Arnulf of Montgomery
| Arnulf de Montgomery | |
|---|---|
| Earl of Pembroke | |
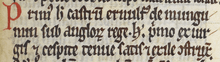 Excerpt from Royal MS 13 B VIII folio 89r (Gerald of Wales' Itinerarium Kambriae) detailing Arnulf's involvement in the erection of an earth and timber castle at Pembroke.[1] There are several manuscript versions of Itinerarium Kambriae.[2] One transcription of this excerpt reads in Latin "Primus hoc castrum Arnulfus de Mungumeri, sub Anglorum rege Henrico primo, ex virgis et cespite, tenue satis et exile construxit".[3] | |
| Wife | Lafracoth |
| Father | Roger de Montgomery |
| Mother | Mabel de Bellême |
| Born | c. 1066 |
| Died | 1118×22 |
Arnulf de Montgomery (c. 1066–1118×22), also known as Arnulf of Montgomery, was an Anglo-Norman magnate. A younger son of a leading magnate in Normandy and England, Arnulf played an active part in the Anglo-Norman invasion of southwestern Wales in the late eleventh century. Following his successes against the Welsh, Arnulf established himself at Pembroke, built an earth and timber castle, and was likely rewarded with the title Earl of Pembroke. At the turn of the twelfth century Arnulf reached his height, with his lordship including much of the former Welsh kingdom of Deheubarth and lands in Yorkshire. A short time later, he joined his elder brother's rebellion against the king of England, and married a daughter of the king of Munster in an effort to gain military support against his English sovereign. Following the ultimate collapse of the rebellion, Arnulf and his brothers were outlawed and banished from the realm, and Arnulf appears to have spent much of the next twenty-odd years in a peripatetic life in Ireland and Normandy.
Background
.jpg)
Arnulf was likely born in the late 1060s,[4] possibly about 1066.[5] He was a younger son of Roger de Montgomery, vicomte of the Hièmois (died 1094) and Mabel de Bellême (died 1077).[6] Arnulf's parents likely married in about 1050.[7] His mother was a daughter of, and eventual heiress of, Guillaume de Bellême, lord of Alençon (died c. 1063).[6] Arnulf's father, an apparent kinsman and close companion of William, duke of Normandy (died 1087), was an eminent magnate in Normandy.[8] As tutor to Matilda, duchess of Normandy (died 1083), Roger and his eldest sons did not embark on the 1066 Norman invasion of England. When William returned to Normandy as king in 1067, Roger accompanied him back to England, and was granted extensive lands, including the Sussex rapes of Arundel and Chichester, followed by the county of Shropshire. Soon afterwards, Roger was made Earl of Shrewsbury. By 1086, he was one of the wealthiest tenants-in-chief in England.[7] Arnulf makes his first appearance at about this time, in 1082/83, when he and his elder brother, Roger the Poitevin (died before 1140), witnessed William's confirmation of their father's grant to the Norman abbey of Troarn.[9][note 1]
In 1088, Roger and at least three of his sons participated in plot to eject William Rufus, king of England (died 1100) from the throne, with the intent to replace him with Robert Curthose, duke of Normandy (died 1134), William Rufus' elder brother.[11] This rebellion is documented in several sources, such as the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, the Worcester Chronicle, and the twelfth-century historians William of Malmesbury (died in or after 1142) and Henry of Huntingdon.[12] According to the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, the only strictly contemporary source of the four, Robert Curthose's followers captured Odo, Bishop of Bayeux, and thereby gained control of the castle of Rochester. The aforesaid source identifies several leading members of the insurrection, including three sons of Roger.[13] Although these unnamed brothers appear to have been Roger's eldest sons Robert de Bellême (died in or after 1130), Hugh de Montgomery (died 1098), and Roger the Poitevin,[14] it is not impossible that the latter took no part in the rising, and that the third brother was in fact Arnulf himself.[15] Although the rebellion was an ultimate failure, the king imposed no penalty upon Roger, and allowed Roger the Poitevin to be reinstated with most of the lands that Domesday Book shows he previously held.[16]
Rise
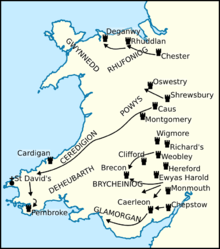
Arnulf's father was one of three close supporters of the king who were settled along the Anglo-Welsh border, in a region known as the Welsh marches. Although the first real penetration of Anglo-Norman power occurred in the 1070s, it wasn't until the last decade of the eleventh century that more permanent marcher settlements were envisaged in Wales.[17] In 1093, encroaching marcher lords engaged and slew Rhys ap Tewdwr, king of Deheubarth in Brycheiniog.[18] Contemporaries marked Rhys' fall as the end of kingship amongst the Welsh,[19] and his demise left a power-vacuum in which men such as Arnulf seized upon.[20] The south-west Welsh gwladoedd ("countries") of Ceredigion and Dyfed were thus overwhelmed and settled by the conquering incomers.[19] In the latter gwlad ("country"), Arnulf's father founded an earth and timber castle in which Arnulf established himself.[21] This ringwork,[22] strategically seated on the highest point of a promontory between two tidal inlets, sat on the site where the present castle of Pembroke stands today. Although nothing now remains of the original castle,[23] it was described by the twelfth-century chronicler Gerald of Wales (died 1220×1223) as a "slender fortress built of stakes and turf".[24]
William Rufus subsequently rewarded Arnulf with a lordship seated at his castle.[25] There is substantial evidence indicating that Arnulf was, in fact, made Earl of Pembroke.[26] For example, he was accorded forms of the Latin style comes by men such as Anselm, archbishop of Canterbury (died 1109),[27] the historian Eadmer of Canterbury (died in or after 1126),[28] the chronicler Geffrei Gaimar (died 1137),[29] Gerald of Wales,[30] the historian Orderic Vitalis (died c. 1142);[31] and in documentary sources such as Brut y Tywysogion,[32] the Hyde Chronicle,[33] and the cartulary of the abbey of Saint-Martin de Sées.[34] The castle at Pembroke is remarkable in the fact that, unlike other Anglo-Norman or English fortresses in west Wales, it never fell into the hands of the Welsh.[35] At some time between 1097 and 1108, Arnulf's castellan at Pembroke, Gerald de Windsor (died 1116×1136), married Rhys' daughter, Nest (died c. 1130).[36] According to Brut y Tywysogion, Arnulf captured and imprisoned Rhys' young son, Hywel, before the latter was able to escape after suffering certain bodily injuries.[37] Having established himself at Pembroke, Arnulf appears to have resided in England, leaving Gerald de Windsor at Pembroke as his de facto custos or steward.[38][note 2]
The people and the priest are despised by the word, heart and work of the Normans. For they increase our taxes and burn our properties. One vile Norman intimidates a hundred natives with his command, and terrifies them with his look ... Families do not now delight in offspring; the heir does not hope for the paternal estates; the rich man does not aspire to accumulate flocks.[40]
On his father's death in 1094, Arnulf's elder brother, Hugh de Montgomery, inherited the earldom of Shrewsbury. Surviving sources reveal that the brothers were closely associated with each other.[41] Within two years they made a joint grant to the far-off abbey of La Sauve-Majeure.[42][note 3] Furthermore, Arnulf appears to have witnessed a grant of Hugh de Montgomery's dapfier to the abbey, in a charter dated to 1095–1098.[44] In a Latin grant to the abbey of Saint-Martin de Sées,[41] founded by his father,[45] Arnulf bestowed a donation on behalf of his ancestors, lord, friends, and "very dear brother Hugh" ("carissimi fratris sui Hugonis").[46][note 4] Although the particular wording in this grant may reveal genuine affection for his brother, it may also be evidence that William Rufus, and the childless and unmarried Hugh de Montgomery, intended to designate Arnulf as Hugh de Montgomery's heir.[41]

Partly as a result of the political conquest of Wales in the late eleventh century, the Anglo-Norman church endeavoured to subjugate and exploit the Welsh church. To Norman eyes, the Welsh church was isolated, archaic, deviant, and backward-looking. Conversely, Normans regarded themselves as religious reformers, and sought to impose their own standards and practices upon the Welsh. One way in which the Anglo-Normans imposed their ecclesiastical authority upon the Welsh was through the appointment and control of bishops.[50] Within a year of his consecration as archbishop of Canterbury in December 1093, Anselm temporarily suspended the Welsh bishops of Glamorgan and St David's, revealing that these diocesan territories had indeed fallen under Canterbury's archiepiscopal authority.[51][note 5] In May 1095, Wilfrid, bishop of St David's (died 1115) came to terms with Anselm.[54] In turn, the latter admonished several leading Anglo-Normans holding lands in the diocese of St David's, urging them to regard Wilfrid as their bishop, and to return the lands, tithes, and churches that they had unjustly seized from him. Two marcher lords specifically singled out by Anselm were Arnulf, and Robert de Bellême.[55][note 6] As a friend of the archbishop, Arnulf may have been more liable to respect this call of restraint from Anselm than from anyone else.[57]
