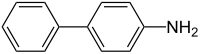
4-Aminobiphenyl
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-Aminobiphenyl | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
| 92-67-1 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:1784 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL44201 |
| ChemSpider | 6835 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| KEGG | C10998 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C12H11N |
| Molar mass | 169.22 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white to purple crystals |
| Odor | floral[1] |
| Density | 1,16 g·cm−3[2] |
| Melting point | 52 to 54 °C (126 to 129 °F; 325 to 327 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 302 °C (576 °F; 575 K)[2] |
| practically insoluble in water,[2] soluble in alcohol, ether and chloroform | |
| Vapor pressure | 20 mbar (191 °C)[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | potential occupational carcinogen[1] |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 147 °C (297 °F; 420 K) |
| 450 °C (842 °F; 723 K) | |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| REL (Recommended) |
carcinogen[1] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
4-Aminobiphenyl is an amine derivative of biphenyl. It is used to manufacture azo dyes. It is a known human carcinogen[3] and so it has been largely replaced by less toxic compounds. It is similar to benzidine.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0025". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Record of CAS RN 92-67-1 in the GESTIS Substance Database of the IFA, accessed on 8. April 2009
- ↑ National Toxicology Program
