American Century
| United States of America | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
.svg.png) |
American Century[1][2] is a characterization of the period since the middle of the 20th century as being largely dominated by the United States in political, economic, and cultural terms. It is comparable to the description of the period 1815–1914 as Britain's Imperial Century.[3] Critical to the American Century was US control of the world's oil resources.[4] The United States' influence grew throughout the 20th century, but became especially dominant after the end of World War II, when only two superpowers remained, the United States and the Soviet Union. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the United States remained the world's only superpower,[5] and became the hegemon, or what some have termed a hyperpower.[6]
Origin of the phrase
The term was coined by Time publisher Henry Luce to describe what he thought the role of the United States would be and should be during the 20th century.[7] Luce, the son of a missionary, in a February 17, 1941 Life magazine editorial[8] urged the United States to forsake isolationism for a missionary's role, acting as the world's Good Samaritan and spreading democracy. He called upon the US to enter World War II to defend democratic values:
Throughout the 17th century and the 18th century and the 19th century, this continent teemed with manifold projects and magnificent purposes. Above them all and weaving them all together into the most exciting flag of all the world and of all history was the triumphal purpose of freedom.
It is in this spirit that all of us are called, each to his own measure of capacity, and each in the widest horizon of his vision, to create the first great American Century.[9]
According to David Harvey, Luce believed "the power conferred was global and universal rather than territorially specific, so Luce preferred to talk of an American century rather than an empire."[10] In the same article he called upon United States "to exert upon the world the full impact of our influence, for such purposes as we see fit and by such means as we see fit."[11]
Early characteristics
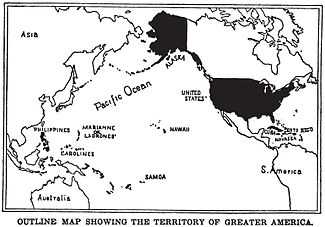
Beginning at the end of the 19th Century, with the Spanish–American War in 1898 and the Boxer Rebellion, the United States began to play a more important role in the world beyond the North American continent. The government adopted protectionism after the Spanish–American War to develop its native industry and built up the navy, the "Great White Fleet". When Theodore Roosevelt became president in 1901, he accelerated a foreign policy shift away from isolationism and towards foreign involvement, a process which had begun under his predecessor William McKinley.
For instance, the United States fought the Philippine–American War against the First Philippine Republic to solidify its control over the newly acquired Philippines.[12] In 1904, Roosevelt committed the United States to building the Panama Canal, creating the Panama Canal Zone. Interventionism found its formal articulation in the 1904 Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine, proclaiming a right for the United States to intervene anywhere in the Americas, a moment that underlined the emergent US regional hegemony.
After the outbreak of World War I in 1914, the United States pursued a policy of non-intervention, avoiding conflict while trying to broker a peace. President Woodrow Wilson later argued that the war was so important that the US had to have a voice in the peace conference.[13] The United States was never formally a member of the Allies but entered the war in 1917 as a self-styled "Associated Power". Initially the United States had a small army, but, after the passage of the Selective Service Act, it drafted 2.8 million men,[14] and, by summer 1918, was sending 10,000 fresh soldiers to France every day. The war ended in 1919 with the Treaty of Versailles. The United States then adopted a policy of isolationism, having refused to endorse the 1919 Versailles Treaty or formally enter the League of Nations.[15]
During the interwar period, economic protectionism took hold in the United States, particularly as a result of the Smoot–Hawley Tariff Act which is credited by economists with prolongment and worldwide propagation of the Great Depression.[16]:33 From 1934, trade liberalization began to take place through the Reciprocal Trade Agreements Act.
With the onset of World War II in 1939, Congress loosened the Neutrality Acts of 1930s but remained opposed to entering the European war.[17] In 1940, the United States ranked 18th in terms of military power.[18] The Neutrality Patrol had US destroyers fighting at sea, but no state of war had been declared by Congress. American public opinion remained isolationist. The 800,000-member America First Committee vehemently opposed any American intervention in the European conflict, even as the US sold military aid to the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union through the Lend-Lease program.
