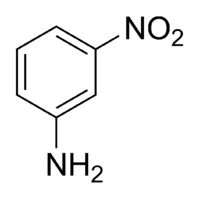
3-Nitroaniline
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Nitroaniline | |
| Other names
meta-Nitroaniline, m-nitroaniline | |
| Identifiers | |
| 99-09-2 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL14068 |
| ChemSpider | 7145 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 138.14 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow, Solid |
| Melting point | 114 °C (237 °F; 387 K) |
| Boiling point | 306 °C (583 °F; 579 K) |
| 0.1 g/100 ml (20°C) | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.47 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
2-Nitroaniline, 4-Nitroaniline |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Nitroaniline, also known as 'meta'-nitroaniline and m-nitroaniline, is a non-volatile stable solid commonly used as a raw material for dyes. 3-Nitroaniline is an aniline carrying a nitro functional group in position 3. It is stable in neutral, acidic or alkaline solutions and is classified as "not readily biodegradable" with "low bioaccumulation potential" .
It is used as a chemical intermediate for azo coupling component 17 and the dyes disperse yellow 5 and acid blue 29. The chemical is changed to other substances (dyestuffs and m-nitrophenol) during the dyeing process.
Synthesis
It can be synthesised by nitration of benzamide followed by the Hofmann rearrangement of the 3-Nitrobenzamide previously formed. It consist in treating the 3-Nitrobenzamide with sodium hypobromite or sodium hypochlorite to transform the amide group into an amine.