In 1098, together with Hugh d'Avranches, earl of Chester (died 1101), Hugh de Montgomery led a summer invasion of Gwynedd. Although the Anglo-Normans easily defeated the Welsh defenders, the attackers were later overwhelmed on Anglesey, in a chance encounter with the forces of Magnús Óláfsson, king of Norway (died 1103).[58] Arnulf appears to have learned of his brother's fate about a month later in Normandy, since he travelled to Sées, and founded a priory of the abbey's monks at Pembroke, in dedication to the memory of Hugh de Montgomery and his father.[59] Although Arnulf may well have hoped to inherit his Hugh's title and lands, William Rufus granted them to Arnulf's older brother Robert de Bellême,[60] who had captured Helias de la Flèche, count of Maine (died 1110) only months before, dutifully handing the count over to the king.[61][note 7]
Downfall

At the turn of the twelfth century, the Montgomerys were one of the leading families in England. At this point, Robert de Bellême had reached the height of his power,[63] and appears to have been the most powerful and prosperous magnate in the Anglo-Norman world.[64] Besides inheriting the expansive continental lands of the Montgomery and Bellême families, and succeeding to the earldom of Shrewsbury and the rape of Arundel, Robert de Bellême also obtained the honour of Tickhill in Nottinghamshire and southern Yorkshire. Furthermore, by right of his wife's inheritance, Robert de Bellême gained the small but important continental county of Ponthieu.[65]
His brother Roger the Poitevin was one of the most powerful magnates in northwest England,[66] holding lands in Lancashire, Nottinghamshire, Essex, Yorkshire, and Suffolk. By right of his wife, he gained the continental county of La Marche.[67][note 8]
Their brother Arnulf of Montgomery likely held the earldom of Pembroke, a lordship which appears to have constituted the core of the former kingdom of Deheubarth.[69] Arnulf gained the lordship of Holderness, following the downfall of its former lord, the disgraced Odo, count of Champagne (died after 1115–1118).[70][note 9]
In August 1100, whilst Robert Curthose was absent en route from the Holy Land, the reigning William Rufus was killed, and the vacant English throne was seized by their younger brother, Henry, count of Cotentin (died 1135).[66] Fearing an invasion from Normandy by Robert Curthose, an early act of Henry's reign was an alliance with Robert, count of Flanders (died 1111), formalised by treaty in March 1101.[78] One of the guarantors recorded lending surety for the English king was Arnulf, himself.[79] Guarantors to such acts often led negotiations between involved parties, which suggests that Arnulf acted as an intermediary between the king and count.[78] Although his involvement on Henry's behalf further evidences Arnulf's considerable status, his career in the king's service was short-lived.[5]
Although Robert de Bellême had initially accepted Henry as king,[80] by the time Robert Curthose asserted his claim to the throne at Alton in 1101, Robert de Bellême was supporting the duke's cause.[66] According to Orderic, the king spent a year collecting evidence against Robert de Bellême; and in 1102, Henry summoned the latter, charging him with forty-five different offences against himself and Robert Curthose.[81] According to Brut y Tywysogion, Arnulf was likewise summoned and charged.[82] Arnulf appears to have fled to Wales,[83] and Robert de Bellême is recorded by Orderic to have fortified his English castles against Henry's men.[84] Whilst Robert de Bellême made alliances with the Welsh,[66] and perhaps attempted to align himself with the Norwegians as well,[85] Arnulf reached out to the Irish.[86] Brut y Tywysogion reveals that Arnulf sent Gerald de Windsor to Ireland, in order to arrange military assistance from Muirchertach Ua Briain, king of Munster (died 1119).[87] The alliance was formalised by a remarkable marriage between Arnulf and one of Muirchertach's daughters, the record of which is preserved by Orderic and Brut y Tywysogion, and alluded to in the Annals of Inisfallen.[88] These sources are further corroborated by a particular letter from Muirchertach to Anselm,[89] likely dating to about 1106–1107,[90] in which Muirchertach expressed his gratitude to the archbishop for intervening with Henry on behalf of "my son-in-law Arnulf".[89] Although the native Gaelic form of the bride's name is unknown,[91] Orderic Vitalis named her "Lafracoth" in Latin.[92] It is unknown for certain what motivated Muirchertach to agree to this alliance across the Irish Sea. One possibility is that he may have attempted to secure the valuable trade route from south Wales and the Bristol Channel to Waterford.[93][note 10] His involvement may well have part of a larger plan to not only increase power in Ireland but further exert influence throughout the Irish Sea region.[94][note 11] Although Brut y Tywysogion reveals that Muirchertach lent the brothers military support,[96] and it is possible that Roger the Poitevin aided them as well, the Bellême-Montgomery insurrection ended in utter failure.[97]
Surviving sources give differing accounts of the rebellion.[99] Arnulf's principal contribution appears to have been his participation in a predatory strike into Staffordshire.[100] According to the historian Symeon of Durham (died c. 1128) and the Worcester Chronicle, Robert de Bellême and Arnulf, supported by Welsh allies, ravaged a part of the county, before carrying off livestock and men to Wales.[101] Orderic's detailed account of the general uprising appears to be the most reliable record of events. His account reveals that, following Robert de Bellême's flight from the king's summons, Henry appears to have raised a feudal host consisting of his tenants-in-chief (who owed him knight-service) and the old English fyrd (a levy of one armed man from about every five hides or six carucates).[102] Orderic stated that Henry's host besieged the castle of Arundel for three months before it's capitulation, after which the king led his forces to the castle of Tickhill which immediately surrendered.[103] After temporarily standing down his army, Henry resumed operations in the autumn, and Orderic records that he seized the castle of Bridgnorth after a three-week siege. At about this point, Orderic records that, William Pantulf (died probably 1112), a former vassal of the Montgomerys, offered his services to Robert de Bellême. When the latter rebuffed the knight's support, Orderic records that he went over to Henry's side, and was instrumental in convincing Robert de Bellême's Welsh allies desert him and support the king instead.[104][note 12] Brut y Tywysogion specifically states that Iorwerth ap Bleddyn (died 1111), a leading Welshman, was bought off by the king and began to harry his former ally's lands.[106] After Henry's forces marched to Shrewsbury itself, Orderic records that Robert de Bellême's submitted to the king in person.[107] Defeated, the three surviving sons of Roger de Montgomery were banished from the kingdom, with their lands and titles declared forfeit.[108][note 13]
Aftermath

Whilst Robert fled to the continent, surviving sources suggest that Arnulf, and likely others from the ill-fated insurrection, sought refuge in Ireland.[113] For instance, William of Malmesbury recorded a brief deterioration of relations between Muirchertach and the English, before an English trade embargo forced reconciliation upon Muirchertach.[114] Furthermore, Orderic claimed that Arnulf and other Normans assisted the Irish in campaigning against Magnús; and that following the latter's death, Muirchertach forced Arnulf from Ireland altogether.[115] The details of Orderic's account of Magnús' death are likely erroneous, however, since the latter was slain in the north of Ireland by Ulstermen.[116] Orderic's description of Arnulf's flight from Ireland, and Muirchertach's enmity, may be mistaken as well, since the aforementioned letter between Muirchertach and Anselm suggests continued good relations between Muirchertach and Arnulf.[117] Orderic's account, however, may be evidence of English mercenarial involvement in Ireland during Henry's reign.[118][note 14]
