Arsenous acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Arsorous acid | |
| Other names
Arsenious acid Arsenic oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 13464-58-9 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:49900 |
| ChemSpider | 530 |
| DrugBank | DB04456 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 545 |
| |
| Properties | |
| H3AsO3 | |
| Molar mass | 125.94 g/mol |
| Appearance | Only exists in aqueous solutions |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Toxic, corrosive |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Arsenic acid |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
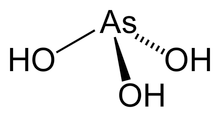
Arsenous acid (or arsenious acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula H3AsO3. It is known to occur in aqueous solutions, but it has not been isolated as a pure material, although this fact does not detract from the significance of As(OH)3.[1]
Properties
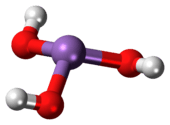
As(OH)3 is a pyramidal molecule consisting of three hydroxyl groups bonded to arsenic. The 1H NMR spectrum of arsenous acid solutions consists of a single signal consistent with the molecule's high symmetry.[2] In contrast, the nominally related phosphorus species H3PO3 mainly adopts the structure HPO(OH)2; P(OH)3 is a very minor equilibrium component of such solutions. The differing behaviors of the As and P compounds reflect a trend whereby high oxidation states are more stable for lighter members of main group elements than their heavier congeners.<ref name = Greenwood">Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0080379419.</ref>
Reactions
The preparation of As(OH)3 involves a slow hydrolysis of arsenic trioxide in water. Addition of base converts arsenous acid to the arsenite ions [AsO(OH)2]−, [AsO2(OH)]2−, and [AsO3]3−. The first pKa is 9.2, As(OH)3 is a weak acid.<ref name = Greenwood"/> Reactions attributed to aqueous arsenic trioxide are due to arsenous acid and its conjugate bases.
Toxicology
Arsenic-containing compounds are highly toxic and carcinogenic. The anhydride form of arsenous acid, arsenic trioxide, is used as a herbicide, pesticide, and rodenticide.
References
- ↑ Munoz-Hernandez, M.-A. (1994). "Arsenic: Inorganic Chemistry". In King, R. B. Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons.
- ↑ Kolozsi, A.; Lakatos, A.; Galbács, G.; Madsen, A. Ø.; Larsen, E.; Gyurcsik, B. (2008). "A pH-Metric, UV, NMR, and X-ray Crystallographic Study on Arsenous Acid Reacting with Dithioerythritol" (PDF). Inorganic Chemistry 47: 3832–3840. doi:10.1021/ic7024439. PMID 18380458.
- "Arsenic trioxide". Retrieved January 29, 2006.