Ambrisentan
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
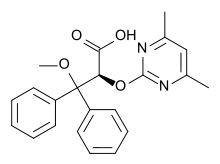
| (2S)-2-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]-3-methoxy- 3,3-diphenylpropanoic acid | |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| Licence data | EMA:Link, US FDA:link |
| |
| Oral | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Undetermined |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Half-life | 15 hours (terminal) |
| Identifiers | |
|
177036-94-1 | |
| C02KX02 | |
| PubChem | CID 6918493 |
| ChemSpider |
5293690 |
| UNII |
HW6NV07QEC |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1111 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C22H22N2O4 |
| 378.421 g/mol | |
|
SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Ambrisentan (U.S. trade name Letairis; E.U. trade name Volibris; India trade name pulmonext by MSN labs ) is a drug indicated for use in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension.
It functions as an endothelin receptor antagonist, and is selective for the type A endothelin receptor (ETA).[1] Once daily oral ambrisentan 2.5 to 10 mg/day significantly improved exercise capacity (6-minute walk distance) compared with placebo in two double-blind, multicenter trials (ARIES-1 & ARIES-2).[2]
Ambrisentan was approved for sale by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on June 15, 2007 for the once-daily treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.[3][4][5] It was later approved by the European Medicines Agency for use in the EU on April 2008.[6] Ambrisentan had previously been designated an orphan drug by both the FDA and the European Commission, in August 2004 and May 2005 respectively.[7]
Clinical uses
Ambrisentan is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (WHO Group 1) in patients with WHO class II or III symptoms to improve exercise capacity and delay clinical worsening.
The LETAIRIS Education and Access Program
The LETAIRIS Education and Access Program (LEAP) is a program to help physicians and patients learn about the risks of LETAIRIS, including the serious risks of liver injury and birth defects.
LEAP works by:
- Providing information to prescribers on the risks of LETAIRIS
- Providing comprehensive education to patients and assistance with obtaining LETAIRIS
- Requiring enrollment of both prescriber and patient in LEAP
- Controlling dispensing through a specialized distribution network (specialty pharmacies)
External links
- Letairis website run by Gilead Sciences
- Prescribing information
- Information on the LETAIRIS Education and Access Program (LEAP)
References
- ↑ Vatter H, Seifert V (2006). "Ambrisentan, a non-peptide endothelin receptor antagonist". Cardiovasc Drug Rev 24 (1): 63–76. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3466.2006.00063.x. PMID 16939634.
- ↑ Frampton JE. Ambrisentan. American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs August 1, 2011; 11 (4): 215-226.Link text
- ↑ Pollack, Andrew (2007-06-16). "Gilead’s Drug Is Approved to Treat a Rare Disease". New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 June 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-25.
- ↑ "U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approves Gilead's Letairis Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension" (Press release). Gilead Sciences. 2007-06-15. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- ↑ "FDA Approves New Orphan Drug for Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension" (Press release). Food and Drug Administration. 2007-06-15. Archived from the original on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 2007-06-22.
- ↑ "GlaxoSmithKline's Volibris (ambrisentan) receives authorisation from the European Commission for the treatment of Functional Class II and III Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension" (Press release). GlaxoSmithKline. 2008-04-25. Archived from the original on 30 April 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-29.
- ↑ Waknine, Yael (2005-05-09). "International Approvals: Ambrisentan, Oral-lyn, Risperdal". Medscape. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||