Aloe dichotoma
| Quiver tree | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Xanthorrhoeaceae |
| Subfamily: | Asphodeloideae |
| Genus: | Aloe |
| Species: | A. dichotoma |
| Binomial name | |
| Aloe dichotoma Masson | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
Aloe dichotoma (the quiver tree or kokerboom) is a tall, branching species of aloe, indigenous to Southern Africa, specifically in the Northern Cape region of South Africa, and parts of Southern Namibia.
Naming
Known as Choje to the indigenous San people, the quiver tree gets its English common name from their practice of hollowing out the tubular branches of Aloe dichotoma to form quivers for their arrows. The species name "dichotoma" refers to how the stems repeatedly branch into two ("dichotomous" branching) as the plant grows.
Subspecies and taxonomy
As of May 2011, the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families recognizes three subspecies, A. dichotoma subsp. dichotoma, A. dichotoma subsp. pillansii and A. dichotoma subsp. ramosissima.[1]
These are also treated as three separate species, A. dichotoma, A. pillansii and A. ramosissima, which are then grouped within the Dracoaloe subsection of the genus Aloe. All inhabit the same arid areas of the Richtersveld and the Namib Desert around the South African-Namibian border. Treated as separate species, the three have been given different ratings on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: 'vulnerable' for A. dichotoma, 'critically endangered' for A. pillansii and 'endangered' for A. ramossisima.
The three subspecies can be distinguished. In A. dichotoma subsp. pillansii, the inflorescences hang from below the lowest leaves, rather than growing erect. A. dichotoma subsp. ramosissima is considerably smaller - rarely reaching more than 2 m in height - and assumes a more shrub-like shape. While there is a gradation between tree-like dichotoma and the shrubby ramosissima, the relatively unique pillansii population is separated by a different flowering time and therefore does not interbreed with the other two subspecies.[2]
Distribution and conservation
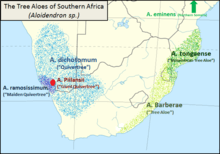
One of the few examples of spontaneous forests of A. dichotoma is the Quiver Tree Forest, about 14 km north of Keetmanshoop, in Namibia. Another is located in the Northern Cape of South Africa at Gannabos.
Throughout much of its range this species is in decline. Modeling of Aloe dichotoma in South Africa and Namibia has contributed to understanding the needs of protected areas in response to climate change. Modelled range declines in this species due to climate change have recently been confirmed by field surveys.[3]
Cultivation
Aloe dichotoma is cultivated in arid areas around the world, for use in landscaping. The slow growth rate and relative rarity of the plant make it a particularly expensive specimen.
In cultivation it requires extremely well-drained coarse mineral soil, full sun, good aeration and extremely little water - primarily in the winter (as it mainly occurs in winter rainfall desert).
It can be propagated from seed and (with more difficulty) from cuttings or truncheons. Cuttings need to be thoroughly dried for several weeks in a shaded area, before being planted.
Gallery
-

Quiver trees in a greenhouse
-

Aloe dichotoma in bloom
-
Quiver tree in southern Namibia
-

Growth of a young Aloe dichotoma from May to August
-
Quiver tree at Fish River Canyon, Namibia
-

Quiver Tree Forest near Keetmanshoop, Namibia, in the evening.
See also
- Aloe pillansii (syn. for A. dichotoma subsp. pillansii)
- Aloe ramosissima (syn. for A. dichotoma subsp. ramosissima)
- Aloe barberae
References
- ↑ WCSP (2011), World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, retrieved 2011-05-23, search for "Aloe dichotoma"
- ↑ Court, D. (2010), Succulent Flora of Southern Africa, Cape Town: Struik Nature, ISBN 978-1-77007-587-0
- ↑ Foden, Wendy; Midgley, Guy F.; Hughes, Greg; Bond, William J.; Thuiller, Wilfried; Hoffman, M. Timm; Kaleme, Prince; Underhill, Les G. et al. (2007), "A changing climate is eroding the geographical range of the Namib Desert tree Aloe through population declines and dispersal lags", Diversity and Distributions 13 (5): 645–653, doi:10.1111/j.1472-4642.2007.00391.x, retrieved 2011-07-16
External links
- Desert-tropicals.com profile
- Plantzafrica.com profile
- Dressler, S.; Schmidt, M. & Zizka, G. (2014). [http://www.africanplants.senckenberg.de/root/index.php?submitForm=true&page_id=77&searchTextMenue=Aloidendron+dichotomum&filterRegionIDs[]=6&filterRegionIDs[]=1&filterRegionIDs[]=2&filterRegionIDs[]=3&filterRegionIDs[]=5 "Aloidendron dichotomum"]. African plants – a Photo Guide. Frankfurt/Main: Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aloe dichotoma. |


