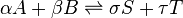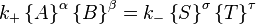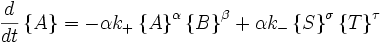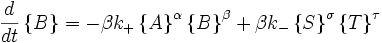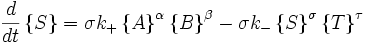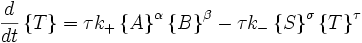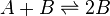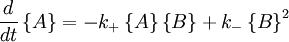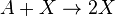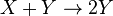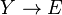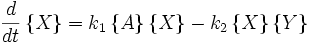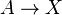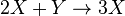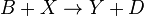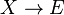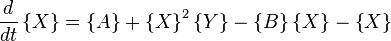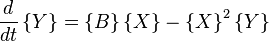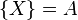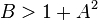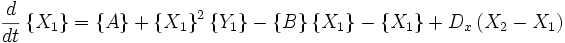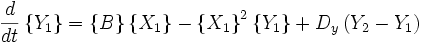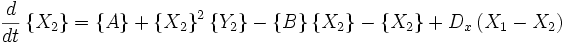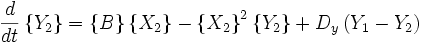Autocatalytic reaction
Autocatalytic reactions are chemical reactions in which at least one of the reactants is also a product. The rate equations for autocatalytic reactions are fundamentally nonlinear. This nonlinearity can lead to the spontaneous generation of order. A dramatic example of this order is that which is found in living systems. This spontaneous order creation seems to contradict the Second Law of Thermodynamics. This contradiction is resolved when the disorder of both the system and its surroundings are taken into account.
Background
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the disorder (entropy) of a physical or chemical system and its surroundings (a closed system) must increase with time. In other words, systems left to themselves must become increasingly random. To say it yet another way, orderly energy of a system like uniform motion must degrade eventually to the random motion of particles in a heat bath.
This seems to run counter to experience. There are many instances in which physical systems spontaneously become emergent or orderly. For example, despite the destruction they cause, hurricanes have a very orderly vortex motion when compared to the random motion of the air molecules in a closed room. Even more spectacular is the order created by chemical systems; the most dramatic being the order associated with life.
Our experience is consistent with the Second Law. The Second Law states that the total disorder of a system and its surroundings must increase with time. Order can be created in a system by an even greater decrease in order of the systems surroundings.[1] In the hurricane example, hurricanes are formed from unequal heating within the atmosphere. The Earth's atmosphere is then far from thermal equilibrium. The order of the Earth's atmosphere increases, but at the expense of the order of the sun. The sun is becoming more disorderly as it ages and throws off light and material to the rest of the universe. The total disorder of the sun and the earth increases despite the fact that orderly hurricanes are generated on earth.
A similar example exists for living chemical systems. The sun provides energy to green plants. The green plants are food for other living chemical systems. The energy absorbed by plants and converted into chemical energy generates a system on earth that is orderly and far from chemical equilibrium. Here, the difference from chemical equilibrium is determined by an excess of reactants over the equilibrium amount. Once again, order on earth is generated at the expense of entropy increase of the sun. The total entropy of the earth and the rest of the universe increases, consistent with the Second Law.
Not all chemical reactions, however, generate order. The class of reactions most closely associated with order creation is the class of autocatalytic reactions. These are reactions in which one or more of the products are the same as one or more of the reactants. Simple autocatalytic reactions (clock reactions) are known to oscillate in time, thus creating temporal order. Other simple reactions can generate spatial separation of chemical species generating spatial order. More complex reactions are involved in metabolic pathways and metabolic networks in biological systems.
The transition to order as the distance from equilibrium increases is not usually continuous. Order typically appears abruptly. The threshold between the disorder of chemical equilibrium and order is known as a phase transition. The conditions for a phase transition can be determined with the mathematical machinery of non-equilibrium thermodynamics.
Chemical reactions
A chemical reaction of two reactants and two products can be written as
where the Greek letters are stoichiometric coefficients and the capital Latin letters represent chemical species. The chemical reaction proceeds in both the forward and reverse direction. This equation is easily generalized to any number of reactants, products, and reactions.
Chemical equilibrium
In chemical equilibrium the forward and reverse reaction rates are such that each chemical species is being created at the same rate it is being destroyed. In other words, the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
Here, the curly brackets indicate the amount of the chemical species, in moles, and k+ and k− are rate constants.
Far from equilibrium
Far from equilibrium, the forward and reverse reaction rates no longer balance and the concentration of reactants and products is no longer constant. For every forward reaction 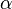 molecules of A are destroyed. For every reverse reaction
molecules of A are destroyed. For every reverse reaction 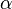 molecules of A are created. The change in number of moles of A is then
molecules of A are created. The change in number of moles of A is then
This system of equations has a single stable fixed point when the forward rates and the reverse rates are equal. This means that the system evolves to the equilibrium state, and this is the only state to which it evolves.
Autocatalytic reactions
Autocatalytic reactions are those in which at least one of the products is a reactant. Perhaps the simplest autocatalytic reaction can be written
with the rate equations
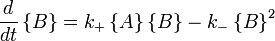 .
.
This reaction is one in which a molecule of species A interacts with a molecule of species B. The A molecule is converted into a B molecule. The final product consists of the original B molecule plus the B molecule created in the reaction.
The key feature of these rate equations is that they are nonlinear; the second term on the right varies as the square of the concentration of B. This feature can lead to multiple fixed points of the system, much like a quadratic equation can have multiple roots. Multiple fixed points allow for multiple states of the system. A system existing in multiple macroscopic states is more orderly (has lower entropy) than a system in a single state.
