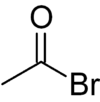
Acetyl bromide
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Acetyl bromide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 506-96-7 | |||
| ChemSpider | 10050 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image | ||
| PubChem | 10482 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H3BrO | |||
| Molar mass | 122.95 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.663 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | −96 °C (−141 °F; 177 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| MSDS | ILO MSDS | ||
| EU classification | | ||
| R-phrases | R14 R34 | ||
| S-phrases | S26 S36/37/39 S45 | ||
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Acetyl bromide is an acyl bromide compound. As is expected, it may be prepared by reaction between phosphorus tribromide and acetic acid:[2]
- 3 CH3COOH + PBr3 → 3 CH3COBr + H3PO3
As usual for an acid halide, acetyl bromide hydrolyzes rapidly in water, forming acetic acid and hydrobromic acid. It also reacts with alcohols and amines to produce acetate esters and acetamides, respectively.
References
- ↑ Acetyl bromide at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Theodore M. Burton and Ed. F. Degering (1940). "The Preparation of Acetyl Bromide". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 62: 227. doi:10.1021/ja01858a502.