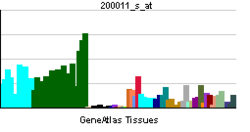
ARF3
ADP-ribosylation factor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARF3 gene.[1][2]
Function
ADP-ribosylation factor 3 (ARF3) is a member of the human ARF gene family. These genes encode small guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that stimulate the ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of cholera toxin and play a role in vesicular trafficking and as activators of phospholipase D. The gene products include 6 ARF proteins and 11 ARF-like proteins and constitute 1 family of the RAS superfamily. The ARF proteins are categorized as class I (ARF1, ARF2,and ARF3), class II (ARF4 and ARF5) and class III (ARF6) and members of each class share a common gene organization. The ARF3 gene contains five exons and four introns.[2]
Interactions
ARF3 has been shown to interact with:
References
- ↑ Hirai M, Kusuda J, Hashimoto K (February 1997). "Assignment of human ADP ribosylation factor (ARF) genes ARF1 and ARF3 to chromosomes 1q42 and 12q13, respectively". Genomics 34 (2): 263–5. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0283. PMID 8661066. Check date values in:
|year= / |date= mismatch(help) - ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Entrez Gene: ARF3 ADP-ribosylation factor 3".
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kanoh H, Williger BT, Exton JH (February 1997). "Arfaptin 1, a putative cytosolic target protein of ADP-ribosylation factor, is recruited to Golgi membranes". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (9): 5421–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.9.5421. PMID 9038142.
- ↑ Williger BT, Provost JJ, Ho WT, Milstine J, Exton JH (July 1999). "Arfaptin 1 forms a complex with ADP-ribosylation factor and inhibits phospholipase D". FEBS Lett. 454 (1-2): 85–9. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00771-1. PMID 10413101.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Boman AL, Salo PD, Hauglund MJ, Strand NL, Rensink SJ, Zhdankina O (September 2002). "ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) interaction is not sufficient for yeast GGA protein function or localization". Mol. Biol. Cell 13 (9): 3078–95. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-02-0078. PMC 124144. PMID 12221117.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Boman AL, Zhang C, Zhu X, Kahn RA (April 2000). "A family of ADP-ribosylation factor effectors that can alter membrane transport through the trans-Golgi". Mol. Biol. Cell 11 (4): 1241–55. doi:10.1091/mbc.11.4.1241. PMC 14844. PMID 10749927.
- ↑ Boman AL, Kuai J, Zhu X, Chen J, Kuriyama R, Kahn RA (October 1999). "Arf proteins bind to mitotic kinesin-like protein 1 (MKLP1) in a GTP-dependent fashion". Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 44 (2): 119–32. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0169(199910)44:2<119::AID-CM4>3.0.CO;2-C. PMID 10506747.
Further reading
- Lee FJ, Moss J, Vaughan M (1992). "Human and Giardia ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) complement ARF function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (34): 24441–5. PMID 1447192.
- Lee CM, Haun RS, Tsai SC, Moss J, Vaughan M (1992). "Characterization of the human gene encoding ADP-ribosylation factor 1, a guanine nucleotide-binding activator of cholera toxin". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (13): 9028–34. PMID 1577740.
- Tsai SC, Haun RS, Tsuchiya M, Moss J, Vaughan M (1991). "Isolation and characterization of the human gene for ADP-ribosylation factor 3, a 20-kDa guanine nucleotide-binding protein activator of cholera toxin". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (34): 23053–9. PMID 1744102.
- Stearns T, Willingham MC, Botstein D, Kahn RA (1990). "ADP-ribosylation factor is functionally and physically associated with the Golgi complex". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (3): 1238–42. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.3.1238. PMC 53446. PMID 2105501.
- Bobak DA, Nightingale MS, Murtagh JJ, Price SR, Moss J, Vaughan M (1989). "Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression of human ADP-ribosylation factors: two guanine nucleotide-dependent activators of cholera toxin". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86 (16): 6101–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.16.6101. PMC 297783. PMID 2474826.
