Archibald Baxter
Archibald McColl Learmond Baxter (13 December 1881 – 10 August 1970) was a New Zealand pacifist, socialist, and anti-war activist.
| Archibald McColl Learmond Baxter | |
|---|---|
| Born |
13 December 1881 Saddle Hill, Otago, New Zealand |
| Died |
10 August 1970 (aged 88) Dunedin, New Zealand |
| Nationality | New Zealand |
| Ethnicity | European |
| Education | Primary |
| Occupation | Farmer |
| Known for | pacifist, socialist and conscientious objector |
| Notable work | We Will Not Cease |
| Movement | No More War and Peace Pledge Union |
| Religion | Christian |
| Denomination | Roman Catholic |
| Spouse(s) | Millicent Amiel Macmillan Brown |
| Children | Terence and James Kier |
| Parent(s) | John Baxter and Mary McColl |
Background
Baxter was born at Saddle Hill, Otago on 13 December 1881. His parents were John Baxter and Mary McColl. His father had migrated to New Zealand from Scotland in 1861. Leaving school at 12, Baxter worked on a farm and became Head Ploughman at Gladbrook Station.[1]
Pacifism
During the 1899–1902 Second Boer War New Zealand sent troops to help the British. Baxter considered enlisting, but heard a Dunedin lawyer, possibly Alfred Richard Barclay, speak about pacifism before he did so and decided against enlisting. He read pacifist and anti-military literature, forming a Christian Socialist view. Baxter also heard Keir Hardie speak during his 1908 visit to New Zealand and concluded that war would not solve problems.[2] He convinced six of his seven brothers that war was wrong.
World War One
Conscription
With the introduction of conscription under the Military Service Act 1916, Baxter and his brothers refused to register on the grounds that
all war is wrong, futile, and destructive alike to victor and vanquished.[3]
The Act did not recognise their stand as the only grounds for conscientious objection were:
That he was on the fourth day of August, nineteen hundred and fourteen, and has since continuously been a member of a religious body the tenets and doctrines of which religious body declare the bearing of arms and the performance of any combatant service to be contrary to Divine revelation, and also that according to his own conscientious religious belief the bearing of arms and the performance of any combatant service is unlawful by reason of being contrary to Divine revelation.[4]
This was a considerable contraction of the exemption under the Defence Amendment Act 1912 which had allowed under Section 65(2)
On the application of any person a Magistrate may grant to the applicant a certificate of exemption from military training and service if the Magistrate is satisfied that the applicant objects in good faith to such training and service on the ground that it is contrary to his religious belief.
Only Christadelphians, Seventh-day Adventists, and Quakers were recognised as conscientious objectors under the 1916 legislation. As Baxter wasn't a member of these or any denomination he could not appeal against his call-up. According to the Act Baxter was a First Division Reservist.[5] Failure to report for duty was considered as either desertion or absent without leave within the Army Act.[6] The Army Act 1881 was Imperial (British) legislation that was recognised in New Zealand at that time.[7]
Baxter, along with his brothers – Alexander and John, were arrested in early 1917 for failing to comply with the Act and detained at Trentham Military Camp. On 21 March Baxter and William Little refused to put on the detention clothing. His other brother, Alexander, refused to work. All were Court Martialed, with all stating that they did not consider themselves soldiers having never volunteered or taken the oath of allegiance. None were represented by legal counsel.[8] The four were sentenced to 84 days imprisonment with hard labour at both the Terrace Goal and Mount Cook Prison.[9] At the end of their sentence they were to be sent back to Trentham Camp,[10] Back at Trentham he continued to refuse orders and was sentenced to 28 days detention.
Deportation to the front
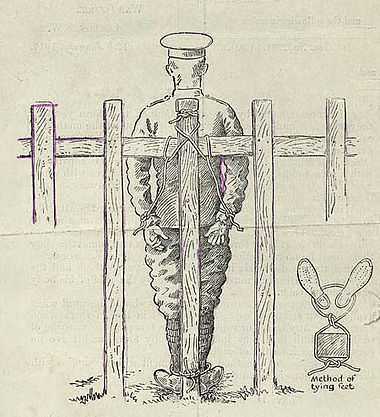
In 1917 the Minister of Defence, Sir James Allen, decided that all conscientious objectors who were not accepted as such should be sent to the front.[11] Based on this orders were given by Colonel H R Potter, Trentham Camp Commandant during Baxter detention that he along with 13 other conscientious objectors (including his two brothers) were to be shipped out. They were taken on board the Waitemata[12] to the western front in July of that year.[13] Baxter had been assigned to E Company of the 28th Reinforcements.[14] Jean Batten's father, Captain Frederick Harold Batten was in charge of E company.[15] On arrival in England Baxter was still refusing to put on a uniform or doing any work for the army. He was kept under detention and then sent to France. British newpapers of the time reported that because he had been sent to the front he could be shot for disobeying orders.[16]
There he remained under detention and continued to refuse any involvement. His two brothers only made it as far as Cape Town before being taken off the ship sick.[17]
Baxter was placed under Lt Col George Mitchell, 3rd Otago Reserve Battalion. Mitchell questioned Baxter about his beliefs. As a result Mitchell investigated his case and found that Baxter was considered a soldier by the New Zealand Government. He told Baxter that if he did not obey his orders he, Mitchell, was expected to punish him. Eventually Mitchell punished Baxter with 28 days of Field Punishment No.1 at Oudredoum.
