Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar
The Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar was an aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley. The Jaguar was a petrol-fuelled air-cooled 14-cylinder two-row radial engine design. The Jaguar III was first used in 1923, followed in 1925 by the Jaguar IV and in 1927 by the Jaguar VI.
Design and development
The Jaguar was developed from the Royal Aircraft Factory RAF.8 design proposal of 1917, and was engineered to use a gear driven supercharger. First run on 21 June 1922 initial performance was not as expected, as a result the bore was increased to 5.5 in (139.7 mm) with all variants after the Jaguar I using this dimension. Throughout its career the Jaguar suffered from vibration due to a lack of a crankshaft centre bearing.[1]
The most powerful version of the engine, the Jaguar VIC, produced a maximum of 490 hp (365 kW) on takeoff at 1,950 rpm and weighed 910 lbs (413 kg).[2] The later Lynx was designed using one row of Jaguar cylinders.[3]
Variants
- Jaguar I
- 1922, 300 hp.
- Jaguar II
- 1923, 385 hp, increased bore, capacity 1,512.5 cu in (24.8 L).
- Jaguar III
- 1923, 385 hp.
- Jaguar IIIA
- 1923, 380 hp.
- Jaguar IV
- 1925, 385 hp, twin carburettors
- Jaguar IVA
- 420 hp, Geared propeller drive.
- Jaguar IVC
- 1928, 400 hp, revised connecting rod design, enclosed valve gear.
- Jaguar IV(S)
- 1925, 365 hp, fully supercharged.
- Jaguar V
- 1928.
- Jaguar VI
- 1927.
- Jaguar VI(S)
- 1928, supercharged version of Jaguar VI.
- Jaguar VIC
- 1927, 470 hp, geared propeller drive version of Jaguar VI.
- Jaguar VID
- 1928.
- Jaguar VIIA
- 1929, 400 hp, fully supercharged.
- Jaguar VIII
- 1928, 405 hp, fully supercharged, geared propeller drive
Applications
Engines on display
A preserved Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar is on public display at the Science Museum (London).
Specifications (Jaguar I)
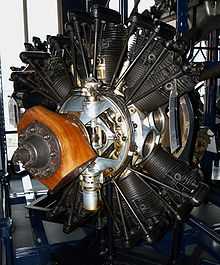
Sectioned Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar on display at the Science Museum (London)
Data from Lumsden[4]
General characteristics
- Type: 14 cylinder 2-row radial engine
- Bore: 5 in (127 mm)
- Stroke: 5 in (127 mm)
- Displacement: 1,375 cu in (22.5 L)
- Length: 41 in (1,041 mm)
- Diameter: 43 in (1,092 mm)
- Dry weight: 710 lb (322 kg)
Components
- Supercharger: Gear driven
- Fuel system: Carburettor
- Cooling system: Air-cooled
Performance
See also
- Related development
- Comparable engines
- Related lists
References
Notes
- ↑ Lumsden 2003, p.63.
- ↑ Lumsden 2003, Part 4 - Engine Performance Figures.
- ↑ Gunston 1989, p.18.
- ↑ Lumsden 2003, pp.63-66.
Bibliography
- Lumsden, Alec. British Piston Engines and their Aircraft. Marlborough, Wiltshire: Airlife Publishing, 2003. ISBN 1-85310-294-6.
External links
|
|---|
| | Piston engines | |
|---|
| | Turbojets | |
|---|
| | Turboprops | |
|---|
| | Rocket engines | |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| | General | |
|---|
| | Military | |
|---|
| | Accidents / incidents | |
|---|
| | Records | |
|---|
| | Misc. | |
|---|
|
