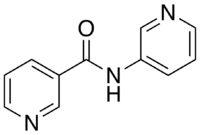
3-Pyridylnicotinamide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-pyridin-3-ylpyridine-3-carboxamide | |
| Other names
3-pna 3-pyridinecarboxamide, N-3-pyridinyl- N-(Pyridin-3-yl)nicotinamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 13160-06-0 | |
| ChemSpider | 175548 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H9N3O | |
| Molar mass | 199.20 g/mol |
| Density | 1.287 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 286.08 °C (546.94 °F; 559.23 K) |
| Structure | |
| Dipole moment | 0 D |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 127 °C (261 °F; 400 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
4,4'-bipyridine Pyridine Nicotinamide 3-Aminopyridine 4-Pyridylnicotinamide |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
The organic compound 3-pyridylnicotinamide (3-pna), also known as N-(pyridin-3-yl)nicotinamide, is a kinked dipodal dipyridine that is synthesized through the reaction of nicotinoyl chloride and 3-aminopyridine.[1] The nitrogen atoms on its pyridine rings, like those of its isomer 4-pyridylnicotinamide, can donate their electron lone pairs to metal cations, allowing it to bridge metal centers and act as a bidentate ligand in coordination polymers.[2][3][4][5][6] It can be used to synthesize polymers that have potentially useful gas adsorption properties.[2][3]
References
- ↑ Zheng, X.; Salgia, S. R.; Thompson, W. B.; Dillingham, E. O.; Bond, S. E.; Feng, Z.; Prasad, K. R.; Gollamudi, R. (1995). "Design and Synthesis of Piperidine-3-carboxamides as Human Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 38 (1): 180–188. doi:10.1021/jm00001a023. PMID 7837229.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Uemura, K.; Kitagawa, S.; Fukui, K. I.; Saito, K. (2004). "A Contrivance for a Dynamic Porous Framework: Cooperative Guest Adsorption Based on Square Grids Connected by Amide−Amide Hydrogen Bonds". Journal of the American Chemical Society 126 (12): 3817–3828. doi:10.1021/ja039914m. PMID 15038736.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kazuhiro Uemura, Susumu Kitagawa Prof. Dr., Mitsuru Kondo Dr., Kôichi Fukui Dr., Ryo Kitaura, Ho-Chol Chang Dr., Tadashi Mizutani Dr. (2002). "Novel Flexible Frameworks of Porous Cobalt(II) Coordination Polymers That Show Selective Guest Adsorption Based on the Switching of Hydrogen-Bond Pairs of Amide Groups". Chemistry - A European Journal 8 (16): 3586–3600. doi:10.1002/1521-3765(20020816)8:16%3C3586::AID-CHEM3586%3E3.0.CO;2-K.
- ↑ Kumar, D. K.; Das, A.; Dastidar, P. (2007). "Supramolecular structural diversities in the metal?organic frameworks derived from pyridylamide ligands: Studying the effects of ligating topologies, hydrogen bonding backbone of the ligands and counter anions". CrystEngComm 9 (7): 548. doi:10.1039/B701782K.
- ↑ Banerjee, S.; Adarsh, N. N.; Dastidar, P. (2010). "Selective Separation of the Sulfate Anion by in Situ Crystallization of CdII Coordination Compounds Derived from Bis(pyridyl) Ligands Equipped with a Urea/Amide Hydrogen-Bonding Backbone". European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry 2010 (24): 3770. doi:10.1002/ejic.201000359.
- ↑ Kumar, D. K.; Das, A.; Dastidar, P. (2007). "Conformation dependent network structures in the coordination polymers derived from pyridylisonicotinamides, carboxylates and Co(ii): Entrapment of (H2O)14 water cluster of an unprecedented topology". CrystEngComm (Royal Society of Chemistry) 9 (10): 895. doi:10.1039/B705851A.