In the 1941 State of the Union address, known as the Four Freedoms speech, President Franklin D. Roosevelt made a break with the tradition of non-interventionism. He outlined the US role in helping allies already engaged in warfare. By August, President Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill had drafted the Atlantic Charter to define goals for the post-war world.[19] In December 1941, Japan attacked American and British holdings with near-simultaneous offensives against Southeast Asia and the Central Pacific including an attack on the US fleet at Pearl Harbor.[20] These attacks led the United States and United Kingdom to declare war on Japan. Three days later, Germany and Italy declared war on the United States, which the United States reciprocated.[21]
In an effort to maintain peace after World War II,[22] the Allies formed the United Nations, which came into existence on 24 October 1945,[23] and adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in 1948, as a common standard for all member states.[24]
Pax Americana
Pax Americana represents the relative peace in the Western world, resulting in part from the preponderance of power enjoyed by the United States of America starting around the middle of the 20th century. Although the term finds its primary utility in the late 20th century, it has been used in other times in the 20th century. Its modern connotations concern the peace established after the end of World War II in 1945.
Post-1945 characteristics
The American Century existed through the Cold War and demonstrated the status of the United States as the foremost of the world's two superpowers. After the Cold War, the most common belief held that only the United States fulfilled the criteria to be considered a superpower.[5] Its geographic area composed the fourth-largest state in the world, with an area of approximately 9.37 million km².[25] The population of the US was 248.7 million in 1990, at that time the third-largest nation.[26]
In the mid-to-late 20th century, the political status of the US was defined as a strongly capitalist federation and constitutional republic. It had a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council plus two allies with permanent seats, France and the United Kingdom. The US had strong ties with capitalist Western Europe, Latin America, British Commonwealth, and several East Asian countries (Korea, Taiwan, Japan). It allied itself with both right-wing dictatorships and capitalist democracies.[27]
The American Century includes the political influence of the United States but also its economic influence. Many states around the world would, over the course of the 20th century, adopt the economic policies of the Washington Consensus, often against the wishes of their populations. The economic force of the US was powerful at the end of the century due to it being by far the largest economy in the world. The US had large resources of minerals, energy resources, metals, and timber, a large and modernized farming industry and large industrial base. The United States dollar was the dominant world reserve currency under the Bretton Woods system. US systems were rooted in capitalist economic theory based on supply and demand, that is, production determined by customers' demands. America was allied with the G7 major economies. US economic policy prescriptions were the "standard" reform packages promoted for crisis-wracked developing countries by Washington, DC-based international institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, as well as the US Treasury Department.[28]
The military of the United States was a naval-based advanced military with by far the highest military expenditure in the world.[29] The United States Navy was the world's largest navy, with the largest number of aircraft carriers, bases all over the world (particularly in an incomplete "ring" bordering the Warsaw Pact states to the west, south and east). The US had the largest nuclear arsenal in the world during the first half of the Cold War, one of the largest armies in the world and one of the two largest air forces in the world. Its powerful military allies in Western Europe (the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation states) had their own nuclear capabilities. The US also possessed a powerful global intelligence network in the Central Intelligence Agency.
The cultural impact of the US, often known as Americanization, is seen in the influence on other countries of US music, TV, films, art, and fashion, as well as the desire for freedom of speech and other guaranteed rights its residents enjoy. US pop stars such as Elvis Presley, Michael Jackson, and Madonna have become global celebrities.[30]
Criticism
Critics have condemned Luce's "jingoistic missionary zeal."[31] Others have noted the end of the 20th Century and the American Century, most famously the late gonzo journalist Hunter S. Thompson who titled his autobiography Kingdom Of Fear: Loathsome Secrets of A Star Crossed Child in the Last Days of the American Century.
With the advent of the new millennium, critics have stated that it is a matter of debate whether America's influence is leading it to be a hegemon or if it is losing its superpower status,[32] especially in relation to China's rise.
See also
- American imperialism
- Britain's Imperial Century
- New World Order
- Pax Americana
- Project for the New American Century
References
- ↑ Lamb, Brian, and Harold Evans. The American Century. West Lafayette, IN: C-SPAN Archives, 1999.
- ↑ The American Century. randomhouse.com.
- ↑ Hyam, Ronald (2002). Britain's Imperial Century, 1815–1914: A Study of Empire and Expansion. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-7134-3089-9. Retrieved 2013-12-15.
- ↑ Painter 2012, p. 24: "Understanding how oil fueled the 'American century' is fundamental to understanding the sources, dynamics, and consequences of U.S. global dominance. Essential to both military power and the functioning of modern society, oil fueled American power and prosperity during the twentieth century. . . . Control of oil bolstered U.S. military and economic might and enabled the United States and its allies to win both world wars and the Cold War. The U.S. government worked closely with the oil industry to gain and maintain control of overseas oil reserves, reflecting a symbiosis of national security interests and the interests of the oil companies. Maintaining access to oil became a key priority of U.S. foreign policy and involved the United States in regional and local conflicts in Latin America, the Middle East, and other oil-producing areas in ways that distorted development in many countries. Most of the major doctrines of postwar U.S. foreign policy—the Truman, Eisenhower, Nixon, and Carter Doctrines—related, either directly or indirectly, to the Middle East and its oil."
