ACF (gene)
| APOBEC1 complementation factor | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 2cpd. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | A1CF ; ACF; ACF64; ACF65; APOBEC1CF; ASP | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1917115 HomoloGene: 16363 GeneCards: A1CF Gene | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
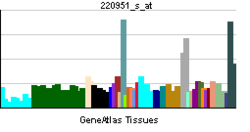 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 29974 | 69865 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000148584 | ENSMUSG00000052595 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | Q9NQ94 | Q5YD48 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001198818 | NM_001081074 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001185747 | NP_001074543 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 10: 52.56 – 52.65 Mb | Chr 19: 31.87 – 31.95 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
APOBEC1 complementation factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the A1CF gene.[1][2][3]
Gene
Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and three full-length transcript variants, encoding three distinct isoforms, have been described. Additional splicing has been observed but the full-length nature of these variants has not been determined.[3]
Function
Mammalian apolipoprotein B mRNA undergoes site-specific C to U deamination, which is mediated by a multi-component enzyme complex containing a minimal core composed of APOBEC1 and a complementation factor encoded by this gene.[4] The gene product has three non-identical RNA recognition motifs and belongs to the hnRNP R family of RNA-binding proteins. It has been proposed that this complementation factor functions as an RNA-binding subunit and docks APOBEC1 to deaminate the upstream cytidine. Studies suggest that the protein may also be involved in other RNA editing or RNA processing events.[3]
Its deletion results in lethality in mice.[5]
Interactions
ACF has been shown to interact with APOBEC1,[6][7] CUGBP2,[8] and SYNCRIP.[9][6]
References
- ↑ Dance GS, Sowden MP, Cartegni L, Cooper E, Krainer AR, Smith HC (April 2002). "Two proteins essential for apolipoprotein B mRNA editing are expressed from a single gene through alternative splicing". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (15): 12703–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111337200. PMID 11815617.
- ↑ Chester A, Scott J, Anant S, Navaratnam N (December 2000). "RNA editing: cytidine to uridine conversion in apolipoprotein B mRNA". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1494 (1-2): 1–13. doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(00)00219-0. PMID 11072063.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Entrez Gene: ACF apobec-1 complementation factor".
- ↑ Henderson JO, Blanc V, Davidson NO (November 2001). "Isolation, characterization and developmental regulation of the human apobec-1 complementation factor (ACF) gene". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1522 (1): 22–30. doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(01)00295-0. PMID 11718896.
- ↑ Blanc V, Henderson JO, Newberry EP, Kennedy S, Luo J, Davidson NO (August 2005). "Targeted deletion of the murine apobec-1 complementation factor (acf) gene results in embryonic lethality". Mol. Cell. Biol. 25 (16): 7260–9. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.16.7260-7269.2005. PMC 1190267. PMID 16055734.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Blanc V, Navaratnam N, Henderson JO, Anant S, Kennedy S, Jarmuz A et al. (March 2001). "Identification of GRY-RBP as an apolipoprotein B RNA-binding protein that interacts with both apobec-1 and apobec-1 complementation factor to modulate C to U editing". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (13): 10272–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006435200. PMID 11134005.
- ↑ Mehta A, Kinter MT, Sherman NE, Driscoll DM (March 2000). "Molecular cloning of apobec-1 complementation factor, a novel RNA-binding protein involved in the editing of apolipoprotein B mRNA". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (5): 1846–54. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.5.1846-1854.2000. PMC 85365. PMID 10669759.
- ↑ Anant S, Henderson JO, Mukhopadhyay D, Navaratnam N, Kennedy S, Min J et al. (December 2001). "Novel role for RNA-binding protein CUGBP2 in mammalian RNA editing. CUGBP2 modulates C to U editing of apolipoprotein B mRNA by interacting with apobec-1 and ACF, the apobec-1 complementation factor". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (50): 47338–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104911200. PMID 11577082.
- ↑ Lau PP, Chang BH, Chan L (April 2001). "Two-hybrid cloning identifies an RNA-binding protein, GRY-RBP, as a component of apobec-1 editosome". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 282 (4): 977–83. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4679. PMID 11352648.