Robert Curthose initially agreed to support Henry against the banished Robert de Bellême, who was now in Normandy and hostile to the duke.[120] At some point before June 1103, Arnulf appears to have betrayed his brother's trust, since Orderic stated that Arnulf took the castle of Alménêches, a Montgomery family stronghold, and handed it over to the duke.[121] It may have been at this point that Arnulf sought refuge in Ireland.[122] Whatever the case, Robert de Bellême's efforts to recover the castle led to his razing of the nearby nunnery of Alménêches, where his sister, Emma (died 1113), was abbess.[66] By 1104, his military successes against the duke forced the latter to come to terms. With Robert de Bellême and Robert Curthose thus reconciled, Henry turned against the two and finally defeated them outright in battle, near the castle of Tinchebray in September 1106.[123] Although a version of Brut y Tywysogion suggests that Arnulf took part in the battle, Orderic's account of Arnulf's earlier betrayal at Alménêches may contradict this.[124] Despite the aforementioned correspondence evidencing Anselm's reconciliation of Henry with Arnulf, the latter never held land in England ever again,[125] and appears to have endured a peripatetic career for about twenty years.[126] Evidence that he visited England, at least on one occasion, may be preserved in Eadmer's Latin Vita Anselmi, which states that Arnulf made a returning voyage from Normandy ("de Normannia Angliam rediens").[127][note 15]
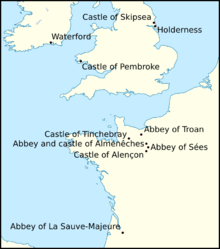
Between 1110 and 1112, Robert de Bellême involved himself in uprisings in southern Normandy, encouraged by Henry's opponent, the recently inaugurated Foulques, count of Anjou and Maine (died 1143). Henry responded by bringing charges against Robert de Bellême, and finally seizing him in November 1112. The latter's lands were declared forfeit, and he was imprisoned by the king for the rest of his life.[66] During the first quarter of the twelfth century, Arnulf attested eight charters of Foulques, making Arnulf one of the count's most frequent witnesses.[132] In about 1114, Arnulf witnessed an act between his great-niece, Philippa, countess of Poitou, and Bernard-Aton, vicomte of Béziers.[133] Arnulf's influence at Foulques's court appears to be evidenced by particular actions in 1118.[5] That year the townsfolk of Alençon rebelled against Henry and their lord Stephen, count of Mortain (died 1154),[134] whilst the latter were campaigning against a continental coalition attempting to replace the king with Robert Curthose's illegitimate son, William Clito (died 1128).[135][note 16] The region of Alençon was a former power centre of the Bellême family, and according to Orderic, the townsfolk requested that Arnulf intervene with Foulques on their behalf against Stephen's injustices and oppression.[137] In what turned out to be Henry's single greatest defeat,[138] Foulques' troops then seized the town and besieged the citadel, before crushing Henry's relief forces, after which Foulques secured the citadel once and for all.[139] Arnulf, probably now in his fifties, is not noted in any of the surviving sources documenting the clash.[140] He and his family may well have been responsible for an uprising that appears to flared up at about the same time, in what were former Montgomery-Bellême lands in central Normandy. This insurrection seems to have contributed to Henry's restoration of much of the former Montgomery-Bellême lands in Normandy to Robert de Bellême's son, William, count of Ponthieu (died 1171), in June 1119.[141]
The next certain record concerning Arnulf occurs in 1122, when his name is listed in a mortuary roll, circulated after the death of churchman Vitalis of Savigny (died 1122), in which the nuns of the abbey of Alménêches commemorated his parents, himself, and his younger brother, Philip (died 1099).[142][note 17] Arnulf, therefore, died sometime between 1118 and 1122.[144] Orderic's depiction of Arnulf's death is likely unhistorical.[140] This account relates that, following Magnús' death, Arnulf was forced from Ireland by Muirchertach, only to return about twenty years later, whereupon he remarried the latter's daughter, and died following the feast.[145] There is no evidence that Arnulf left any descendants.[146][note 18]
Legacy
Our limbs are cut off, we are lacerated, our necks condemned to death, and chains are put on our arms. The honest man's hand is branded by burning metals. A woman [now] lacks her nose, a man his genitals. [More] dire losses of our faculties follow, and prison shuts us in for many years. Serfdom is brought to the neck with a meat-hook, and learns that nothing can be had at will.[150]
There are numerous instances where contemporaries noted members of the Montgomery family for unusual cruelty—Robert de Bellême in particular.[151] According to Orderic, Mabel was murdered by a vassal, a particular act that may evidence her unpleasantness.[152][note 19] Orderic described Hugh de Montgomery in Latin as the only "mild and loveable" (mansuetus et amabilis) of Mabel's sons,[154] whilst Welsh sources present him in a much more negative light.[155] A source concerning Arnulf may be Planctus Ricemarch, a sorrowful Latin lament composed by scholar Rhygyfarch ap Sulien (died 1099). This source, a contemporary composition bewailing the cultural upheaval and oppression inflicted upon the Welsh after the Anglo-Norman conquests of 1093, may refer to subjugation suffered under Arnulf and his father.[156]
The actions of the Montgomery family illustrate the remarkable speed at which Norman families could spread across far-flung regions. Although Norman families tended to practice primogeniture, the conquest of England and the opening up of Britain contributed a new area of exploitation for landless younger sons of the aristocracy.[157] The careers of younger sons of the Anglo-Norman aristocracy are often obscure, with few surviving sources documenting their activities. The younger sons of Roger de Montgomery and Mabel are an exception,[78] and Arnulf's career illustrates the various opportunities available to men of his rank.[158] Despite losing his lands later in his career, Arnulf's numerous and regular attestations in court circles reveal that he retained substantial personal prestige. The far-flung nature of these attestations may well indicate that his skills as a negotiator were well-known and valued. Indeed, Arnulf's career reveals the importance of personal-connections in the courtly-world of the Anglo-Norman era.[159]
Arnulf's family, traced with certainty only two patrilineal generations previous,[160] derived its surname from lands now known as Sainte-Foy-de-Montgommery and Saint-Germain-de-Montgommery, in Calvados, Normandy.[161] Although descendants of Arnulf's siblings survived for several generations, the family's toponymic surname died with Arnulf.[162]
Ancestry
| Ancestors of Arnulf of Montgomery | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes
- ↑ This charter marks the first appearance of Roger the Poitevin.[10]
- ↑ The southern march suffered from a Welsh resurgence in the years immediately following the successes of 1093. A somewhat fanciful tale of Arnulf's castle was recounted by Gerald of Wales, Gerald de Windsor's grandfather. In this account, the castle was besieged by the Welsh whilst under the command of Gerald de Windsor. Running short on supplies, and losing men to poor moral, Gerald of Wales stated that his grandfather not only had the carcasses of four pigs thrown over the stockade, to convince the attackers that the defenders were well-stocked with supplies, but even had a fake letter to Arnulf planted outside the castle, in which he declared that the castle did not need any reinforcements or supplies in the foreseeable future. Through these machinations, Gerald of Wales stated that the Welsh abandoned the siege, and that Gerald de Windsor saved the castle of Pembroke.[39]
- ↑ A later grant to this religious house evidences Arnulf's patronage in the last years of William Rufus' reign.[43]
- ↑ This grant was later confirmed by Robert Curthose.[47]
- ↑ This was the first act of Canterbury's jurisdiction over Wales.[52] In effect, Canterbury's authority over Wales lasted from then until 1920.[53]
- ↑ Others specifically named by Anselm include Ralph de Mortimer (died 1104), Philip de Briouze, and Bernard de Neufmarché (died probably 1121×1125).[56]
- ↑ Earlier in the year, Robert de Bellême and William Rufus had campagined against Helias, as the king vied to renew control over the county of Maine. According to Orderic, Robert de Bellême had to pay the king a relief of £3000 before he was rewarded with the earldom.[62]
- ↑ Roger the Poitevin disappears from William Rufus' acta in 1094, which may be evidence that he relocated to La Marche, where his wife was deeply involved in a succession dispute.[68]
