Albiorix (moon)
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | M. J. Holman et al. |
| Discovered | in 2000 |
| Mean Orbital elements [2] | |
| Epoch 2000 Feb. 26.00 | |
| Semi-major axis | 16.182 Gm |
| Eccentricity | 0.4770 |
| Inclination | 34.207° * |
| Orbital period |
783 d (2.15 yr) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | 32 km[3] ** |
| Rotation period | 13:19 h[4] |
| Albedo | 0.04[3] assumed |
| Color |
light red (varying) B-V=0.89 R-V=0.50[5] |
| Spectral type | ? |
|
*to the ecliptic **based on the albedo | |
Albiorix (/ˌælbiˈɒrɨks/ AL-bee-ORR-iks) is a prograde irregular satellite of Saturn. It was discovered by Holman, et al. in 2000, and given the temporary designation S/2000 S 11.[6][7][8]
Albiorix is the largest member of the Gallic group of irregular satellites.
It was named in August 2003[9] for Albiorix, "a Gallic giant who was considered to be the king of the world."[10] The name is known from an inscription found near the French town of Sablet which identifies him with the Roman god Mars (an interpretatio romana).[11]
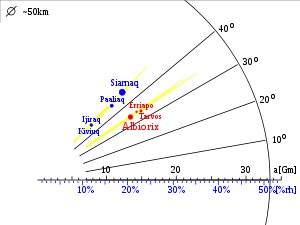
Albiorix orbits Saturn at a distance of about 16 million km and its diameter is estimated at 32 kilometers, assuming an albedo of 0.04. The rotation period was measured by the ISS camera of the Cassini spacecraft to 13 hours and 19 minutes.[4]
The diagram illustrates the Albiorigian orbit in relation to other prograde irregular satellites of Saturn. The eccentricity of the orbits is represented by the yellow segments extending from the pericentre to the apocentre.
Given the similarity of the orbital elements and the homogeneity of the physical characteristics with other members of the Gallic group, it was suggested that these satellites could have a common origin in the break-up of a larger moon.[5][8]
Varying colours revealed recently suggest a possibility of a large crater, leading to an alternative hypothesis that Erriapus and Tarvos could be fragments of Albiorix following a near-break-up collision with another body.[12]
References
- ↑ Discovery Circumstances (JPL)
- ↑ Mean orbital parameters from JPL
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Scott Sheppard pages
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 T. Denk, S. Mottola, et al. (2011): Rotation Periods of Irregular Satellites of Saturn. EPSC/DPS conference 2011, Nantes (France), abstract 1452.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Grav, T.; Holman, M. J.; Gladman, B. J.; Aksnes, K.; Photometric survey of the irregular satellites, Icarus, 166 (2003), pp. 33-45
- ↑ IAUC 7545: S/2000 S 11 December 19, 2000 (discovery)
- ↑ MPEC 2000-Y13: S/2000 S 11 December 19, 2000 (discovery and ephemeris)
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Gladman, B. J.; Nicholson, P. D.; Burns, J. A.; Kavelaars, J. J.; Marsden, B. G.; Holman, M. J.; Grav, T.; Hergenrother, C. W.; Petit, J.-M.; Jacobson, R. A.; and Gray, W. J.; Discovery of 12 satellites of Saturn exhibiting orbital clustering, Nature, 412 (July 12, 2001), pp. 163–166
- ↑ IAUC 8177: Satellites of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus August 8, 2003 (naming the moon)
- ↑ "Planet and Satellite Names and Discoverers". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology. Archived from the original on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ↑ Maier, Bernhard, Dictionary of Celtic religion and culture (1997), p. 11.
- ↑ Grav, T.; and Bauer, J.; A deeper look at the colors of Saturnian irregular satellites
- Ephemeris from IAU-MPC NSES
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||