Anterior triangle of the neck
| Anterior triangle of the neck | |
|---|---|
 Anterior triangle | |
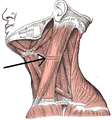
 Side of neck, showing chief surface markings. (Nerves are yellow, arteries are red.) | |
| Identifiers | |
| Gray's | p.563 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck.
Structure
The triangle is inverted with its apex inferior to its base which is under the chin.
| Inferior boundary (apex) | Jugular notch in the manubrium of the sternum |
| Anterior boundary | Midline of the neck from chin to the jugular notch |
| Posterior boundary | The anterior margin of Sternocleidomastoideus |
| Superior boundary (base) | The lower border of the body of the mandible, and a line extending from the angle of the mandible to the mastoid process |
Investing fascia covers the roof of the triangle while visceral fascia covers the floor.
Anatomy
Muscles:
- Suprahyoid muscles - Digastric (Ant and Post Belly) and Stylohyoid.
- Infrahyoid muscles - Omohyoid, Sternohyoid, Sternothyroid, and Thyrohyoid.
Nerve supply
2 Bellies of Digastric
- Anterior: Mylohyoid nerve
- Posterior: Facial nerve
Stylohyoid: by the facial nerve, by a branch from that to the posterior belly of digastric.
Mylohyoid: by its own nerve, a branch of the inferior alveolar ( from the mandibular division of trigemminal nerve), which arises just before the parent nerve enters the mandibular foramen, pierces the sphenomandibular ligament, and runs forward on the inferior surface of the mylohyoid, supplying it and the anterior belly of the digastric.
Geniohyoid: by a branch from the hypoglossal nerve consisting of fibres from the C1 nerve.
Sternohyoid, Omohyoid, Sternthyroid are supplied by Ansa cervicalis.
Thyrohyoid: by a branch of hypoglossal nerve but the fibres are all 'hitch-hiking' from C1.
Development
- Anterior: 1st Pharyngeal arch
- Posterior: 2nd Pharyngeal arch
Divisions
This space is subdivided into four smaller triangles by the Digastricus above, and the superior belly of the Omohyoideus.
These smaller triangles are named:
- the muscular triangle
- the carotid triangle
- the submandibular triangle
- the submental triangle
Additional images
-

Muscles of the neck. Anterior view.
-

The triangles of the neck. (Anterior triangles to the left; posterior triangles to the right. Suprahyoid labeled at left.)
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- lesson5 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (necktriangle)
- lesson6 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||