4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase
| 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 4.1.1.61 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 37290-53-2 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.61) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- 4-hydroxybenzoate
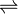 phenol + CO2
phenol + CO2
Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, 4-hydroxybenzoate, and two products, phenol and CO2.
This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically the carboxy-lyases, which cleave carbon-carbon bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 4-hydroxybenzoate carboxy-lyase (phenol-forming). Other names in common use include p-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase, and 4-hydroxybenzoate carboxy-lyase. This enzyme participates in benzoate degradation via coa ligation.
References
- Grant DJW and Patel JC (1969). "Non-oxidative decarboxylation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, gentisic acid, protocatechuic acid, and gallic acid by Klebsiella aerogenes (Aerobacter aerogenes)". J. Microbiol. Serol. 35: 325–343.
- Tschech A and Fuchs G (1989). "Anaerobic degradation of phenol via carboxylation to 4-hydroxybenzoate - in vitro study of isotope exchange between (CO2)-C-14 and 4-hydroxybenzoate". Arch. Microbiol. 152 (6): 594–599. doi:10.1007/BF00425493.