1979 Pacific typhoon season
| |
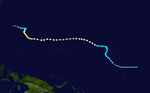
| Season summary map |
| First system formed |
December 31, 1978 |
| Last system dissipated |
December 23, 1979 |
| Strongest storm |
Tip (Most intense tropical cyclone ever recorded) – 870 hPa (mbar), 260 km/h (160 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| Total depressions |
28 |
| Total storms |
23 |
| Typhoons |
13 |
| Super typhoons |
4 |
| Total fatalities |
> 541 |
| Total damage |
Unknown |
Pacific typhoon seasons
1977, 1978, 1979, 1980, 1981 |
The 1979 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1979, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the international date line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1979 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical Storms formed in the entire west Pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions in this basin have the "W" suffix added to their number. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.
Storms
28 tropical depressions formed this year in the Western Pacific, of which 23 became tropical storms. 13 storms reached typhoon intensity, of which 4 reached super typhoon strength.

Typhoon Alice
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 31, 1978 – January 15, 1979 |
| Peak intensity |
175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min) 930 mbar (hPa) |
Very early on January 1 a tropical depression developed over the low latitudes of the open West Pacific. It tracked northwestward, reaching tropical storm strength that night and typhoon strength on the 5th. Alice turned to the west, and continued to intensify with generally favorable conditions to a peak of 130 mph winds on the 8th.[1] Cooler, drier air to the north caused Alice to weaken to a minimal typhoon, but as the typhoon turned to the northwest it briefly re-strengthened to a 115 mph typhoon on the 11th. Upper level winds, combined with the dry air, weakened Alice for good, causing it to dissipate on the 14th after stalling for three days. Alice caused extensive damage in the Marshall Islands, and the name was dropped from usage as new naming lists went into effect later in the year.
Typhoon Bess (Auring)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
March 19 – March 25 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min) 955 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Cecil (Bebeng)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
April 10 – April 20 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min) 965 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Dot (Katring)
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 9 – May 17 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 985 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 05W (Diding)
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 17 – May 24 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 992 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Ellis (Etang)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 29 – July 7 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min) 955 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Storm Faye (Gening)
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 1 – July 9 |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Depression 08W
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 23 – July 27 |
| Peak intensity |
35 km/h (25 mph) (1-min) 1005 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Hope (Ising)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 24 – August 8 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 900 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical depression formed southeast of Guam on July 24.[1] It headed to the west-northwest, but upper level shear from the TUTT caused the depression to dissipate on the 27th. It turned northward then westward, where it regenerated on the 28th. Intensification became more steady, with the depression reaching storm strength on the 28th and typhoon strength on the 29th. On the 31st, Hope reached a peak of 150 mph winds, but land interaction with Taiwan to the north weakened the storm. On August 2 95 mph Typhoon Hope hit southern China, only 10 miles east of Hong Kong. It weakened over the country while moving westward, but retained its satellite signature. Upon reaching the Bay of Bengal on the 7th, Hope restrengthened to a tropical storm, but moved over India and dissipated on the 8th. In Guangdong Province in China, the typhoon was responsible for around 100 deaths or missing people. Twelve people died along with 260 injured in Hong Kong. This was the strongest tropical cyclone to hit Hong Kong since Typhoon Rose in 1971.
Severe Tropical Storm Gordon (Herming)
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 25 – July 31 |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) 975 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Depression 11W (Luding)
| Tropical depression (PAGASA) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 2 – August 7 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 998 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Irving (Mameng)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 7 – August 18 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min) 955 mbar (hPa) |
The monsoon trough spawned a tropical depression on August 7 east of the Philippines. It tracked to the north then to the west. Steering currents weakened, causing the depression to loop to the north. It was able to strengthen there, reaching tropical storm status on the 11th and typhoon status on the 13th. Irving continued to the north, attaining a peak of 100 mph winds on the 15th.[1] Its broad, loose wind field prevented it from strengthening further, and Irving weakened as it continued northward. On the 17th, Irving hit southwest South Korea as a minimal typhoon, and merged with a frontal boundary over extreme eastern Russia on the 18th. Torrential rains led to 150 fatalities, with damage at $10–$20 million (1979 USD).
