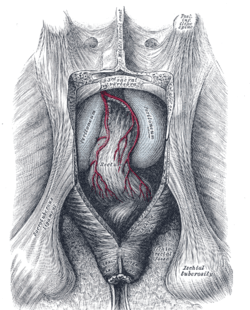
Anal triangle
| Anal triangle | |
|---|---|
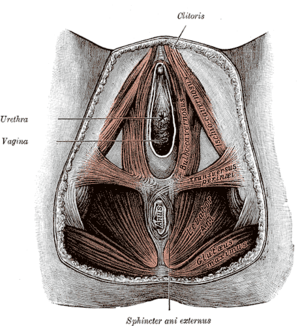 Muscles of the female perineum. (Anal triangle is roughly equal to bottom half of diagram.) | |
 Muscles of male perineum. (Anal triangle is roughly equal to bottom half of diagram.) | |
| Details | |
| Latin | regio analis |
| Identifiers | |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | 12700160 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anal triangle is the posterior part of the perineum. It contains the anal canal.
Structure
The anal triangle can be defined either by its vertices or its sides.
- Vertices
- one vertex at the coccyx bone
- the two ischial tuberosities of the pelvic bone
- Sides
- perineal membrane (posterior border of perineal membrane forms anterior border of anal triangle)
- the two sacrotuberous ligaments
Contents
Some components of the anal triangle include:[1]
- Ischioanal fossa
- Anococcygeal body
- Sacrotuberous ligament
- Sacrospinous ligament
- Pudendal nerve
- Internal pudendal artery and Internal pudendal vein
- Anal canal
- Muscles
- Sphincter ani externus muscle
- Gluteus maximus muscle
- Obturator internus muscle
- Levator ani muscle
- Coccygeus muscle
Additional images
-
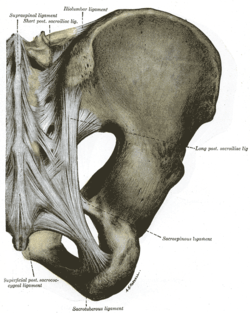
Articulations of pelvis. Posterior view.
-
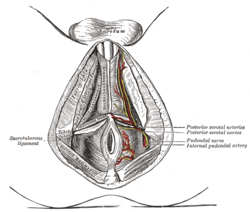
The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery.
See also
References
- ↑ Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. ISBN 9788131225561.
External links
- Anatomy photo:41:01-0202 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Perineum: Boundaries of the Female Perineum"
- perineum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (perineumboundaries)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||