- Orcl L, Palmer DJ, Amherdt M, Rothman JE (1993). "Coated vesicle assembly in the Golgi requires only coatomer and ARF proteins from the cytosol". Nature 364 (6439): 732–4. doi:10.1038/364732a0. PMID 8355790.
- Haun RS, Moss J, Vaughan M (1993). "Characterization of the human ADP-ribosylation factor 3 promoter. Transcriptional regulation of a TATA-less promoter". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (12): 8793–800. PMID 8473323.
- Helms JB, Palmer DJ, Rothman JE (1993). "Two distinct populations of ARF bound to Golgi membranes". J. Cell Biol. 121 (4): 751–60. doi:10.1083/jcb.121.4.751. PMC 2119793. PMID 8491770.
- Hosaka M, Toda K, Takatsu H, Torii S, Murakami K, Nakayama K (1996). "Structure and intracellular localization of mouse ADP-ribosylation factors type 1 to type 6 (ARF1-ARF6)". J. Biochem. 120 (4): 813–9. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021484. PMID 8947846.
- Kanoh H, Williger BT, Exton JH (1997). "Arfaptin 1, a putative cytosolic target protein of ADP-ribosylation factor, is recruited to Golgi membranes". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (9): 5421–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.9.5421. PMID 9038142.
- Williger BT, Provost JJ, Ho WT, Milstine J, Exton JH (1999). "Arfaptin 1 forms a complex with ADP-ribosylation factor and inhibits phospholipase D". FEBS Lett. 454 (1-2): 85–9. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00771-1. PMID 10413101.
- Boman AL, Kuai J, Zhu X, Chen J, Kuriyama R, Kahn RA (1999). "Arf proteins bind to mitotic kinesin-like protein 1 (MKLP1) in a GTP-dependent fashion". Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 44 (2): 119–32. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0169(199910)44:2<119::AID-CM4>3.0.CO;2-C. PMID 10506747.
- Takeya R, Takeshige K, Sumimoto H (2000). "Interaction of the PDZ domain of human PICK1 with class I ADP-ribosylation factors". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 267 (1): 149–55. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1932. PMID 10623590.
- Boman AL, Zhang C, Zhu X, Kahn RA (2000). "A family of ADP-ribosylation factor effectors that can alter membrane transport through the trans-Golgi". Mol. Biol. Cell 11 (4): 1241–55. doi:10.1091/mbc.11.4.1241. PMC 14844. PMID 10749927.
- Nevrivy DJ, Peterson VJ, Avram D, Ishmael JE, Hansen SG, Dowell P et al. (2000). "Interaction of GRASP, a protein encoded by a novel retinoic acid-induced gene, with members of the cytohesin family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (22): 16827–36. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.22.16827. PMID 10828067.
- Zhdankina O, Strand NL, Redmond JM, Boman AL (2001). "Yeast GGA proteins interact with GTP-bound Arf and facilitate transport through the Golgi". Yeast 18 (1): 1–18. doi:10.1002/1097-0061(200101)18:1<1::AID-YEA644>3.0.CO;2-5. PMID 11124697.
- Irobi J, Nelis E, Verhoeven K, De Vriendt E, Dierick I, De Jonghe P et al. (2002). "Mutation analysis of 12 candidate genes for distal hereditary motor neuropathy type II (distal HMN II) linked to 12q24.3". J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 7 (2): 87–95. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8027.2002.02014.x. PMID 12090300.
- Li F, Mandal M, Mishra SK, Barnes CJ, Kumar R (2002). "Heregulin promotes expression and subcellular redistribution of ADP-ribosylation factor 3". FEBS Lett. 524 (1-3): 49–53. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02994-0. PMID 12135740.
- Boman AL, Salo PD, Hauglund MJ, Strand NL, Rensink SJ, Zhdankina O (2002). "ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) interaction is not sufficient for yeast GGA protein function or localization". Mol. Biol. Cell 13 (9): 3078–95. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-02-0078. PMC 124144. PMID 12221117.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||