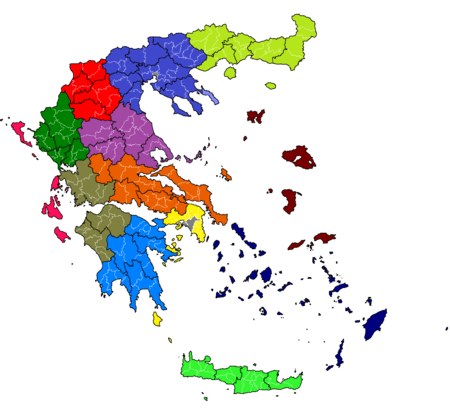
The administrative divisions of Greece, showing regions and municipalities
Greece is internally administered through a system of 7 decentralized administrations, 13 regions and 325 municipalities. The regions and municipalities are fully self-governed.
The decentralized administrations are run by a general secretary appointed by the Greek Government. The Autonomous Monastic State of the Holy Mountain, as an autonomous self-governing entity, is exempt from these reforms.
Administrative divisions
Municipalities
The first level of government is constituted by the municipalities (δήμοι, dímoi; sing. δήμος, dímos), which have resulted from merging several former municipalities and communities (themselves the subject of a previous reform with the 1997 Kapodistrias plan). They are run by a mayor (δήμαρχος, dímarchos) and a municipal council (δημοτικό συμβούλιο, dimotikó symvoúlio), elected every 5 years. The municipalities are further subdivided into municipal units (δημοτικές ενότητες, dimotikés enótites) and finally into communities (κοινότητες, koinótites). Although communities have their own councils, their role is purely advisory to the municipal-level government.
Regions
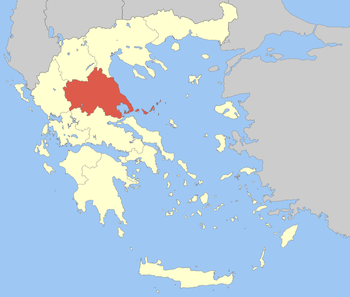
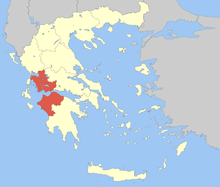
The second level is composed of the regions (περιφέρειες, periféreies; sing. περιφέρεια, periféreia), run by a regional governor (περιφερειάρχης, perifereiárchis) and a regional council (περιφερειακό συμβούλιο, perifereiakó symvoúlio), popularly elected every 5 years. The regions are divided into regional units (περιφερειακές ενότητες, perifereiakés enótites), usually but not always coterminous with the former prefectures. Each regional unit is headed by a vice-regional governor (αντιπεριφερειάρχης, antiperifereiárchis), drawn from the same political block as the regional governor.
Decentralized administrations
The third level is composed of the new decentralized administrations (αποκεντρωμένες διοικήσεις, apokentroménes dioikíseis), comprising two or three regions (except for Attica and Crete), run by a government-appointed general secretary, assisted by an advisory council drawn from the regional governors and the representatives of the municipalities.
History
From 1 January 2011, in accordance with the Kallikratis programme, the administrative system of Greece was drastically overhauled. The former system of 13 regions, 54 prefectures and 1033 municipalities and communities was replaced by 7 decentralized administrations, 13 regions and 325 municipalities.
The first elections to Greek local government areas were held between 7 November and 14 November 2010.
Administration of Attica
- Decentralized Administration of Attica
- Seat: Athens
- General-Secretary: Manolis Angelakas
- Supervised regions: 1
Attica region
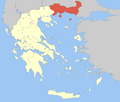
Administration of Macedonia and Thrace
- Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace
- Seat: Thessaloniki
- General-Secretary: Thymios Sokos
- Supervised regions: 2
Eastern Macedonia and Thrace region
|
|---|
|
- Area
- 14,157 km2 (5,466 sq mi)
- Population
- 608,182 (as of 2011)
- Municipalities
- 22 (since 2011)
- Capital
- Komotini
| | | Regional unit of Drama | | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Evros | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Kavala | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Rhodope | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Thasos | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Xanthi | |
|---|
| |
|
Central Macedonia region
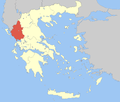
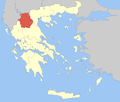
Administration of Epirus and Western Macedonia
- Decentralized Administration of Epirus and Western Macedonia
- Seat: Ioannina
- General-Secretary: Dimitra Georgakopoulou-Basta
- Supervised regions: 2
Epirus region
|
|---|
|
- Area
- 9,203 km2 (3,553 sq mi)
- Population
- 336,856 (as of 2011)
- Municipalities
- 18 (since 2011)
- Capital
- Ioannina
| | | Regional unit of Arta | | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Ioannina | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Preveza | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Thesprotia | |
|---|
| |
|
Western Macedonia region
|
|---|
|
- Area
- 9,451 km2 (3,649 sq mi)
- Population
- 283,689 (as of 2011)
- Municipalities
- 12 (since 2011)
- Capital
- Kozani
| | | Regional unit of Florina | | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Grevena | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Kastoria | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Kozani | |
|---|
| |
|
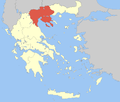
Administration of Thessaly and Central Greece
- Decentralized Administration of Thessaly and Central Greece
- Seat: Larissa
- General-Secretary: Popi Gerakoudi
- Supervised regions: 2
Thessaly region
Central Greece region
Administration of the Peloponnese, Western Greece and the Ionian Islands
- Decentralized Administration of Peloponnese, Western Greece and the Ionian
- Seat: Patras
- General-Secretary: Manolis Angelakas
- Supervised regions: 3
Peloponnese region
Western Greece region
|
|---|
|
- Area
- 11,350 km2 (4,380 sq mi)
- Population
- 679,796 (as of 2011)
- Municipalities
- 19 (since 2011)
- Capital
- Patras
| | | Regional unit of Achaea | | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Aetolia-Acarnania | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Elis | |
|---|
| |
|
Ionian Islands region
Administration of the Aegean
- Decentralized Administration of the Aegean
- Seat: Piraeus
- General-Secretary: Fotis Hatzimichalis
- Supervised regions: 2
North Aegean region
|
|---|
|
- Area
- 3,836 km2 (1,481 sq mi)
- Population
- 199,231 (as of 2011)
- Municipalities
- 9 (since 2011)
- Capital
- Mytilini (Lesbos)
| | | Regional unit of Chios | | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Ikaria | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Lemnos | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Lesbos | |
|---|
| | Regional unit of Samos | |
|---|
| |
|
South Aegean region
Administration of Crete
- Decentralized Administration of Crete
- Seat: Heraklion
- General-Secretary: Thanasis Karoutzos
- Supervised regions: 1
Crete Region
|
|---|
| | People | |
|---|
| | History | |
|---|
| | Major cities | |
|---|
| | Gorges | |
|---|
| | Landmarks | | Ancient | |
|---|
| | Museums | |
|---|
| | Religious | |
|---|
| | Fortresses | |
|---|
| | Natural | |
|---|
| | Other | |
|---|
|
|---|
| | Culture | |
|---|
|
See also
References
Administrative divisions of Europe |
|---|
| | Sovereign states | |
|---|
| | |
|---|
| |
- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
|
|---|
|