Creation of order
Temporal order
Idealized example: Lotka-Volterra equation
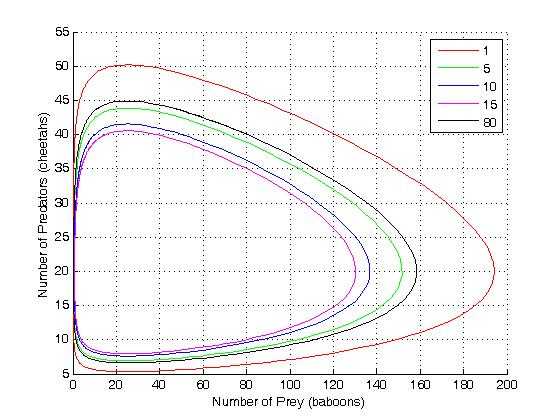
Consider a coupled set of two autocatalytic reactions in which the concentration of one of the reactants A is much larger than its equilibrium value. In this case the forward reaction rate is so much larger than the reverse rates that we can neglect the reverse rates.
with the rate equations
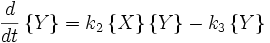 .
.
Here, we have neglected the depletion of the reactant A, since its concentration is so large. The rate constants for the three reactions are 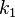 ,
, 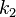 , and
, and 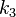 , respectively.
, respectively.
This system of rate equations is known as the Lotka-Volterra equation and is most closely associated with population dynamics in predator-prey relationships. This system of equations has an oscillatory behavior. The amplitude of the oscillations depends on the concentration of A. Oscillations of this type are a form of emergent temporal order that is not present in equilibrium.
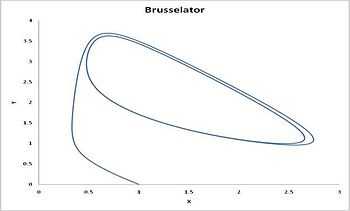
Another idealized example: Brusselator
Another example of a system that demonstrates temporal order is the Brusselator (see Prigogine reference). It is characterized by the reactions
with the rate equations
where, for convenience, the rate constants have been set to 1.
The Brusselator has a fixed point at
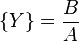 .
.
The fixed point becomes unstable when
leading to an oscillation of the system. Unlike the Lotka-Volterra equation, the oscillations of the Brusselator do not depend on the amount of reactant present initially. Instead, after sufficient time, the oscillations approach a limit cycle.[2]
Real examples
Real examples of clock reactions are the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction (BZ reaction), the Briggs-Rauscher reaction, the Bray-Liebhafsky reaction and the iodine clock reaction. These are oscillatory reactions, and the concentration of products and reactants can be approximated in terms of damped oscillations.
The best-known reaction, the BZ reaction, can be created with a mixture of potassium bromate 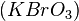 , malonic acid
, malonic acid 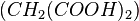 , and manganese sulfate
, and manganese sulfate 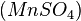 prepared in a heated solution of sulfuric acid
prepared in a heated solution of sulfuric acid 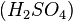 .[3]
.[3]
Spatial order
An idealized example of spatial spontaneous symmetry breaking is the case in which we have two boxes of material separated by a permeable membrane so that material can diffuse between the two boxes. It is assumed that identical Brusselators are in each box with nearly identical initial conditions. (see Prigogine reference)
Here, the numerical subscripts indicate which box the material is in. There are additional terms proportional to the diffusion coefficient D that account for the exchange of material between boxes.
If the system is initiated with the same conditions in each box, then a small fluctuation will lead to separation of materials between the two boxes. One box will have a predominance of X, and the other will have a predominance of Y.
Biological example
It is known that an important metabolic cycle, glycolysis, displays temporal order.[4] Glycolysis consists of the degradation of one molecule of glucose and the overall production of two molecules of ATP. The process is therefore of great importance to the energetics of living cells. The global glycolysis reaction involves glucose, ADP, NAD, pyruvate, ATP, and NADH.
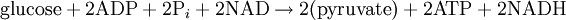 .
.
The details of the process are quite involved, however, a section of the process is autocatalyzed by Phosphofructokinase (PFK). This portion of the process is responsible for oscillations in the pathway that lead to the process oscillating between an active and an inactive form. Thus, the autocatalytic reaction can modulate the process.
Phase transitions
The initial amounts of reactants determine the distance from chemical equilibrium of the system. The greater the initial concentrations the further the system is from equilibrium. As the initial concentration increases, an abrupt change in order occurs. This abrupt change is known as phase transition. At the phase transition, fluctuations in macroscopic quantities, such as chemical concentrations, increase as the system oscillates between the more ordered state (lower entropy, such as ice water) and the more disordered state (higher entropy, such as liquid water). Also, at the phase transition, macroscopic equations, such as the rate equations, fail. Rate equations can be derived from microscopic considerations. The derivations typically rely on a mean field theory approximation to microscopic dynamical equations. Mean field theory breaks down in the presence of large fluctuations (see Mean field theory article for a discussion). Therefore, since large fluctuations occur in the neighborhood of a phase transition, macroscopic equations, such as rate equations, fail. As the initial concentration increases further, the system settles into an ordered state in which fluctuations are again small. (see Prigogine reference)
See also
- Autocatalysis
- Catalytic cycle
- Reaction-diffusion
- Abiogenesis
- Stuart Kauffman
- Morphogenesis
References
- ↑ Ilya Prigogine (1980). From Being to Becoming: Time and Complexity in the Physical Sciences. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-1107-9.
- ↑ http://www.math.ohio-state.edu/~ault/Papers/Brusselator.pdf Dynamics of the Brusselator
- ↑ BZ reaction
- ↑ G. Nicolis and Ilya Prigogine (1977). Self-Organization in Nonequilibrium Systems. New York: John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 0-471-02401-5.