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Analyzing American Power in the Post-Cold War Era". Archived from the original on 11 March 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ↑ Definition and Use of the Word Hyperpower
- ↑ David Harvey, The New Imperialism, (New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2003)
- ↑ Luce, Henry (1941-02-17) The American Century, Life Magazine
- ↑ Luce, H. R: "The American Century" reprinted in The Ambiguous Legacy, M. J. Hogan, ed. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1999.
- ↑ David Harvey, The New Imperialism, (New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 2003), 50.
- ↑ Michael J. Hogan, The ambiguous legacy: U.S. foreign relations in the "American century", (Cambridge University Press, 1999), page 20.
- ↑ John M. Gates, "War-Related Deaths in the Philippines", Pacific Historical Review , v. 53, No. 3 (August, 1984), 367–378.
- ↑ Karp 1979
- ↑ "Selective Service System: History and Records". Sss.gov. Retrieved 27 July 2010.
- ↑ Kennedy, David M., Freedom From Fear: The American People in Depression and War, 1929–1945 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1999) 386
- ↑ Eun, Cheol S.; Resnick, Bruce G. (2011). International Financial Management, 6th Edition. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill/Irwin. ISBN 978-0-07-803465-7.
- ↑ Schmitz 2000, p. 124.
- ↑ "WWII Overview". The National WWII Museum. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ↑ Langer and Gleason, chapter 21
- ↑ Wohlstetter 1962, pp. 341–3.
- ↑ Dunn 1998, p. 157
- ↑ Yoder 1997, p. 39.
- ↑ "History of the UN". United Nations. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- ↑ Waltz 2002
- ↑ US geography
- ↑ US Census census.gov
- ↑ Stephen Kinzer (2007). Overthrow: America's Century of Regime Change from Hawaii to Iraq. Times Books.
- ↑ Williamson, John: What Washington Means by Policy Reform, in: Williamson, John (ed.): Latin American Readjustment: How Much has Happened, Washington: Institute for International Economics 1989.
- ↑ Military spending
- ↑ Biddle, Julian (2001). What Was Hot!: Five Decades of Pop Culture in America. New York: Citadel, p. ix. ISBN 0-8065-2311-5.
- ↑ Michael, Terry (2011-02-16) The End of the American Century, Reason
- ↑ Unger J (2008), U.S. no longer superpower, now a besieged global power, scholars say University of Illinois
Bibliography
- Dunn, Dennis J. (1998). Caught Between Roosevelt & Stalin: America's Ambassadors to Moscow. Lexington, KY: University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 978-0-8131-2023-2.
- Hogan, Michael J. (1999). The Ambiguous Legacy: U.S. Foreign Relations in The "American Century". Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77019-4.
A symposium of scholarly articles assessing aspects of Luce's editorial and its significance originally published in Diplomatic History 23 (2 & 3), 1999 - Karp, Walter (1979), The Politics of War (1st ed.), ISBN 0-06-012265-X, OCLC 4593327, Wilson's maneuvering US into war
- Langer, William L.; Gleason, S. Everett (1953), The Undeclared War 1940-1941: The World Crisis and American Foreign Policy, Harper & Brothers, ISBN 978-1258766986
- Northedge, FS (1986), The League of Nations: Its Life and Times, 1920–1946, New York: Holmes & Meier, ISBN 0-7185-1316-9
- Painter, David S. (2012). "Oil and the American Century" (PDF). The Journal of American History 99 (1): 24–39. doi:10.1093/jahist/jas073.
- Schmitz, David F. (2000), Henry L. Stimson: The First Wise Man, Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield, ISBN 978-0-8420-2632-1
- Waltz, Susan (2002). "Reclaiming and Rebuilding the History of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights". Third World Quarterly 23 (3): 437–448. doi:10.1080/01436590220138378. JSTOR 3993535.
- Wohlstetter, Roberta (1962), Pearl Harbor: Warning and Decision, Palo Alto, CA: Stanford University Press, ISBN 978-0-8047-0597-4
- Yoder, Amos (1997). The Evolution of the United Nations System (3rd ed.). London & Washington, DC: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 1-56032-546-1.
Further reading
- Henry Luce, The American Century, Life Magazine (February 17, 1941)
- Andrew Bacevich, Farewell to the American Century, Salon.com (April 30, 2009)
- Terry Michael, The End of the American Century, Reason (February 16, 2011)
- The Unmaking of a Company Man By Andrew Bacevich
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||