key to the proof: for instance, if
are key to the proof: for instance, if 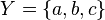 is equipped with the discrete topology and
is equipped with the discrete topology and 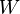 consists of all non-empty subsets of
consists of all non-empty subsets of 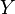 , then
, then 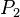 has no winning strategy if
has no winning strategy if 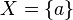 (as a matter of fact, her opponent has a winning strategy). Similar effects happen if
(as a matter of fact, her opponent has a winning strategy). Similar effects happen if 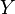 is equipped with indiscrete topology and
is equipped with indiscrete topology and 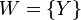 .
.
A stronger result relates 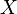 to first-order sets.
to first-order sets.
Fact: Let 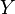 be a topological space, let
be a topological space, let 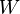 be a family of subsets of
be a family of subsets of 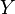 satisfying the two properties above, and let
satisfying the two properties above, and let 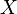 be any subset of
be any subset of 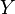 .
. 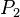 has a winning strategy if and only if
has a winning strategy if and only if 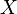 is meagre.
is meagre.
This does not imply that 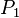 has a winning strategy if
has a winning strategy if 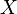 is not meagre. In fact,
is not meagre. In fact, 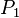 has a winning strategy if and only if there is some
has a winning strategy if and only if there is some 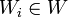 such that
such that 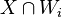 is a comeagre subset of
is a comeagre subset of 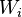 . It may be the case that neither player has a winning strategy: when
. It may be the case that neither player has a winning strategy: when 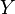 is
is ![[0,1]](../I/m/ccfcd347d0bf65dc77afe01a3306a96b.png) and
and 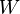 consists of the closed intervals
consists of the closed intervals ![[a,b]](../I/m/2c3d331bc98b44e71cb2aae9edadca7e.png) , the game is determined if the target set has the property of Baire, i.e. if it differs from an open set by a meagre set (but the converse is not true). Assuming the axiom of choice, there are subsets of
, the game is determined if the target set has the property of Baire, i.e. if it differs from an open set by a meagre set (but the converse is not true). Assuming the axiom of choice, there are subsets of ![[0,1]](../I/m/ccfcd347d0bf65dc77afe01a3306a96b.png) for which the Banach–Mazur game is not determined.
for which the Banach–Mazur game is not determined.
References
- [1957] Oxtoby, J.C. The Banach–Mazur game and Banach category theorem, Contribution to the Theory of Games, Volume III, Annals of Mathematical Studies 39 (1957), Princeton, 159–163