- ↑ Odo had been implicated in a plot against William Rufus in 1095. After Arnulf's own forfeiture in 1102, his lands of Holderness were returned to Odo's son, Stephen, count of Aumâle (died c. 1127).[71] This particular back-and-forth changing of hands of the honour illustrates the risks suffered by undertenants whose liege was only a temporary interloper.[72] Specifically, whilst Arnulf held the honour, he granted gifts from the Holderness lands of Carlton, Easington, Frodingham, Paghill, Preston, Skeekling, Tunstall, Withernsea, and gifts from a castle[73] (perhaps one at Aldbrough[74] or that of Skipsea),[75] to the abbey of Saint-Martin de Sées and a cell of the abbey's monks that he had founded at Pembroke.[73] He further granted gifts from Barrow and Bytham, both Holderness lands in Lincolnshire, to the abbey of La Sauve-Majeure.[76] After his downfall and Stephen's reinstatement, the aforementioned grants of Arnulf lapsed, and Stephen made grants of his own.[72] The historicity of a castle at Aldbrough is uncertain. Contemporary evidence for its existence depends on a single source, a charter of Stephen dated to 1115, which may be a mere misreading.[77]
- ↑ The capture of Waterford by Richard de Clare, earl of Pembroke in 1170 may have been undertaken for similar reasons.[93]
- ↑ Probably at about the same time as the marriage between Arnulf and Lafracoth, Muirchertach married another one of his daughters to Magnús' young son, Sigurðr (died 1130).[95]
- ↑ In the 1070s, William Pantulf, a tenant of Roger de Montgomery in Normandy, was suspected to have participated in Mabel's murder. Although William Pantulf suffered the confiscation of his lands following her murder, he later gained lands in Shropshire, Staffordshire, and Warwickshire. Once Robert de Bellême succeeded to the earldom of Shrewsbury, he deprived William Pantulf of his lands.[105]
- ↑ Henry's 1102 confirmation of the gifts that Arnulf granted to the abbey of Saint-Martin de Sées in 1098 dates before the Bellême-Montgomery rebellion.[109] The nunnery of Arnulf's sister, Emma (died 1113), also lost its English lands.[110] Having vanquished the rebels, Henry transformed the Welsh marches, settling not only new lords in the region, but disposing lordships upon the native Welsh as well. He kept personal control of Arnulf's lordship of Pembroke;[111] and the latter's steward, Gerald de Windsor, entered the king's service.[112] From Pembroke, Henry appears to have exercised lordship over the lords of Cemais, Draughleddau, Emlyn, Narberth, Rhos, and personal overlordship over the Castlemartin peninsula.[111]
- ↑ Although the Irish Annals make no mention of Arnulf or any of his men, decades later when the exiled Diarmait Mac Murchada (died 1171) returned to Ireland, enstrengthened with Flemings from Pembrokeshire, the Annals of Inisfallen and the Annals of Ulster fail to mention these foreigners, suggesting that mercenarial involvement in Ireland was not uncommon.[119]
- ↑ The particular passage in this source relates that, during this voyage across the channel, Arnulf's boat was caught in a storm for two days. Eadmer states that, when Arnulf implored his fellow passengers to pray to Anselm for protection, the storm miraculously cleared; and that, once the boat had made landfall, the disembarked passengers reported the miracle at Henry's court.[128] Anselm was a candidate for canonisation later in the twelfth century.[129] Eadmer's account is evidence that Arnulf was one of Anselm's earliest devotees.[130] The aforementioned incident likely took place shortly after Anselm's death.[131]
- ↑ Stephen was Henry's nephew and a future king of England.[136]
- ↑ Philip died on crusade, in Antioch.[143]
- ↑ Although it is sometimes asserted that Arnulf and Lafracoth had a daughter, Alice, who married Maurice fitz Gerald (died 1176), ancestor of the Irish Fitzgerald family, the claim is unsupported, and dates no earlier than the nineteenth century.[147] Likewise, Arnulf has been claimed, without any evidence, to have been an ancestor of the Scottish Montgomery family.[148] In fact, the latter family is unlikely to be related to Arnulf's, and probably derived its surname from the honour of Montgomery, in Shropshire.[149]
- ↑ Orderic's description of Mabel's demise—that she was slain in bed whilst resting after taking a bath—may not be an accurate account of events. The details may have been borrowed from the epic tradition of a warrior's death in a bath, dating as far back as the tales of Agamemnon.[153]
- ↑ Roger de Montgomery, Arnulf's paternal-grandfather, was a leading Norman magnate. He is the earliest certain member of the Montgomery family on record.[164] Surviving sources give contradictory accounts of his parentage. According to chronicler Robert of Torigni (died 1186), in Gesta Normannorum Ducum, the father was a certain Hugh, husband of Josceline.[165] However, Robert of Torigni contradicted himself in his De Immutatione Ordinis Monachorum, stating that the father was named Roger.[166]
- ↑ Surviving sources give contradictory accounts of Josceline's parentage. According to Robert of Torigny, in Gesta Normannorum Ducum, her mother was Wevia, sister of Gunnor, wife of Richard, count of Rouen (died 996)—Gunnor and Richard being ancestors of later dukes of Normandy.[168] According to a later genealogy composed by Ivo, bishop of Chartres (died 1115), however, Josceline's mother was Seufria, sister of Gunnor.[169] Although the identity of Josceline's mother is uncertain, her apparent kinship with Gunnor, and thus the ruling family of Normandy, may well have been the catalyst for the documented rise of the Montgomery family in the first half of the eleventh century.[170]
- ↑ Roger's mother was still living in 1068. She may have been named Emma.[154]of sta1. Arnulf de Montgomery (c. 1066–1118×22)24. Ivo de Bellême (fl. 1005)[171][note 23]
- ↑ Ivo's father may have been Ivo de Creil.e MonWhite (1940) pp. 70, 98.
- ↑ Although Godeheut's parentage is unknown, she appears to have been a sister of Seinfroy, bishop of Le Mans.[171]In 109
6. Guillaume de Bellême (fl. 1060)[173]13. Maud[174]3. Mabel de Bellême (died 1077)14. Arnulf[175]7. Hildeburg921)]] p. 118, 118 nWhite (1940) pp. 85, 98.
Citations
- ↑ The Itinerary Through Wales (1908) p. 82; Dimock (1868) p. 89; Royal MS 13 B VIII (n.d.).
- ↑ Dimock (1868) pp. ix–x.
- ↑ Dimock (1868) p. 89.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 8.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Thompson (2004b).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Mason (2004b); Keats-Rohan (1999) pp. 399–400.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Mason (2004b).
- ↑ Keats-Rohan (1999) pp. 399–400; Mason (1963) pp. 1–5.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) pp. 2, 2 n. 3, 8; Davis (1913) p. 47 (§ 172).
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 2.
- ↑ Mason (2004b); Lewis (1989) pp. 572–573; Mason (1963) p. 16.
- ↑ Lewis (1989) pp. 572–573; Arnold (1879) pp. 213–215; Forester 1854a, pp. 186–191 (§ 1088); Forester (1853) pp. 222–223; Thorpe (1849) pp. 21–26; Giles (1847) pp. 327–330; Hardy (1840) pp. 486–490 (§ 306).
- ↑ Lewis (1989) pp. 572–573; Stevenson (1853) pp. 135–137 (§ 1088).
- ↑ Lewis (1989) p. 573; Mason (1963) p. 16; Freeman (1882) p. 57 n. 3.
- ↑ Lewis (1989) p. 573, 573 n. 2.
- ↑ Mason 2004b; Mason (1963) p. 16.
- ↑ Kenyon (2003) p. 247.
- ↑ Turvey (2002) p. 44.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Lloyd; Thornton (2004).
- ↑ Turvey (2002) p. 44; Davies (2000) p. 34.
- ↑ Kenyon (2010) p. 89; Brown (1989) p. 177.
- ↑ Coulson (2003) p. 52 n. 178.
- ↑ Brown (1989) p. 177.
- ↑ Davies (2000) p. 91; The Itinerary Through Wales (1908) p. 82; Dimock (1868) p. 89.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) pp. 8–9.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) pp. 8–9, 9 n. 50; Mason (1963) pp. 17–19.
- ↑ Thompson (1991) pp. 275–276 n. 56; Mason (1963) pp. 17–18 n. 4; Schmitt (1949) p. 185 (§ 270).
- ↑ Mason (1963) pp. 17–18 n. 4; Southern (1962) pp. 146–147, 152–153; Rule (1884) pp. 419, 425.
- ↑ Mason (1963) pp. 17–18 n. 4; Bell (1960) p. 187 (§ 5888).
- ↑ Mason (1963) pp. 17–18 n. 4; The Itinerary Through Wales (1908) p. 83; Dimock (1868) p. 90.
- ↑ Mason (1963) pp. 17–18 n. 4; Southern (1962) p. 146 n. 1; Forester (1854b) pp. 33–34, 338; Le Prévost (1845) pp. 425–426; Le Prévost (1852) p. 177.
- ↑ Mason (1963) pp. 17–18 n. 4.
- ↑ Mason (1963) pp. 17–18 n. 4; Edwards (1868) p. 306.
- ↑ Mason (1963) pp. 17–18 n. 4; Round (1899) p. 239 (§ 670).
- ↑ Kenyon (2010) p. 89; Lloyd (1912) p. 401.
- ↑ MacCotter; Nicholls (2009) p. 49; Crouch (2004); Lloyd; Thornton (2004); Walker (2004).
- ↑ Lloyd; Thornton (2004); Turvey (2002) p. 44; Lloyd (1912) p. 401, 401 n. 6; Rhŷs; Evans (1890) pp. 294–295 (§§ 267–268); Williams Ab Ithel (1860) pp. 120–121.
- ↑ MacCotter; Nicholls (2009) p. 49; Rowlands (1981) p. 145.