Further reading
- Mehta A, Kinter MT, Sherman NE, Driscoll DM (2000). "Molecular cloning of apobec-1 complementation factor, a novel RNA-binding protein involved in the editing of apolipoprotein B mRNA". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (5): 1846–54. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.5.1846-1854.2000. PMC 85365. PMID 10669759.
- Lellek H, Kirsten R, Diehl I, Apostel F, Buck F, Greeve J (2000). "Purification and molecular cloning of a novel essential component of the apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme-complex". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (26): 19848–56. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001786200. PMID 10781591.
- Yang Y, Sowden MP, Smith HC (2000). "Induction of cytidine to uridine editing on cytoplasmic apolipoprotein B mRNA by overexpressing APOBEC-1". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (30): 22663–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M910406199. PMID 10833526.
- Blanc V, Navaratnam N, Henderson JO, Anant S, Kennedy S, Jarmuz A et al. (2001). "Identification of GRY-RBP as an apolipoprotein B RNA-binding protein that interacts with both apobec-1 and apobec-1 complementation factor to modulate C to U editing". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (13): 10272–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006435200. PMID 11134005.
- Harrington JJ, Sherf B, Rundlett S, Jackson PD, Perry R, Cain S et al. (2001). "Creation of genome-wide protein expression libraries using random activation of gene expression". Nat. Biotechnol. 19 (5): 440–5. doi:10.1038/88107. PMID 11329013.
- Lau PP, Chang BH, Chan L (2001). "Two-hybrid cloning identifies an RNA-binding protein, GRY-RBP, as a component of apobec-1 editosome". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 282 (4): 977–83. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4679. PMID 11352648.
- Blanc V, Henderson JO, Kennedy S, Davidson NO (2001). "Mutagenesis of apobec-1 complementation factor reveals distinct domains that modulate RNA binding, protein-protein interaction with apobec-1, and complementation of C to U RNA-editing activity". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (49): 46386–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107654200. PMID 11571303.
- Anant S, Henderson JO, Mukhopadhyay D, Navaratnam N, Kennedy S, Min J et al. (2001). "Novel role for RNA-binding protein CUGBP2 in mammalian RNA editing. CUGBP2 modulates C to U editing of apolipoprotein B mRNA by interacting with apobec-1 and ACF, the apobec-1 complementation factor". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (50): 47338–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104911200. PMID 11577082.
- Henderson JO, Blanc V, Davidson NO (2001). "Isolation, characterization and developmental regulation of the human apobec-1 complementation factor (ACF) gene". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1522 (1): 22–30. doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(01)00295-0. PMID 11718896.
- Xu XR, Huang J, Xu ZG, Qian BZ, Zhu ZD, Yan Q et al. (2001). "Insight into hepatocellular carcinogenesis at transcriptome level by comparing gene expression profiles of hepatocellular carcinoma with those of corresponding noncancerous liver". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (26): 15089–94. doi:10.1073/pnas.241522398. PMC 64988. PMID 11752456.
- Mehta A, Driscoll DM (2002). "Identification of domains in apobec-1 complementation factor required for RNA binding and apolipoprotein-B mRNA editing". RNA 8 (1): 69–82. doi:10.1017/S1355838202015649. PMC 1370230. PMID 11871661.
- Chester A, Somasekaram A, Tzimina M, Jarmuz A, Gisbourne J, O'Keefe R et al. (2003). "The apolipoprotein B mRNA editing complex performs a multifunctional cycle and suppresses nonsense-mediated decay". EMBO J. 22 (15): 3971–82. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg369. PMC 169042. PMID 12881431.
- Blanc V, Kennedy S, Davidson NO (2003). "A novel nuclear localization signal in the auxiliary domain of apobec-1 complementation factor regulates nucleocytoplasmic import and shuttling". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (42): 41198–204. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302951200. PMID 12896982.
- Xie K, Sowden MP, Dance GS, Torelli AT, Smith HC, Wedekind JE (2004). "The structure of a yeast RNA-editing deaminase provides insight into the fold and function of activation-induced deaminase and APOBEC-1". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (21): 8114–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400493101. PMC 419566. PMID 15148397.
| |||||||||