A Doctor examined him before the punishment and despite telling Baxter he thought he was unfit for the punishment, passed him as fit out of spite. Because the personnel at Oudredoum wouldn't punish him he was moved to Mud Farm near Dickebusch (also known as Dikkebus) in West Flanders where he was put under 2 hours punishment each day. Eventually he was sent to Abeele and back to Mitchell. On 5 March Mitchell then ordered him up to the lines at Ypres. Provost Sergeant Booth was put in charge of Baxter and at one time punched him in the face and beat him up. Booth said he had been ordered to do so. Baxter was placed under Captain Phillips and taken to the Otago Regiment Camp. He was then returned to Booth's "care".
At one stage Booth on direction from a Captain Stevenson placed Baxter by an ammunition dump being shelled by the Germans. Despite a heavy barrage Baxter was unharmed. After further abusive treatment including starvation he suffered a complete physical and mental breakdown, and was hospitalised in England about May 1918.[18] At the time of his hospitalisation he had been assigned to the 3rd New Zealand Entrenching Battalion according to his records.
Baxter was said to have been diagnosed as suffering from melancholia.[19] He was then returned to New Zealand but during the voyage was diagnosed as being in good mental and physical health. He arrived on 21 September 1918 and returned to his Otago farm after the war.[20][21]
The physical treatment given to Baxter can to a large extent be directly attributed to the attitudes of the Minister of Defence, Allen; the Commander of New Zealand forces based in England, Brigadiar-General Sir George Richardson, and General Godley, Commander of the New Zealand Expeditionary Forces.[22] Godley gave orders that if Baxter and the others failed to comply he was to "summarily punished or dealt with at reinforcement camps, where they are now, and that they are not to be sent up to the front." Both Allen and Richardson had no such qualms and were likely to be the reason behind Baxter being taken to the front.[23]
Reaction in New Zealand and England
Concern began to be raised about the fate of Baxter and the others sent to France by the Dunedin branch of the Women's International League. The Canterbury Women's Institute also wrote expressing concern. In late 1917 an English Quaker, Maria Rountree, wrote about trying to find the fate of the 14 objectors only to be stonewalled by the Commander of the New Zealand forces, Richardson.[24] Harry Holland MP, citing an article in the Dominion on 21 November, deduced that the British Government had condemned the New Zealand governments sending of conscientious objectors to the front.[25][26] The paper had written "the Imperial authorities have no wish to be troubled with men who will not fight,..". This effectively ended such deportations, but did not mean the release of those already in France.
In February 1918 the National Peace Council of New Zealand, wrote to the Minister of Defence, James Allen, expressing concern about the treatment of Baxter and the others. Of particular concern was the sending of the objectors to the front where they could be court-martialled and shot for not fighting the enemy.[27] Harry Holland MP also took up their cases writing to the Prime Minister and newspapers.[28]
As further news came the inhumane way Baxter had been treated by the military was the subject of a Women's International League delegation to the Acting Prime Minister and Minister of Defence, Sir James Allen in June 1918.[29] The treatment of both him and the other objectors continued to be raised after the war by Harry Holland MP and others.[30][31] In 2014 a docu-drama of his treatment entitled Field Punishment No 1 was televised.[32]
The attitude of the military of the day towards Baxter was summed up in a letter from Colonel Robert Tate, Adjudant-General, New Zealand Military Headquarters, in which he stated
Regarding Archibald Baxter ... the sympathy of many earnest people who would like to see the lot of the conscientious objector alleviated, is wasted on men [Baxter] who are in no sense conscientious but are merely defiant of all control and willing to be subject to no law but their own inclinations. ...[33]
Inter-war Period
On 12 February 1921 he married Millicent Amiel Macmillan Brown, daughter of John Macmillan Brown, foundation chair of Canterbury College.[34] Millicent's father was opposed to the marriage. Millicent, in her autobiography, stated that she had heard of Baxter in 1918 and become a pacifist a short time later. During the 1920s the Baxters farmed at Brighton and had two children.
