1983–84 Australian region cyclone season
1983–84 Australian region cyclone season
| |
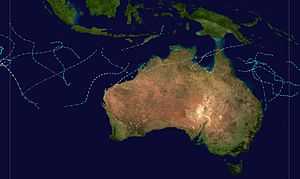
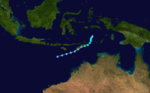
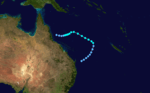
| Season summary map |
| First system formed |
22 October 1983 |
| Last system dissipated |
7 April 1984 |
| Strongest storm |
Kathy – 920 hPa (mbar), 205 km/h (125 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| Tropical lows |
24 |
| Total storms |
22 |
| Severe tropical cyclones |
11 |
| Total fatalities |
1 |
| Total damage |
$19 million (1984 USD) |
Australian region tropical cyclone seasons
1981–82, 1982–83, 1983–84, 1984–85, 1985–86 |
| Related articles |
|
|
The 1983–84 Australian region cyclone season was one of the most active seasons on record. It officially started on 1 November 1983, and officially ended on 30 April 1984.
Storms
Cyclone 01S
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 11 – July 15 |
| Peak intensity |
65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min) 1000 mbar (hPa) |
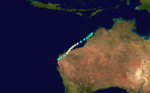
Severe Tropical Cyclone Oscar
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
22 October – 1 November |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min) 968 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Low Pearl
| Tropical low (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
11 November – 14 November |
| Peak intensity |
60 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 997 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Quenton
| Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
26 November – 30 November |
| Peak intensity |
170 km/h (105 mph) (10-min) 955 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Fritz
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
9 December – 13 December |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 992 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Esther
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
19 December – 21 December |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Unnamed Tropical Cyclone
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
21 December – 24 December |
| Peak intensity |
70 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 994 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Sharon
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
25 December – 31 December |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 984 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Tim
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
2 January – 10 January |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Grace
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
11 January – 20 January |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min) 970 mbar (hPa) |
Grace struck Queensland on January 1, 1984 causing $7 million (1998 USD) in damage.[1]
Tropical Cyclone Vivienne-Fanja
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
23 January – 27 January (Crossed 80°E) |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 975 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Willy
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
2 February – 11 February |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (95 mph) (10-min) 960 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Annette-Jaminy
| Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
3 February – 16 February (Crossed 80°E) |
| Peak intensity |
160 km/h (100 mph) (10-min) 960 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Harvey
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
3 February – 7 February (Crossed 160°E) |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Bobby
| Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
17 February – 23 February |
| Peak intensity |
170 km/h (105 mph) (10-min) 950 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Ingrid
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
20 February – 26 February |
| Peak intensity |
120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min) 975 mbar (hPa) |
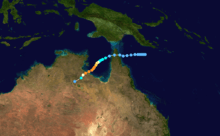
Severe Tropical Cyclone Chloe
| Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
26 February – 3 March |
| Peak intensity |
170 km/h (105 mph) (10-min) 955 mbar (hPa) |
On 29 February 1984 Chloe crossed the coast near Roebourne, Western Australia where three houses were destroyed and twelve others unroofed. Fifty people required evacuation as floodwaters from the Harding River rose to the lower steps of the Police Station. Parts of the Wickham High Schools were severely damaged and two buildings and a boat were destroyed in the Cossack/Point Samson area. The Dampier Yacht Club was unroofed.[2]
Tropical Cyclone Ferdinand
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
2 March – 5 March |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 983 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Jim
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
6 March – 10 March |
| Peak intensity |
125 km/h (80 mph) (10-min) 970 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Daryl
| Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
6 March – 20 March |
| Peak intensity |
160 km/h (100 mph) (10-min) 955 mbar (hPa) |
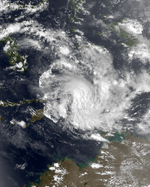
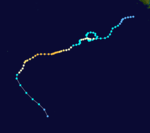
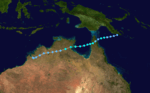
Severe Tropical Cyclone Kathy
| Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
March 16 – March 23 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 920 mbar (hPa) |
Main article:
Cyclone KathySevere Tropical Cyclone Kathy was a powerful tropical cyclone that devastated the Sir Edward Pellew Group of Islands in March 1984. Originating from a tropical low off the southern coast of Papua New Guinea. Tracking westward, the system attained gale-force winds by 18 March before striking the Cape York Peninsula. After crossing the area, Kathy entered the Gulf of Carpentaria where environmental conditions favored significant development. On 22 March, the storm attained its peak intensity as a Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian tropical cyclone intensity scale) with ten-minute sustained winds of 205 km/h (125 mph). By this time, the storm had been tracking towards the southwest and struck the Sir Edward Pellew Group of Islands later on 22 March before moving over the Australian mainland as a slightly weaker system. Once over land, Kathy rapidly degraded, losing gale-force winds within 24 hours; the storm dissipated over the Northern Territory on 24 March.
One person died and damaged totaled to 12 million.[3][4][5]
Tropical Cyclone Lance
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
4 April – 7 April |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 992 mbar (hPa) |
Lance affected Queensland before dissipating on April 17.[6]
References