- ↑ Walker (2004).
- ↑ Rowlands (1981) p. 142.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 41.2 Chandler (1989) p. 9.
- ↑ Mason (2002) ch. 7; Chandler (1989) p. 9; Mason (1963) p. 19; Davis (1913) p. 103 (§ 410); Round (1899) p. 446 (§ 1234).
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 9 n. 53; Round (1899) p. 446 (§ 1235).
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 9, 9 n. 55; Mason (1963) p. 19 n. 3; Round (1899) p. 447 (§ 1238).
- ↑ Keats-Rohan (1999) pp. 399–400.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 9, 9 n. 54.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 9 n. 54; Haskins (1918) p. 70 (§ 37).
- ↑ Hull (2009) p. 17 illust.
- ↑ Kenyon (2010) pp. 89–92.
- ↑ Davies (2008) pp. 86–87; Davies (2000) p. 179.
- ↑ Davies (2008) p. 86–87; Southern (2009); Davies (2000) p. 179; Southern (2000) p. 337; Vaughn (1987) p. 195; Schmitt (1949) pp. 56–57 (§ 175); Rule (1884) p. 72.
- ↑ Southern (2000) p. 337; Vaughn (1987) p. 195.
- ↑ Southern (2000) p. 338.
- ↑ Davies (2008) p. 86–87; Southern (2000) pp. 337–338; Vaughn (1987) p. 195.
- ↑ Davies (2008) p. 87; Southern (2000) pp. 337–338; Vaughn (1987) p. 195, 195 n. 226; Schmitt (1949) p. 185 (§ 270).
- ↑ Davies (2008) pp. 87, 88 n. 25; Vaughn (1987) p. 195 n. 226; Schmitt (1949) p. 185 (§ 270).
- ↑ Southern (2000) pp. 337–338, 339.
- ↑ Mason (2004a); Chandler (1989) p. 9; Forester (1854b) pp. 218–219.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) pp. 9–10; Round (1899) pp. 237–238 (§ 666).
- ↑ Thompson (2004a); Thompson (2004b); Chandler (1989) p. 10; Mason (1963) p. 20.
- ↑ Thompson (2004a); Mason (2002) ch. 7; Mason (1963) p. 20.
- ↑ Thompson (2004a); Mason (2002) ch. 7; Thompson (1991) p. 275; Chandler (1989) p. 10; Mason (1963) p. 20.
- ↑ Thompson 2004a; Thompson (1991) p. 276.
- ↑ Hollister (2003) pp. 154–155; Thompson (1991) p. 286.
- ↑ Thompson 2004a; Hollister (2003) pp. 154–155; Thompson (1991) pp. 275–276.
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 66.2 66.3 66.4 66.5 66.6 Thompson (2004a).
- ↑ Hollister (2003) p. 155; Lewis (1989) p. 571.
- ↑ Thompson (1991) p. 275 n. 56.
- ↑ Crouch (2002) p. 174.
- ↑ Dalton (2002) pp. 86, 93; Chandler (1989) p. 9; Farrer (1989) pp. 27–28 (§ 1300); Davis (1913) p. 116 (§ 483); Round (1899) pp. xl–xli, 238 (§ 667), 446–447 (§ 1235), 446 (§ 1236).
- ↑ Holt (2006) p. 93 n. 139; Dalton (2002) pp. 86, 93; Round (1899) pp. xl–xli.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 Holt (2006) pp. 94–95; Round (1899) pp. xl–xli.
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 Kent (2002); Farrer (1989) pp. 27–28 (§ 1300); Round (1899) pp. xl–xli, 238 (§ 667).
- ↑ Round (1899) p. xli.
- ↑ Kent (2002) pp. 374–405.
- ↑ Speight (1993) p. 242; Davis (1913) p. 116 (§ 483); Round (1899) pp. xl–xli, 446 (§ 1236).
- ↑ Kent (2002) pp. 5–27; Farrer (1989) pp. 30–33 (§ 1304).
- ↑ 78.0 78.1 78.2 Thompson (1995) p. 49.
- ↑ Thompson (2004b); van Houts (1999) pp. 169–174; Thompson (1995) p. 49; Thompson (1991) p. 276 n. 62; Chandler (1989) p. 10; Johnson; Cronne (1956) p. 7 (§ 515).
- ↑ Thompson (2004a); Thompson (1991) p. 276, 276 n. 59.
- ↑ Thompson (2004a); Hollister (2003) p. 157; Forester (1854b) p. 331; Le Prévost (1852) pp. 169–170.
- ↑ Strevett (2005) p. 161; Hollister (2003) p. 157.
- ↑ Strevett (2005) p. 161; Crouch (2002) p. 174.
- ↑ Thompson (2004a); Hollister (2003) p. 157; Crouch (2002) p. 174.
- ↑ Oram (2011) p. 52; Green (2000) p. 107.
- ↑ Bracken (2004); Thompson (2004a).
- ↑ Bracken 2004; Curtis (1921) p. 118; Williams Ab Ithel (1860) pp. 68–69.
- ↑ Babcock (2007) p. 53; Power (2005) p. 17, 17 n. 15; Annals of Inisfallen (2010) § 1102.6; Annals of Inisfallen (2008) § 1102.6; Chandler (1989) pp. 10–11; Curtis (1921) p. 118, 118 n. 5; Forester (1854b) p. 338; Le Prévost (1852) pp. 177–178.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 Bracken (2004); Schmitt (1949) p. 372 (§ 426); Curtis (1921) pp. 118, 118–119 n. 6; Elrington; Todd (n.d.), p. 526.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 12.
- ↑ Curtis (1921) p. 118 n. 5.
- ↑ Power (2005) p. 17 n. 15; Chandler (1989) pp. 10–11; Anderson (1922) p. 126 n. 6; Curtis (1921) p. 118, 118 n. 5; Forester (1854b) p. 338.
- ↑ 93.0 93.1 Duffy (2004) pp. 100–101.
- ↑ Oram (2011) pp. 52–53.
- ↑ Duffy (2005) p. 460; Power (2005) p. 17; Chandler (1989) pp. 10–11.
- ↑ Babcock (2007) p. 53.
- ↑ Lieberman (2010) p. 68.
- ↑ Dixon (2008) p. 260.
- ↑ Hollister (2003) p. 158.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 11.
- ↑ Hollister (2003) p. 158; Morillo (1997) p. 101; Chandler (1989) p. 11; Arnold (1885) p. 234; Forester (1854a) p. 210; Thorpe (1849) p. 50.
- ↑ Hollister (1998) p. 142, 142 n. 1; Hollister (2003) p. 159.
- ↑ Hollister (2003) p. 159; Forester (1854b) p. 332.
- ↑ Hollister (2003) p. 159; Forester (1854b) pp. 334–336.
- ↑ Bateson; Suppe (2004).
- ↑ Hollister (2003) p. 160; Williams Ab Ithel (1860) pp. 70–71.
- ↑ Hollister (2003) p. 160; Forester (1854b) p. 337.
- ↑ Babcock (2007) p. 53; Mason (2004b); Thompson (2004a).
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 10; Johnson; Cronne (1956) p. 28 (§ 623); Round (1899) p. 238 (§ 668).
- ↑ Thompson (1991) p. 276.
- ↑ 111.0 111.1 Rowlands (1981) pp. 151–152.
- ↑ MacCotter; Nicholls (2009) p. 49; Rowlands (1981) pp. 151–152.
- ↑ Babcock (2007) pp. 53–54; Duffy (2004) p. 101.
- ↑ Duffy (2009) pp. 297–298; Babcock (2007) pp. 53–54; Duffy (2005) p. 460; Hudson (2004) p. 52; Giles (1847) p. 443; Hardy (1840) p. 638.
- ↑ Babcock (2007) p. 54; Duffy (2004) p. 101; Forester (1854b) pp. 350–351.
- ↑ Babcock (2007) p. 54.
- ↑ Duffy (2009) pp. 297–298; Babcock (2007) p. 54.
- ↑ Babcock (2007) p. 54; Duffy (2004) p. 101.
- ↑ Duffy (2004) p. 101.
- ↑ Thompson (2004c).
- ↑ Thompson (2004a); Thompson (2004b); Thompson (2004c); Thompson (1995) p. 50, 50 n. 9; Chandler (1989) p. 11; Forester (1854b) p. 339.
- ↑ Thompson (1995) p. 50.
- ↑ Thompson (2004a); Thompson (2004c).
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 11 n. 76.
- ↑ Mason (1963) p. 24 n. 2.
