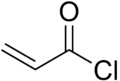
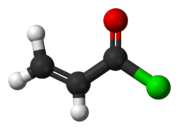
Acryloyl chloride
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-propenoyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
| 814-68-6 | |
| ChemSpider | 12588 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 399362 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C3H3ClO |
| Molar mass | 90.51 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.119 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | N/A |
| Boiling point | 75.0 °C (167.0 °F; 348.1 K) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Acryloyl chloride, also known as 2-propenoyl chloride or acrylic acid chloride, is a clear, light yellow, flammable liquid with an acrid smell.[1][2] It belongs to the acid chlorides group of compounds and is therefore a derivative of acrylic acid.[3]
Preparation
Acryloyl chloride can be prepared by reacting acrylic acid with benzoyl chloride or with thionyl chloride.[3] When preparing this compound adding a small amount of an inhibitor such as hydroquinone can help to avoid light induced polymerisation of acryloyl chloride.
Reaction
This compound will give the common reactions of acid chlorides: it will react violently with water producing acrylic acid while it will form anhydrides when reacted with sodium salts of carboxylic acids. Reactions with alcohols will result in the formation of esters and reactions with amines will generate amides.
Uses
Acryloyl chloride is most commonly employed in organic synthesis for the introduction of acrylic moieties into other compounds and it is also used extensively in the preparation of acrylate monomers and polymers.
References
- ↑ Environmental Chemistry (2007). "Acryloyl chloride". Environmental Chemistry.com (J.K. Barbalace, inc). Retrieved December 21, 2007.
- ↑ Physical & Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory (2005). "Safety data for acryloyl chloride". Physical & Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory. Retrieved December 21, 2007.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 PatentStorm LLC (2006). "Process for the manufacture of acryloyl chloride". PatentStorm LLC. Retrieved December 21, 2007.