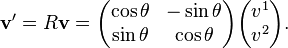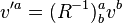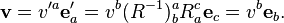Active and passive transformation
In physics and engineering, an active transformation, or alibi transformation, is a transformation which actually changes the physical position of a point, or rigid body, and makes sense even in the absence of a coordinate system whereas a passive transformation, or alias transformation, is a change in the position of the coordinate system from which the object is observed (change of basis). By default, by transformation, mathematicians usually mean active transformations, while physicists and engineers could mean either.
Put differently, a passive transformation refers to observation of the same event from two different coordinate systems.[1] On the other hand, the active transformation is a new position of all points, relative to the same coordinate system. For instance, the active transformation is useful to describe successive positions of a rigid body. On the other hand, the passive transformation may be useful in human motion analysis to observe the motion of the tibia relative to the femur, i.e. its motion relative to a (local) coordinate system which moves together with the femur, rather than a (global) coordinate system which is fixed to the floor.[1]
Example
As an example, in the vector space ℝ2, let {e1,e2} be a basis, and consider the vector v = v1e1 + v2e2. A rotation through angle θ is given by the matrix:
which can be viewed either as an active transformation or a passive transformation, as described below.
Active transformation
As an active transformation, R rotates v . Thus a new vector v' is obtained. For a counterclockwise rotation of v with respect to the fixed coordinate system:
If one views {Re1,Re2} as a new basis, then the coordinates of the new vector v′ in the new basis are the same as those of v in the original basis. Note that active transformations make sense even as a linear transformation into a different vector space. It makes sense to write the new vector in the unprimed basis (as above) only when the transformation is from the space into itself.
Passive transformation
On the other hand, when one views R as a passive transformation, the vector v is left unchanged, while the basis vectors are rotated. In order for the vector to remain fixed, the coordinates in terms of the new basis must change. For a counterclockwise rotation of coordinate systems:
From this equation one sees that the new coordinates (i.e., coordinates with respect to the new basis) are given by
so that
Thus, in order for the vector to remain unchanged by the passive transformation, the coordinates of the vector must transform according to the inverse of the active transformation operator.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Joseph K. Davidson, Kenneth Henderson Hunt (2004). "§4.4.1 The active interpretation and the active transformation". Robots and screw theory: applications of kinematics and statics to robotics. Oxford University Press. p. 74 ff. ISBN 0-19-856245-4.
- ↑ Isaac Amidror (2007). "Appendix D: Remark D.12". The theory of the Moiré phenomenon: Aperiodic layers. Springer. p. 346. ISBN 1-4020-5457-2.
- Dirk Struik (1953) Lectures on Analytic and Projective Geometry, page 84, Addison-Wesley.