With Millicent's support, he founded the Dunedin Branch of the New Zealand No More War Movement in 1931. The movement sought to end conscription and promote disarmament. His father-in-law died in the 1930s and the Baxters inherited enough from his estate to enable them to travel. They first moved to Wanganui and then went to Salisbury, England in 1937. Baxter addressed the 5th and last War Resistors' Conference before World War 2 in Copenhagen between 23 and 26 July.[35] While living at Salisbury, he wrote his account of his World War 1 experiences. These were published in his book We Will Not Cease in 1939. The family returned to New Zealand in 1938.
World War 2
Both of Baxter's sons followed their father's pacifism. His eldest son Terence was imprisoned for refusing to serve during World War II. The National Service Emergency Regulations 1940, under which he was called up were almost as limiting on the grounds for conscientious objection as the 1916 Act. Regulation 21 (2) required the person objecting to prove they held ".. a genuine belief that it is wrong to engage in warfare in any circumstances." The regulation further stated that "Evidence of active and genuine membership of a pacifist religious body may in general be accepted as evidence of the convictions of the objector..." Active and continuous membership of the Society of Friends or Christadelphians prior to the outbreak of war was taken sufficient proof.[36] The Appeal Boards set up under the regulations tended to take a very narrow and sometimes contradictory view of conscientious objectors. After an April 1941 British court case those deemed to be politically based were unlikely to accepted.[37] The continuation of conscription must have been ironic for Baxter as many members of the now governing Labour Party had been imprisoned during World War One for opposing conscription. The Prime Minister, Michael Joseph Savage had been very vocal opposing conscription during that war.
During the war Baxter was an active member of the Dunedin Branch of the New Zealand Peace Pledge Union. The Peace Pledge Union is noted for its white poppy appeal. This is a pacifist alternative to the Remembrance poppy.
Later years
After the war the Baxters continued their involvement with the peace movement. They lobbied against nuclear weapons, supported Amnesty International, and wrote against the Vietnam War, about which in 1968 he said
. . . the only apparent justification that war ever had was that by destroying some lives it might clumsily preserve others. But now even that justification is being stripped away. We make war chiefly on civilians and respect for human life seems to have become a thing of the past. To accept this situation would be to accept the devil's philosophy.[38]
During the 1950s and 60s the Baxters also took a keen interest in botany, discovering on a trip to Dunstan a new species of plant, gingidium baxterii.[39]
Baxter lived in Dunedin until his death on 10 August 1970. Baxter's younger son James Keir Baxter convinced him to become a Catholic in 1965. James Kier Baxter's middle name is in honour to Keir Hardie. James is one of New Zealand's most famous poets and was also a pacifist.
Memorial
In 2013 a group in Dunedin, chaired by Kevin P. Clements of the University of Otago National Centre for Peace and Conflict Studies, set up the Archibald Baxter Memorial Trust to honour Baxter and other conscientious objectors of the First World War. Terence Baxter is the trust's patron.
The Trust proposed an annual lecture in Baxter's name, an annual essay competition commencing in August 2014, and a memorial in Dunedin in Baxter's honour. The Trust hoped to raise $100,000 for what will be the first memorial to honour pacifism in New Zealand. The trust hopes to unveil the memorial on the centenary of the Battle of Passchendaele in 2017.[40] The Trust's proposal for a memorial was controversial provoking negative comments to the local paper.[41]
The first lecture was given on 22 September 2014 by Australian historian and author Professor Henry Reynolds of the University of Tasmania. His lecture was titled Discovering Archibald Baxter and the thoughts on war which followed.[42] The topic for the Trust's first essay competition was They also served who would not fight and was to be set against a backdrop of New Zealand History. There were two age group categories: Junior (New Zealand school years 9-11) and Senior (New Zealand school years 12-13). The senior section was won by Modi Deng of Columba College and the Junior section by Rhys Davie of Tokomairiro High School.[43][44]
Literature and film
- Field Punishment Number One, David Grant, Steel Roberts publishers, Wellington, 2008, page 106, ISBN 978 1 877448 46 1
- My Brother's War, Peter Hill, Penquin, 2012 ISBN 9780143307174 - the story in this book draws from Baxter's experiences.[45]
