Addition chain
In mathematics, an addition chain for computing a positive integer n can be given by a sequence of natural numbers v and a sequence of index pairs w such that each term in v is the sum of two previous terms, the indices of those terms being specified by w:
- v =(v0,...,vs), with v0 = 1 and vs = n
- for each 0< i ≤ s holds: vi = vj + vk, with wi=(j,k) and 0 ≤ j,k ≤ i − 1
Often only v is given since it is easy to extract w from v, but sometimes w is not uniquely reconstructible. An introduction is given by Knuth.[1]
Examples
As an example: v = (1,2,3,6,12,24,30,31) is an addition chain for 31 of length 7, since
- 2 = 1 + 1
- 3 = 2 + 1
- 6 = 3 + 3
- 12 = 6 + 6
- 24 = 12 + 12
- 30 = 24 + 6
- 31 = 30 + 1
Addition chains can be used for addition-chain exponentiation: so for example we only need 7 multiplications to calculate 531:
- 52 = 51 × 51
- 53 = 52 × 51
- 56 = 53 × 53
- 512 = 56 × 56
- 524 = 512 × 512
- 530 = 524 × 56
- 531 = 530 × 51
Methods for computing addition chains
Calculating an addition chain of minimal length is not easy; a generalized version of the problem, in which one must find a chain that simultaneously forms each of a sequence of values, is NP-complete.[2] There is no known algorithm which can calculate a minimal addition chain for a given number with any guarantees of reasonable timing or small memory usage. However, several techniques to calculate relatively short chains exist. One very well known technique to calculate relatively short addition chains is the binary method, similar to exponentiation by squaring. Other well-known methods are the factor method and window method.[3]
Chain length
Let 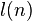 denote the smallest s so that there exists an addition chain
of length s which computes n.
It is known that [4]
denote the smallest s so that there exists an addition chain
of length s which computes n.
It is known that [4]
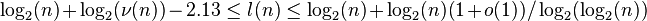 ,
,
where 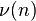 is Hamming weight of binary expansion of n.
is Hamming weight of binary expansion of n.
It is clear that l(2n) ≤ l(n)+1. Strict inequality is possible, as l(382) = l(191) = 11, observed by Knuth.[5] The first integer with l(2n) < l(n) is n = 375494703.[6]
Brauer chain
A Brauer chain or star addition chain is an addition chain in which one of the summands is always the previous chain: that is,
- for each k>0: ak = ak-1 + aj for some j < k.
A Brauer number is one for which the Brauer chain is minimal.[5]
Brauer proved that
- l*(2n−1) ≤ n − 1 + l*(n)
where l* is the length of the shortest star chain. For many values of n,and in particular for n ≤ 2500, they are equal: l(n) = l*(n). But Hansen showed that there are some values of n for which l(n) ≠ l*(n), such as n = 26106 + 23048 + 22032 + 22016 + 1 which has l*(n) = 6110, l(n) ≤ 6109.
Scholz conjecture
The Scholz conjecture (sometimes called the Scholz–Brauer or Brauer–Scholz conjecture), named after A. Scholz and Alfred T. Brauer), is a conjecture from 1937 stating that
- l(2n − 1) ≤ n − 1 + l(n) .
It is known to be true for Hansen numbers, a generalization of Brauer numbers; N. Clift checked by computer that all n≤5784688 are Hansen (while 5784689 is not).[6] Clift further checked that is true with equality for n≤64.[5]
See also
- Addition chain exponentiation
- Addition-subtraction chain
- Vectorial addition chain
- Lucas chain
References
- ↑ D. E. Knuth, The Art of Computer Programming, Vol 2, "Seminumerical Algorithms", Section 4.6.3, 3rd edition, 1997
- ↑ Downey, Peter; Leong, Benton; Sethi, Ravi (1981). "Computing sequences with addition chains". SIAM Journal on Computing 10 (3): 638–646. doi:10.1137/0210047.. A number of other papers state that finding a single addition chain is NP-complete, citing this paper, but it does not claim or prove such a result.
- ↑ Otto, Martin (2001), Brauer addition-subtraction chains, Diplomarbeit, University of Paderborn.
- ↑ A. Schönhage A lower bound on the length of addition chains, Theoret. Comput. Sci. 1 (1975), 1–12.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Guy (2004) p.169
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Clift, Neill Michael (2011). "Calculating optimal addition chains". Computing 91 (3): 265–284. doi:10.1007/s00607-010-0118-8.
- Brauer, Alfred (1939). "On addition chains". Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 45 (10): 736–739. doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1939-07068-7. ISSN 0002-9904. MR 0000245.
- Richard K. Guy (2004). Unsolved Problems in Number Theory. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-20860-7. OCLC 54611248. Zbl 1058.11001. Section C6.