ADAM33
Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 33 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAM33 gene.[1][2]
Function
This gene encodes a member of the ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloprotease domain) family. Members of this family are membrane-anchored proteins structurally related to snake venom disintegrins, and have been implicated in a variety of biological processes involving cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, including fertilization, muscle development, and neurogenesis. This protein is a type I transmembrane protein implicated in asthma and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms.[2]
References
Further reading
- Holgate ST, Davies DE, Rorke S, Cakebread J, Murphy G, Powell RM et al. (Aug 2004). "ADAM 33 and its association with airway remodeling and hyperresponsiveness in asthma". Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology 27 (1): 23–34. doi:10.1385/CRIAI:27:1:023. PMID 15347848.
- Holloway JW, Davies DE, Powell R, Haitchi HM, Keith TP, Holgate ST (Aug 2004). "The discovery and role of ADAM33, a new candidate gene for asthma". Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine 6 (17): 1–12. doi:10.1017/S1462399404007963. PMID 15387895.
- Holgate ST, Yang Y, Haitchi HM, Powell RM, Holloway JW, Yoshisue H et al. (Jul 2006). "The genetics of asthma: ADAM33 as an example of a susceptibility gene". Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 3 (5): 440–3. doi:10.1513/pats.200603-026AW. PMID 16799089.
- Van Eerdewegh P, Little RD, Dupuis J, Del Mastro RG, Falls K, Simon J et al. (Jul 2002). "Association of the ADAM33 gene with asthma and bronchial hyperresponsiveness". Nature 418 (6896): 426–30. doi:10.1038/nature00878. PMID 12110844.
- Garlisi CG, Zou J, Devito KE, Tian F, Zhu FX, Liu J et al. (Jan 2003). "Human ADAM33: protein maturation and localization". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 301 (1): 35–43. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)02976-5. PMID 12535637.
- Chae SC, Yoon KH, Chung HT (2003). "Identification of novel polymorphisms in the Adam33 gene". Journal of Human Genetics 48 (5): 278–81. doi:10.1007/s10038-003-0019-1. PMID 12768445.
- Clark HF, Gurney AL, Abaya E, Baker K, Baldwin D, Brush J et al. (Oct 2003). "The secreted protein discovery initiative (SPDI), a large-scale effort to identify novel human secreted and transmembrane proteins: a bioinformatics assessment". Genome Research 13 (10): 2265–70. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003. PMC 403697. PMID 12975309.
- Howard TD, Postma DS, Jongepier H, Moore WC, Koppelman GH, Zheng SL et al. (Oct 2003). "Association of a disintegrin and metalloprotease 33 (ADAM33) gene with asthma in ethnically diverse populations". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 112 (4): 717–22. doi:10.1016/s0091-6749(03)01939-0. PMID 14564349.
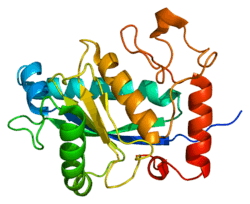
- Orth P, Reichert P, Wang W, Prosise WW, Yarosh-Tomaine T, Hammond G et al. (Jan 2004). "Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human ADAM33". Journal of Molecular Biology 335 (1): 129–37. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.037. PMID 14659745.
- Zou J, Zhu F, Liu J, Wang W, Zhang R, Garlisi CG et al. (Mar 2004). "Catalytic activity of human ADAM33". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (11): 9818–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309696200. PMID 14676211.
- Powell RM, Wicks J, Holloway JW, Holgate ST, Davies DE (Jul 2004). "The splicing and fate of ADAM33 transcripts in primary human airways fibroblasts". American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 31 (1): 13–21. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2003-0330OC. PMID 14742294.
- Haitchi HM, Powell RM, Shaw TJ, Howarth PH, Wilson SJ, Wilson DI et al. (May 2005). "ADAM33 expression in asthmatic airways and human embryonic lungs". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 171 (9): 958–65. doi:10.1164/rccm.200409-1251OC. PMID 15709049.
- Zou J, Zhang R, Zhu F, Liu J, Madison V, Umland SP (Mar 2005). "ADAM33 enzyme properties and substrate specificity". Biochemistry 44 (11): 4247–56. doi:10.1021/bi0476230. PMID 15766253.
- Simpson A, Maniatis N, Jury F, Cakebread JA, Lowe LA, Holgate ST et al. (Jul 2005). "Polymorphisms in a disintegrin and metalloprotease 33 (ADAM33) predict impaired early-life lung function". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 172 (1): 55–60. doi:10.1164/rccm.200412-1708OC. PMID 15805180.
External links
- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: M12.244
PDB gallery |
|---|
| | 1r54: Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human ADAM33 |
| 1r55: Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human ADAM 33 |
|
|
|