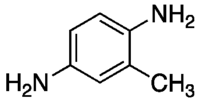
2,5-Diaminotoluene
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,5-diaminotoluene | |
| Other names
2-methyl-1,4-benzenediamine; toluene-2,5-diamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 95-70-5 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:53619 |
| ChemSpider | 6982 |
| |
| KEGG | C19386 |
| UNII | 24JO8Z0RJU |
| Properties | |
| C7H10N2 | |
| Molar mass | 122.17 |
| Appearance | off white crystals |
| Density | 1.107 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 64 °C (147 °F; 337 K) |
| Boiling point | 273 °C (523 °F; 546 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | no |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
2,5-Diaminotoluene is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(NH2)2CH3. It is one isomer of six with this formula. 2,5-Diaminotoluene is a colorless crystalline solid that is commonly used in hair coloring.[2]
Formation and use
2,5-Diaminotoluene is prepared through electrolytic reduction of 2,5-dinitrotoluene.[3] Other methods include the reductive cleavage of 4-amino-2,3'-dimethylazobenzene as well as the condensation of 2-amino-1-methylbenzene and toluene-4-sulphonyl chloride to produce 4-toluenesulphono-2-toluidide which is then coupled with diazotized aminobenzenesulphonic acid and reduced.[3]
2,5-Diaminotoluene is a substitute for phenylenediamine (1,4-diaminobenzene) in commercial hair dyes. It is preferred because of its lower toxicity. However, many home hair dyes still use phenylenediamine. In these applications, these diamines function as a primary intermediate, which means that it is first oxidized with hydrogen peroxide and then combined with a coupler to form the hair dye.[2] 2,5-Diaminotoluene is commonly used to produce black, drab and warm browns, and shades of blonde and gray hair dyes.[3]
2,5-Diaminotoluene is also known to be used in the production of dyes for textiles, furs, leathers, biological stains and indicators, wood stains, and pigments. Two examples of dyes produced by 2,5-diaminotoluene are Cl Basic Red 2 and Cl Acid Brown 103.[3]
References
- ↑ "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0620". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 T. Clausen "Hair Preparations" in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_571.pub2
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 C. Burnett, W. Bergfeld, D. Velsito, C. Klaassen, J. Marks, Jr, R. Shank, T. Slaga, P. Snyder, and F. Andersen "Final Amended Report of the Safety Assessment of Toluene-2,5-Diamine, Toluene-2,5-Diamine Sulfate, and Toluene-3,4-Diamine as Used in Cosmetics" in International Journal of Toxicology, 2010, vol 29, pages 61S-83S