- ↑ Thompson (2004b); Mason (1963) p. 24.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 12, 12 n. 79; Mason (1963) p. 24 n. 2; Southern (1962) p. 146; Rule (1884) pp. 419–420.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 12; Southern (1962) pp. 146–147; Rule (1884) pp. 419–420.
- ↑ Southern (2009).
- ↑ Southern (2000) pp. 337–338.
- ↑ Southern (1962) p. 146 n. 1.
- ↑ Chevalier (2010) p. 476 (§ 439); Barton (2005) p. 34 n. 11; Thompson (2004b); Chandler (1989) p. 12; Denis (1912) pp. 83–85 (§ 60); Métais (1894) pp. 208–209 (§ 434); Marchegay (1843) p. 380 (§ 36).
- ↑ Thompson (2004b); Chandler (1989) p. 12; Richard (1903) pp. 469–470; Devic; Vaissète (1875) p. 845 (§ 451).
- ↑ Thompson (2004b); Chandler (1989) pp. 12–13.
- ↑ Hollister (2004).
- ↑ Chandler (1989) pp. 12–13.
- ↑ Barton (2005) pp. 33–34; Thompson (2004b); Thompson (1995) p. 49; Chandler (1989) pp. 12–13; Forester (1854b) pp. 461–462.
- ↑ Hollister (2003) p. 252.
- ↑ Morillo (1997) pp. 107, 142–143, 170–171.
- ↑ 140.0 140.1 Chandler (1989) p. 13.
- ↑ Thompson (1995) p. 52; Thompson (1994) p. 172.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 13; Delisle (1866) pp. 281–282, 351.
- ↑ Chandler (1989) p. 5.
- ↑ Thompson (2004b); Chandler (1989) p. 13.
- ↑ Power (2005) p. 17 n. 15; Chandler (1989) p. 13; Curtis (1921) p. 122; Forester (1854b) p. 351.
- ↑ Thompson (2004b); Chandler (1989) p. 12 n. 80; Paul (1906) pp. 421–422.
- ↑ Thompson (2004b); Chandler (1989) p. 12 n. 80; Curtis (1921) pp. 123–124, 123 n. 11; Graves (1869) pp. 460–461 pedigree a; FitzGerald (1858) p. 10.
- ↑ Paul (1906) pp. 421–422; Fraser (1859) pp. 6–8.
- ↑ Barrow (1973) pp. 317, 317 n. 5, 334.
- ↑ Davies (2004) p. 222.
- ↑ Thompson (2004a); Thompson (1991) pp. 280–291; Mason (1963) pp. 24–25.
- ↑ Mason (1963) p. 25.
- ↑ Johns (2003) p. 15; Blacker (1998) pp. 51–52.
- ↑ 154.0 154.1 Mason (2004a).
- ↑ Mason (2004a); Thompson (1991) pp. 281–282; Mason (1963) pp. 24–25, 25 n. 1.
- ↑ Mason (1963) p. 25; Lawlor (1914) pp. 120–123.
- ↑ Frame (2001) pp. 36–37.
- ↑ Thompson (2004b); Frame (2001) pp. 36–37.
- ↑ Thompson (1995) pp. 52–53.
- ↑ Mason (2004b); Douglas (1983) p. 91.
- ↑ Mason (2004b); Keats-Rohan (1999) pp. 399–400; Loyd (1992) pp. 68–69.
- ↑ Thompson (1995) p. 53; Chandler (1989) p. 14.
- ↑ White (1940) p. 86.
- ↑ Douglas (1983) p. 91.
- ↑ Hollister (1987) p. 231, 231 nn. 54, 55.
- ↑ Hollister (1987) p. 231, 231 n. 56.
- ↑ White (1940) p. 86, 98.
- ↑ Hollister (1987) p. 231, 231 nn. 54, 55; White (1940) p. 86 n. 5.
- ↑ Mason (2004a); Hollister (1987) pp. 231–232, 232 n. 57; White (1940) p. 86.
- ↑ Hollister (1987) pp. 231–233.
- ↑ 171.0 171.1 171.2 White (1940) pp. 74, 98.
- ↑ White (1940) pp. 80, 98.
- ↑ White (1940) pp. 84–85, 98.
- ↑ White (1940) pp. 78–79, 98.
- ↑
References
Primary sources
- Anderson, AO, ed. (1922). Early Sources of Scottish History, A.D. 500 to 1286. Vol. 2. London: Oliver and Boyd – via Internet Archive.
- "Annals of Inisfallen". Corpus of Electronic Texts (23 October 2008 ed.). University College Cork. 2008. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- "Annals of Inisfallen". Corpus of Electronic Texts (16 February 2010 ed.). University College Cork. 2010. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- Arnold, T, ed. (1879). Henrici Archidiaconi Huntendunensis Historia Anglorum. The History of the English. Rerum Britannicarum Medii Ævi Scriptores. London: Longman & Co – via Internet Archive.
- Arnold, T, ed. (1885). Symeonis Monachi Opera Omnia. Rerum Britannicarum Medii Ævi Scriptores. Vol. 2. London: Longmans & Co – via Google Books.
- Bell, A, ed. (1960). L'Estoire des Engleis. Oxford: Basil Blackwell – via Google Books.
- Chevalier, C, ed. (2010) [1872]. Cartulaire de l'Abbaye de Noyers. Cambridge Library Collection. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-108-01983-5 – via Google Books.
- Davis, HWC, ed. (1913). Regesta Regum Anglo-Normannorum, 1066–1154. Vol. 1, Regesta Willelmi Conquestoris et Willelmi Rufi, 1066–1100. Oxford: Oxford University Press – via Internet Archive.
- Delisle, L, ed. (1866). Rouleaux des Morts du IXe au XVe Siècle Recueillis et Publiés pour la Société de l'Histoire de France. Paris: Mme Ve Jules Renouard – via Internet Archive.
- Denis, LJ, ed. (1912). Archives Historiques du Maine. Vol. 12, Chartes de Saint-Julien de Tours, 1002–1227. Le Mans: Société des Archives Historiques du Maine – via Gallica.
- Devic, CL; Vaissete, J, eds. (1875). Histoire Générale de Languedoc. Vol. 5. Toulouse: Edouard Privat – via Internet Archive.
- Dimock, JF, ed. (1868). Giraldi Cambrensis Opera. Rerum Britannicarum Medii Ævi Scriptores. Vol. 6. London: Longmans, Green, Reader, and Dyer – via Internet Archive.
- Edwards, E, ed. (1868). Liber Monasterii de Hyda: Comprising a Chronicle of the Affairs of England, from the Settlement of the Saxons to the Reign of King Cnut, and a Chartulary of the Abbey of Hyde, in Hampshire, A.D. 455–1023. Rerum Britannicarum Medii Ævi Scriptores. London: Longmans, Green, Reader, and Dyer – via Internet Archive.
- Elrington, CR; Todd, JH, eds. (n.d.). The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, D.D., Lord Archbishop of Armagh, and Primate of All Ireland. Vol. 4. Dublin: Hodges and Smith – via Internet Archive.
- Farrer, W, ed. (1916). Early Yorkshire Charters: Being a Collection of Documents Anterior to the Thirteenth Century Made from the Public Records, Monastic Chartularies, Roger Dodsworth's Manuscripts and other Available Sources. Vol. 3. Edinburgh: n.p. – via Internet Archive.
- FitzGerald, CW (1858). The Earls of Kildare, and Their Ancestors, from 1077 to 1773 (2nd ed.). Dublin: Hodges, Smith, & Co. – via Internet Archive.
- Forester, T, ed. (1853). The Chronicle of Henry of Huntingdon: Comprising the History of England, From the Invasion of Julius Cæsar to the Accession of Henry II. Also, the Acts of Stephen, King of England and Duke of Normandy. Bohn's Antiquarian Library. London: Henry G. Bohn – via Internet Archive.
- Forester, T, ed. (1854a). The Chronicle of Florence of Worcester, with the Two Continuations: Comprising Annals of English History, from the Departure of the Romans to the Reign of Edward I. Bohn's Antiquarian Library. London: Henry G. Bohn – via Internet Archive.
- Forester, T, ed. (1854b). The Ecclesiastical History of England and Normandy, by Ordericus Vitalus. Bohn's Antiquarian Library. Vol. 3. London: Henry G. Bohn – via Internet Archive.
- Giles, JA, ed. (1847). William of Malmesbury's Chronicle of the Kings of England, from the Earliest Period to the Reign of King Stephen. Bohn's Antiquarian Library. London: Henry G. Bohn – via Internet Archive.