- Field Punishment No 1, (2014) - docu-drama based on David Grants book
See also
- Christian pacifism
- Compulsory Military Training in New Zealand
References
- ↑ "Baxter, Archibald McColl Learmond – Biography – Te Ara Encyclopedia of New Zealand". Teara.govt.nz. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ Advertisements Column 7, Otago Daily Times , Issue 14105, 8 January 1908, Page 1
- ↑ "Forced to the front", Bridget Jones, New Zealand Herald, Auckland, 19 April 2014
- ↑ Section 18(e)
- ↑ Section 4(2)(a)
- ↑ Section 13
- ↑ Defence Act 1909 – definitions
- ↑ Objectors on trial, Dominion, Volume 10, Issue 3044, 3 April 1917, Page 8
- ↑ "Soldiers punished", Evening Post, Volume XCIII, Issue 82, 5 April 1917, Page 8
- ↑ "Recalcitrant Reservists", Auckland Star, Volume XLVIII, Issue 83, 7 April 1917, Page 6
- ↑ Field Punishment Number One, David Grant, Steel Roberts publishers, Wellington, 2008, page 39, ISBN 978 1 877448 46 1
- ↑ Author: H. E. Holland. "VII.—Deported by Night | NZETC". Nzetc.victoria.ac.nz. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ "Pacifist objection – conscientious objection in the First World War | NZHistory, New Zealand history online". Nzhistory.net.nz. 23 March 1917. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ "Auckland War Memorial Museum – Baxter-Archibald-McColl-Larmond-World-War-I,-1914-1918". Muse.aucklandmuseum.com. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ "Timespanner: Jean Batten's dad's surgery sign". Timespanner.blogspot.co.nz. 6 August 2010. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ The New Zealand CO's, Birmingham Gazette, West Midlands, England, Wednesday 5 December 1917, page 5
- ↑ Author: H. E. Holland (13 July 1917). "XV.—Mark Briggs. | NZETC". Nzetc.victoria.ac.nz. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ Author: H. E. Holland. "XIII.—The Process of Conversion | NZETC". Nzetc.victoria.ac.nz. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ "Baxter's breakdown", NZ Truth, Issue 680, 29 June 1918, Page 6
- ↑ Archibald Baxter on lestweforget.org.nz, retrieved 25 April 2009
- ↑ "Conscientious objectors", NZ Truth, Issue 697, 26 October 1918, Page 1
- ↑ "Military objectors", New Zealand Herald, Volume LV, Issue 16785, 27 February 1918, Page 9
- ↑ Field Punishment Number One, David Grant, Steel Roberts publishers, Wellington, 2008, page 106, ISBN 978 1 877448 46 1
- ↑ "NZ Conscientious objectors", Maoriland Worker, Volume 9, Issue 351, 30 January 1918, Page 4
- ↑ "The objectors", Dominion, Volume 11, Issue 49, 21 November 1917, Page 6
- ↑ Armageddon or Calvary, page 32
- ↑ Conscientiour objectors, Press, Volume LIV, Issue 16129, 6 February 1918, Page 9
- ↑ "Conscientious objectors", Evening Post, Volume XCV, Issue 41, 16 February 1918, Page 4
- ↑ "Conscientious objectors", Otago Daily Times, Issue 17354, 29 June 1918, Page 11
- ↑ "Outrages alleged", Grey River Argus, 25 October 1919, Page 3
- ↑ Archibald McC L Baxter, H E Holland MP, Armageddon or Calvary, Maoriland Workers Printing and Publishing Company, Brooklyn – Wellington, 1919, pages 75–87
- ↑ "Field Punishment No.1 • NZ On Air". Nzonair.govt.nz. 24 April 2014. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ Conscientious objectors, Press, Volume LIV, Issue 16244, 21 June 1918, Page 2
- ↑ "Baxter, Millicent Amiel – Biography – Te Ara Encyclopedia of New Zealand". Teara.govt.nz. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ↑ War is a crime against humanity – The Story of War Resisters' International, Devi Prasad, War Resisters' International, London, 2005, page 184
- ↑ Statutory Regulations 1940, Government Printer, Wellington, 1941, page 392
- ↑ Chapter 7 Conscientious Objectors and Defaulters, The Home Front, Volume I, Nancy M Taylor, The Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War 1939–1945, page 251
- ↑ Archibald Baxter, The Comman Good, Christchurch, 11 June 2005
- ↑ The New Zealand species of Gingidium (Umbelliferae), J W Dawson, New Zealand Journal of Botany 5, 1967, pages 84–116.
- ↑ "Pacifists Deserve Recognition", Otago Daily Times, 30 December 2013
- ↑ http://www.odt.co.nz/opinion/your-say/304855/archibald-baxter-memorial
- ↑ http://www.odt.co.nz/news/dunedin/316774/australias-own-war-ignored
- ↑ http://archibaldbaxtertrust.com/
- ↑ Columba College newsletter - September 2014 Better source wanted
- ↑ http://www.radionz.co.nz/national/programmes/thereading
External links
- The Archibald Baxter Trust in Dunedin New Zealand
- Military Personnel File online; digitised record at Archives New Zealand.
- ARCHIBALD MCC. L. BAXTER Short autobiographical account published in 1919
- eText of We Will Not Cease Book-length autobiographical account published in 1939
- Dictionary of New Zealand Biography Article updated 2013
- Field Punishment No. 1 – 2014 TV Drama featuring the story of Archibald Baxter.
|