3,3'-Diiodothyronine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodo-phenoxy)-3-iodo-phenyl]propanoic acid | |
| Other names
O-(4-Hydroxy-3-iodophenyl)-3-iodotyrosine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 70-40-6 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:35430 |
| ChemSpider | 59002 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image |
| MeSH | 3,3'-diiodothyronine |
| PubChem | 65559 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H13I2NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 525.077 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
3,3'-Diiodothyronine, also known as T2, is a metabolite of thyroid hormone.
It is formed from the breakdown of triiodothyronine. It is an allosteric regulator of the cytochrome c oxidase, the complex IV of the electron transport chain. It increases its activity by preventing the interaction of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as an allosteric inhibitor.[1]
Levels can be affected in certain disease states.[2]
Reactions
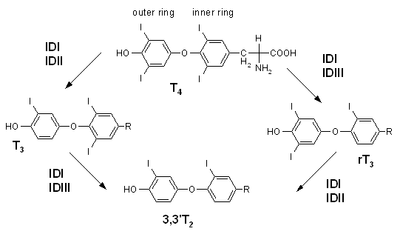
Synthesis of T2 from T3, and from reverse T3
References
- ↑ Arnold S., Goglia F., Kadenbach B. (1998). "3,5-Diiodothyronine binds to subunit Va of cytochrome-c oxidase and abolishes the allosteric inhibition of respiration by ATP.". Eur J Biochem. 252 (2): 325–330. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2520325.x. PMID 9523704.
- ↑ Pinna G, Hiedra L, Meinhold H et al. (September 1998). "3,3'-Diiodothyronine concentrations in the sera of patients with nonthyroidal illnesses and brain tumors and of healthy subjects during acute stress". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83 (9): 3071–7. doi:10.1210/jc.83.9.3071. PMID 9745405.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||