- Graves, J (1869). No. 2. The Earls of Desmond. The Journal of the Historical and Archaeological Association of Ireland. Third series, vol. 1 (No. 2) (Royal Society of Antiquaries of Ireland). pp. 459–498. JSTOR 25497799 – via JSTOR. (subscription required (help)).
- Hardy, TD, ed. (1840). Willelmi Malmesbiriensis Monachi Gesta Regum Anglorum atque Historia Novella. Vol. 2. London: English Historical Society – via Internet Archive.
- Haskins, CH (1918). Norman Institutions. Harvard Historical Studies (series vol. 24). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press – via Internet Archive.
- Johnson, C; Cronne, HA, eds. (1956). Regesta Regum Anglo-Normannorum, 1066–1154. Vol. 2, Regesta Henrici Primi, 1100–1135. Oxford: Oxford University Press – via Internet Archive.
- Lawlor, HJ, ed. (1914). The Psalter and Martyrology of Ricemarch. Henry Bradshaw Society (series vol. 47). Vol. 1, Texts, Notes, Indices. London: Henry Bradshaw Society – via Internet Archive.
- Le Prevost, A, ed. (1845). Orderici Vitalis Historiæ Ecclesiasticæ Libri Tredecim. Vol. 3. Paris: Société de l'histoire de France – via Internet Archive.
- Le Prevost, A, ed. (1852). Orderici Vitalis Historiæ Ecclesiasticæ Libri Tredecim. Vol. 4. Paris: Société de l'histoire de France – via Internet Archive.
- Marchegay, P, ed. (1843). "Le Cartulaire de Saint-Maur-sur-Loire". Archives d'Anjou: Recueil de documents et mémoires inédits sur cette province. Vol. 1. Angers: Charles Labussière. pp. 293–429 – via Internet Archive.
- Métais, CH, ed. (1894). Cartulaire de l'Abbaye Cardinale de la Trinité de Vendôme. Vol. 2. Paris: Alphonse Picard et fils – via Internet Archive.
- Rhŷs, J; Evans, JG, eds. (1890). The Text of the Bruts from the Red Book of Hergest. Oxford: n.p. – via Internet Archive.
- Round, JH, ed. (1899). Calendar of Documents Preserved in France, Illustrative of the History of Great Britain and Ireland. Vol. 1, A.D. 918–1206. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office – via Internet Archive.
- "Royal MS 13 B VIII". British Library. n.d. Retrieved 15 January 2015.
- Rule, M, ed. (1884). Eadmeri Historia Novorum in Anglia et Opuscula Duo de Vita Sancti Anselmi et Quibusdam Miraculis Ejus. Rerum Britannicarum Medii Ævi Scriptores. London: Longman & Co. – via Internet Archive.
- Schmitt, FS, ed. (1949). S. Anselmi Cantuariensis Archiepiscopi Opera Omnia. Vol. 4. Edinburgh: Thomas Nelson & Sons – via Internet Archive.
- Southern, RW, ed. (1962). The Life of St Anselm, Archbishop of Canterbury, by Eadmer. New York: Thomas Nelson and Sons – via Questia. (subscription required (help)).
- Stevenson, J, ed. (1853). The Church Historians of England. Vol. 2, pt. 1. London: Seeleys – via Internet Archive.
- The Itinerary Through Wales and the Description of Wales. Everyman's Library. London: J. M. Dent & Sons. 1908 – via Internet Archive.
- Thorpe, B, ed. (1849). Florentii Wigorniensis Monachi Chronicon ex Chronicis. Vol. 2. London: English Historical Society – via Internet Archive.
- Williams Ab Ithel, J, ed. (1860). Brut y Tywysigion; or, The Chronicle of the Princes. Rerum Britannicarum Medii Ævi Scriptores. London: Longman, Green, Longman, and Roberts – via Internet Archive.
Secondary sources
- Babcock, RS (2007). "The Irish Sea Province and the Accession of Henry I". In Fleming, DF; Pope, JM. Henry I and the Anglo-Norman World: Studies in Memory of C. Warren Hollister. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. pp. 39–62. ISBN 978 1 84383 293 5. ISSN 0963-4959.
- Barrow, GWS (1973). The Kingdom of the Scots: Government, Church and Society From the Eleventh to the Fourteenth Century. New York: St. Martin's Press.
- Barton, R (2005). "Writing Warfare, Lordship and History: The Gesta Consulum Andegavorum's Account of the Battle of Alençon". In Gillingham, J. Anglo-Norman Studies. Vol. 27, Proceedings of the Battle Conference 2004. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. pp. 32–67. ISBN 1 84383 132 5. ISSN 0954-9927.
- Bateson, M; Suppe, F (2004). "Pantulf, William (d. 1112?)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (Revised ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/21242. Retrieved 5 November 2013. (subscription required (help)).
- Blacker, J (1998). "Women, Power, and Violence in Orderic Vitalis's Historia Ecclesiastica". In Roberts, A. Violence Against Women in Medieval Texts. Gainesville: University Press of Florida. pp. 44–55. ISBN 0-8130-1566-9 – via Google Books.
- Bracken, D (2004). "Ua Briain, Muirchertach [Murtagh O'Brien] (c.1050–1119)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/20464. Retrieved 5 July 2011. (subscription required (help)).
- Brown, RA (1989). Castles From the Air. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0 521 329329 – via Google Books.
- Chandler, V (1989). "The Last of the Montgomerys: Roger the Poitevin and Arnulf". Historical Research. Vol. 62 (Iss. 147): 1–14. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2281.1989.tb01075.x.
- Coulson, CLH (2003). Castles in Medieval Society: Fortresses in England, France, and Ireland in the Central Middle Ages. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-820824-3.
- Crouch, D (2002). The Normans: The History of a Dynasty. London: Hambledon Continuum. ISBN 1 85285 387 5.
- Crouch, D (2004). "Nest (b. before 1092, d. c.1130)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/19905. Retrieved 24 October 2013. (subscription required (help)).
- Curtis, E (1921). "Murchertach O'Brien, High King of Ireland, and His Norman Son-in-Law, Arnulf de Mont-Gomery, circa 1100". The Journal of the Royal Society of Antiquaries of Ireland (Royal Society of Antiquaries of Ireland). Vol. 11 (No. 2). JSTOR 25513221 – via JSTOR. (subscription required (help)).
- Dalton, P (2002). Conquest, Anarchy and Lordship: Yorkshire, 1066–1154. Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0 521 45098 5.
- Davies, JR (2008). "Aspects of Church Reform in Wales, c. 1093–c. 1223". In Lewis, CP. Anglo-Norman Studies. Vol. 30, Proceedings of the Battle Conference 2007. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. pp. 85–99. ISBN 978-1-84383-379-6.
- Davies, RR (2000). The Age of Conquest: Wales 1063–1415. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-820878-2 – via Google Books.
- Davies, S (2004). Welsh Military Institutions, 633–1283. Cardiff: University of Wales Press. ISBN 9780708318362 – via Google Books.
- Dixon, PH (2008). "The Influence of the White Tower on the Great Towers of the Twelfth Century". In Impey, E. The White Tower. New Haven: Yale University Press. pp. 242–275. ISBN 9780300112931.
- Douglas, DC (1983). William the Conqueror: The Norman Impact Upon England. London: Methuen London. ISBN 0 413 38380 6.
- Duffy, S (2004). "The 1169 Invasion as a Turning-point in Irish-Welsh Relations". In Smith, B. Britain and Ireland, 900–1300: Insular Responses to Medieval European Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 98–113. ISBN 0-511-03855-0.
- Duffy, S (2005). "Ua Briain, Muirchertach (1050–1119)". In Duffy, S. Medieval Ireland: An Encyclopedia. New York: Routledge. pp. 459–462. ISBN 0-415-94052-4.
- Duffy, S (2009). "Ireland, c.1000–c.1100". In Stafford, P. A Companion to the Early Middle Ages: Britain and Ireland, c.500–c.1100. Blackwell Companions to British History. Chichester: Blackwell Publishing. pp. 285–302. ISBN 978-1-405-10628-3.
- Frame, R (2001). "Conquest and Settlement". In Harvey, B. The Twelfth and Thirteenth Centuries 1066–c.1280. Short Oxford History of the British Isles. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 31–68. ISBN 0-19-873140-X.
- Fraser, W (1859). Memorials of the Montgomeries, Earls of Eglinton. Edinburgh: n.p. – via Internet Archive.
- Freeman, EA (1882). The Reign of William Rufus and the Accession of Henry the First. Vol. 1. Oxford: Clarendon Press – via Internet Archive.
