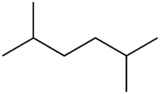
2,5-Dimethylhexane
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,5-Dimethylhexane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1696877 | |
| 592-13-2 | |
| ChemSpider | 11104 |
| EC number | 209-745-8 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 11592 |
| |
| UN number | 3295 |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C8H18 |
| Molar mass | 114.23 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Density | 694 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −93 °C; −136 °F; 180 K |
| Boiling point | 108.1 °C; 226.5 °F; 381.2 K |
| Vapor pressure | 7.582 kPa (at 37.7 °C) |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
3.0 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.392 |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Specific heat capacity (C) |
249.20 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−262.0–−259.0 kJ mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH |
−5.4615–−5.4587 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |     |
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| H225, H304, H315, H336, H410 | |
| P210, P261, P273, P301+310, P331 | |
| EU Index | 601-009-00-8 |
| EU classification | |
| R-phrases | R10, R38, R65, R67, R50/53 |
| S-phrases | (S2), S16, S29, S33 |
| Flash point | 26 °C (79 °F; 299 K) |
| Explosive limits | 0.98–?% |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanes |
|
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
2,5-Dimethylhexane is a branched alkane used in the aviation industry in low revolutions per minute helicopters. As an isomer of octane, the boiling point is very close to that of octane, but can in pure form be slightly lower. 2,5-Dimethylhexane is moderately toxic.
References
- ↑ "2,5-DIMETHYLHEXANE - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 12 March 2012.