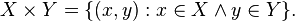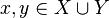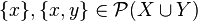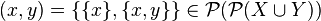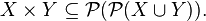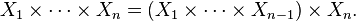Axiom of power set
In mathematics, the axiom of power set is one of the Zermelo–Fraenkel axioms of axiomatic set theory.
In the formal language of the Zermelo–Fraenkel axioms, the axiom reads:
where P stands for the power set of A, 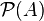 . In English, this says:
. In English, this says:
- Given any set A, there is a set
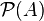 such that, given any set B, B is a member of
such that, given any set B, B is a member of 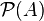 if and only if every element of B is also an element of A.
if and only if every element of B is also an element of A.
Subset is not used in the formal definition because the subset relation is defined axiomatically; axioms must be independent from each other. By the axiom of extensionality this set is unique, which means that every set has a power set.
The axiom of power set appears in most axiomatizations of set theory. It is generally considered uncontroversial, although constructive set theory prefers a weaker version to resolve concerns about predicativity.
Consequences
The Power Set Axiom allows a simple definition of the Cartesian product of two sets 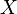 and
and 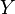 :
:
Notice that
and thus the Cartesian product is a set since
One may define the Cartesian product of any finite collection of sets recursively:
Note that the existence of the Cartesian product can be proved without using the power set axiom, as in the case of the Kripke–Platek set theory.
References
- Paul Halmos, Naive set theory. Princeton, NJ: D. Van Nostrand Company, 1960. Reprinted by Springer-Verlag, New York, 1974. ISBN 0-387-90092-6 (Springer-Verlag edition).
- Jech, Thomas, 2003. Set Theory: The Third Millennium Edition, Revised and Expanded. Springer. ISBN 3-540-44085-2.
- Kunen, Kenneth, 1980. Set Theory: An Introduction to Independence Proofs. Elsevier. ISBN 0-444-86839-9.
This article incorporates material from Axiom of power set on PlanetMath, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
![\forall A \, \exists P \, \forall B \, [B \in P \iff \forall C \, (C \in B \Rightarrow C \in A)]](../I/m/80adb23907ae85d345ca83a3d420b04d.png)