- Green, JA (2000). "Robert Curthose Reassessed". In Harper-Bill, C. Anglo-Norman Studies. Vol. 22, Proceedings of the Battle Conference 1999. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. pp. 95–116. ISBN 0 85115 796 3 – via Google Books.
- Hollister, CW (1987). "The Greater Domesday Tenants-in-Chief". In Holt, JC. Domesday Studies: Novocentenary Conference, Royal History Society and Institute of British Geographers, Winchester 1986. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. pp. 219–248. ISBN 0 85115 477 8 – via Google Books.
- Hollister, CW (1998) [1962]. Anglo-Saxon Military Institutions On the Eve of the Norman Conquest. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-821296-8.
- Hollister, CW (2003). Henry I. Yale English Monarchs. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-09829-4 – via Google Books.
- Hollister, CW (2004). "Henry I (1068/9–1135)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/12948. Retrieved 5 July 2011. (subscription required (help)).
- Holt, JC (2006). "Politics and Property in Medieval England". In Aston, TH. Landlords, Peasants and Politics in Medieval England. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 65–114. ISBN 978-0-521-32403-8.
- Hudson, BT (2004). "The Changing Economy of the Irish Sea Province". In Smith, B. Britain and Ireland, 900–1300: Insular Responses to Medieval European Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 39–66. ISBN 0-511-03855-0.
- Hull, L (2009). Understanding the Castle Ruins of England and Wales: How to Interpret the History and Meaning of Masonry and Earthworks. Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Company. ISBN 978-0-7864-3457-2.
- Johns, S (2003). Noblewomen, Aristocracy and Power in the Twelfth-century Anglo-Norman Realm. Gender In History. Manchester: Manchester University Press. ISBN 0 7190 6304 3.
- Keats-Rohan, KSB (1999). Domesday People: A Prospography of Persons Occurring in English Documents 1066–1166. Vol. 1. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. ISBN 978-0-85115-722-1.
- Kent, GHR, ed. (2002). A History of the County of York East Riding. Vol. 7 – via British History Online.
- Kenyon, JR (2003). "Fluctuating Frontiers: Normanno-Welsh Castle Warfare, c.1075 to 1240". In Liddiard, R. Anglo-Norman Castles. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. pp. 247–258. ISBN 0 85115 904 4.
- Kenyon, JR (2010). The Medieval Castles of Wales. Cardiff: University of Wales Press. ISBN 978-0-7083-2363-2.
- Lewis, CP (1989). "The King and Eye: A Study in Anglo-Norman Politics". The English Historical Review (Oxford University Press). Vol. 104 (No. 412): 569–589. JSTOR 570376 – via JSTOR. (subscription required (help)).
- Lieberman, M (2010). The Medieval March of Wales: The Creation and Perception of a Frontier, 1066–1283. Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought, Fourth Series. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-511-67741-0.
- Lloyd, JE (1912). A History of Wales From the Earliest Times to the Edwardian Conquest. Vol. 2 (2nd ed.). London: Longmans, Green, and Co – via Internet Archive.
- Lloyd, JE; Thornton, DE (2004). "Rhys ap Tewdwr (d. 1093)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (Revised ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/23463. Retrieved 17 October 2013. (subscription required (help)).
- Loyd, LC (1992) [1951]. Clay, CT; Douglas, DC, eds. The Origins of Some Anglo-Norman Families. Baltimore: Genealogical Publishing Co. ISBN 0-8063-0649-1.
- MacCotter, P; Nicholls, K (2009). "Feudal Warlords: The Knights of Glencorby". In O'Donovan, T. The Knights of Glin: Seven Centuries of Change. Glin: Glin Historical Society. pp. 48–79. ISBN 9780953037339 – via Academia.edu.
- Mason, E (2012). King Rufus: The Life & Murder of William II of England (EPUB). Brimscombe Port: The History Press. ISBN 978 0 7524 8683 3.
- Mason, JFA (1963). "Roger de Montgomery and His Sons (1067–1102)". Transactions of the Royal Historical Society (Royal Historical Society). Fifth series, vol. 13: 1–28. JSTOR 3678727 – via JSTOR. (subscription required (help)).
- Mason, JFA (2004a). "Montgomery, Hugh de, Second Earl of Shrewsbury (d. 1098)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/14055. Retrieved 7 September 2011. (subscription required (help)).
- Mason, JFA (2004b). "Montgomery, Roger de, First Earl of Shrewsbury (d. 1094)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/22098. Retrieved 5 July 2011. (subscription required (help)).
- Morillo, S (1997). Warfare Under the Anglo-Norman Kings, 1066–1135. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. ISBN 978-0-85115-555-5.
- Oram, RD (2011). Domination and Lordship: Scotland 1070–1230. The New Edinburgh History of Scotland (series vol. 3). Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978 0 7486 1496 7 – via Google Books and Questia. (subscription required (help)).
- Paul, JB, ed. (1906). The Scots Peerage: Founded on Wood's Edition of Sir Robert Douglas's Peerage of Scotland, Containing an Historical and Genealogical Account of the Nobility of that Kingdom. Vol. 3. Edinburgh: David Douglas – via Internet Archive.
- Power, R (2005). "Meeting in Norway: Norse-Gaelic Relations in the Kingdom of Man and the Isles, 1090–1270" (PDF). Saga-Book (Viking Society for Northern Research). Vol. 29: 5–66. ISSN 0305-9219.
- Richard, A (1903). Histoire des Comtes de Poitou, 778–1204. Vol. 1. Paris: Alphonse Picard & fils – via Internet Archive.
- Rowlands, IW (1981). "The Making of the March: Aspects of the Norman Settlement in Dyfed". In Brown, RA. Anglo-Norman Studies. Vol. 3, Proceedings of the Battle Conference 1980. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. pp. 142–157. ISBN 978-0-85115-141-0 – via Google Books.
- Southern, RW (2000). St. Anselm: A Portrait in a Landscape. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0 521 36262 8 – via Google Books.
- Southern, RW (2009). "Anselm [St Anselm] (c.1033–1109)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (October 2009 ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/572. Retrieved 26 October 2013. (subscription required (help)).
- Speight, S (1993). Family, Faith and Foundation: Yorkshire 1066–1250 (Doctoral thesis). University of Nottingham.
- Strevett, N (2005). The Anglo-Norman Aristocracy Under Divided Lordship, 1087–1106: A Social and Political Study (PhD thesis). University of Glasgow – via Glasgow Theses Service.
- Thompson, K (1991). "Robert de Bellême Reconsidered". In Chibnall, M. Anglo-Norman Studies. Vol. 13, Proceedings of the Battle Conference 1990. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. pp. 263–286. ISBN 0 85115 286 4 – via Google Books and Questia. (subscription required (help)).
- Thompson, K (1994). "William Talvas, Count of Ponthieu". In Bates, D; Curry, A. England and Normandy in the Middle Ages. London: The Hambledon Press. pp. 169–184. ISBN 1 85285 083 3.
- Thompson, K (1995). "Note de Recherche: Arnoul de Montgommery". Annales de Normandie. Vol. 41 (Issue 1): 49–53 – via Persée.
- Thompson, K (2004a). "Bellême, Robert de, Earl of Shrewsbury and Count of Ponthieu (bap. c.1057, d. in or after 1130)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/2042. Retrieved 27 September 2011. (subscription required (help)).
- Thompson, K (2004b). "Montgomery, Arnulf de (c.1066–1118x22)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/696. Retrieved 27 September 2011. (subscription required (help)).
- Thompson, K (2004c). "Robert, duke of Normandy (b. in or after 1050, d. 1134)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/23715. Retrieved 6 September 2011. (subscription required (help)).
- Turvey, R (2002). The Welsh Princes: The Native Rulers of Wales 1063–1283. London: Longman. ISBN 0 582 30811 9.
- van Houts, E (1999). "The Anglo–Flemish Treaty of 1101". In Harper-Bill, C. Anglo-Norman Studies. Vol. 21, Proceedings of the Battle Conference 1998. Woodbridge: The Boydell Press. pp. 169–174. ISBN 0 85115 745 9 – via Google Books.
- Vaughn, SN (1987). Anselm of Bec and Robert of Meulan: The Innocence of the Dove and the Wisdom of the Serpent. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-05674-4 – via Google Books.
- Walker, D (2004). "Windsor, Gerald of (d. 1116x36)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/45551. Retrieved 18 November 2013. (subscription required (help)).
- White, GH (1940). "The First House of Bellême". Transactions of the Royal Historical Society. Fourth series, vol. 22: 67–99. JSTOR 3678582 – via JSTOR. (subscription required (help)).