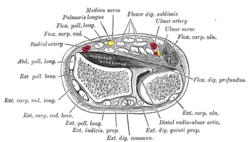
Anterior compartment of the forearm
The anterior compartment of the forearm (or flexor compartment)[1] contains the following muscles:[2]
| Level | Muscle | Extrinsic/Intrinsic | Nerve |
| superficial | flexor carpi radialis | extrinsic | median |
| superficial | palmaris longus | extrinsic | median |
| superficial | flexor carpi ulnaris | extrinsic | ulnar |
| superficial | pronator teres | intrinsic | median |
| superficial (or intermediate) | flexor digitorum superficialis | extrinsic | median |
| deep | flexor digitorum profundus | extrinsic | ulnar + median (as anterior interosseous nerve) |
| deep | flexor pollicis longus | extrinsic | median (as anterior interosseous nerve) |
| deep | pronator quadratus | intrinsic | median (as anterior interosseous nerve) |
The muscles are largely involved with flexion and pronation.[2] The superficial muscles have their origin on the common flexor tendon.[2] The ulnar nerve and artery are also contained within this compartment.[2] The flexor digitorum superficialis lies in between the other four muscles of the superficial group and the three muscles of the deep group. This is why it is also classified as the intermediate group.[2]
See also
References
External links
Additional images
-
Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna.
-
|
|---|
| | Shoulder | |
|---|
| Arm
(compartments) | |
|---|
| | Forearm | |
|---|
| | Hand | | lateral volar | |
|---|
| | medial volar | |
|---|
| | intermediate | |
|---|
| | fascia | |
|---|
|
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- head
- neck
- arms
- chest and back
- diaphragm
- abdomen
- genital area
- legs
- Muscle tissue
- Physiology
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Myopathy
- Soft tissue
- Connective tissue
- Congenital
- abdomen
- muscular dystrophy
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Injury
- Symptoms and signs
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Drugs
- anti-inflammatory
- muscle relaxants
|
|---|
|
|