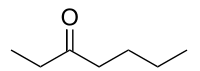
3-Heptanone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Heptan-3-one | |
| Other names
Ethyl-butyl Ketone; 3-oxoheptane; Butyl ethyl ketone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 506161 | |
| 106-35-4 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:50139 |
| ChemSpider | 7514 |
| EC number | 203-388-1 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| MeSH | 3-Heptanone |
| PubChem | 24901132 |
| RTECS number | MJ5250000 |
| |
| UN number | 1224 |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C7H14O |
| Molar mass | 114.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | powerful, fruity[1] |
| Density | 0.812 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | −39 °C (−38 °F; 234 K) |
| Boiling point | 146 °C (295 °F; 419 K) |
| 1% (20°C)[1] | |
| Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | [2] |
| R-phrases | R10, R22 |
| S-phrases | S23 |
| Flash point | 41 °C (106 °F; 314 K) |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 50 ppm (230 mg/m3)[1] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 50 ppm (230 mg/m3)[1] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
1000 ppm[1] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Heptanone (butyl ethyl ketone), is a seven carbon ketone. It is a colorless liquid with a "green odor," also described to have a fruity scent. It is often used as a perfume/fragrance, as a solvent for cellulose, nitrocellulose, or vinyl resins, and as a synthetic building block in the preparation of other organic molecules.[3]
Preparation
3-Heptanone is produced industrially through reductive condensation of propanal with 2-butanone. This reaction does not immediately yield 3-Heptanone. Rather it results in the production of a ketone with an alkene group. This alkene can be removed with hydrogenation.
CH3CH2CHO + CH3C(O)CH2CH3 --> CH3CH2C(O)CH=CHCH2CH3 + H2 --> CH3CH2C(O)CH2CH2CH2CH3
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0266". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ http://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductMSDSDetailCB0852672_EN.htm External MSDS
- ↑ Siegel, Hardo; Eggersdorfer (2012). "Ketones". Ullman's Encyclopedia or Industrial Chemistry 20: 195. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_077.