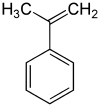
alpha-Methylstyrene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Isopropenylbenzene | |||
| Other names
α-Methylstyrene; 2-Phenyl-1-propene; 1-Methyl-1-phenylethylene; 2-Phenylpropene; (1-Methylethenyl)benzene; beta-Phenylpropene; 2-Phenylpropylene; beta-Phenylpropylene; alpha-Methylstyrol; 1-Phenyl-1-methylethylene; 2-Phenyl-2-propene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| Abbreviations | AMS | ||
| 98-83-9 | |||
| ChemSpider | 7129 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image | ||
| KEGG | C14395 | ||
| PubChem | 7407 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Molecular formula |
C9H10 | ||
| Molar mass | 118.18 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.91 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −24 °C (−11 °F; 249 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 165 °C (329 °F; 438 K) | ||
| Insoluble | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | 45 °C (113 °F; 318 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 1.9%-6.1%[2] | ||
| LD50 (Median lethal dose) |
Oral rat: 4900 mg/kg | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
| PEL (Permissible) |
C 100 ppm (480 mg/m3)[2] | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
α-Methylstyrene (AMS) is a chemical intermediate used in the manufacture of plasticizers, resins and polymers.[3] It is a co-product formed in a variation of the cumene process. The homopolymer obtained from this monomer, poly(α-methylstyrene), is unstable, being characterized by a low ceiling temperature.