Super Typhoon Judy (Neneng)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 16 – August 26 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 910 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical disturbance organized into a tropical storm on August 15. It tracked to the northwest, becoming a tropical storm on the 17th. Judy rapidly intensified, reaching typhoon status on the 18th and a peak of 155 mph winds on the 20th.[1] The super typhoon began to weaken as it passed south of Okinawa, and neared the Chinese coast on the 23rd and 24th. Judy turned to the northeast, and brushed past South Korea as a tropical depression on the 26th, shortly before dissipating. Judy passed through Guam and other Pacific islands, but damage was reported light there. However, the storm brought heavy rain to Korea as a tropical depression, killing 111 and more damage to an area hit by Irving just weeks before.
Tropical Depression 14W
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 18 – August 20 |
| Peak intensity |
35 km/h (25 mph) (1-min) 1005 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Ken (Oniang)
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 30 – September 4 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Lola
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 1 – September 8 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min) 950 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Storm Mac (Pepang)
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 12 – September 24 |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) 985 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Nancy
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 17 – September 22 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 992 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Owen (Rosing)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 22 – October 1 |
| Peak intensity |
165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min) 945 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Pamela
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 23 – September 26 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Roger (Sisang)
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 2 – October 7 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 985 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Sarah (Trining-Uring)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 30 – October 15 |
| Peak intensity |
165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min) 930 mbar (hPa) |
The monsoon trough spawned a tropical depression in the eastern Vietnamese East Sea on September 30. It drifted eastward into Luzon, and looped to the southwest where it strengthened into a tropical storm on October 4.[1] Sarah, with weak steering currents, drifted to the south, becoming a typhoon on the 7th before hitting Palawan Island. The storm turned to the west, peaking at 130 mph winds on the 10th before the mid-level circulation became decoupled from the low-level circulation. Sarah weakened, and hit eastern Vietnam on the 14th as a 60 mph tropical storm. The storm brought heavy flooding and wind, causing massive crop damage and loss of life. Sarah then weakened to a low-pressure area on October 15, but its remnants continued to move east towards east of Manila, Philippines and curved again towards Vietnam and fully dissipated on October 23.
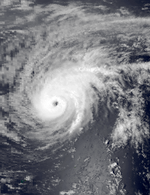
Super Typhoon Tip (Warling)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 4 – October 19 |
| Peak intensity |
260 km/h (160 mph) (10-min) 870 mbar (hPa) |
Main article:
Typhoon TipTyphoon Tip is considered to be the most intense and largest tropical cyclone ever recorded in the world.[1] The cyclone formed on October 5, and after moving into a very favorable environment for development, quickly strengthened into Super Typhoon Tip on the 11th. On the 12th, Super Typhoon Tip continued to intensify, with winds at 190 miles per hour and central pressure at 870 millibars, the lowest barometric pressure ever recorded from a tropical cyclone. Tip ultimately hit Japan, causing 68 deaths and moderate damage. It dissipated on October 19.
Super Typhoon Vera (Yayang)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 2 – November 7 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min) 915 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Storm Wayne (Ading)
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 7 – November 13 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Depression 26W
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 1 – December 2 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min) 1000 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Abby (Barang)
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 1 – December 14 |
| Peak intensity |
165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min) 950 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Ben (Krising)
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 20 – December 23 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 994 mbar (hPa) |
1979 storm names
Western North Pacific tropical cyclones were named by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. The first storm of 1979 was named Alice and the final one was named Ben. The name Alice was retired after this season and replaced by Andy, as Alice is a female name.
- Alice (7901)
- Bess (7902)
- Cecil (7903)
- Dot (7904)
- Ellis (7906)
- Faye (7907)
|
- Gordon (7909)
- Hope (7908)
- Irving (7910)
- Judy (7911)
- Ken (7912)
- Lola (7913)
|
- Mac (7914)
- Nancy (7915)
- Owen (7916)
- Pamela (7917)
- Roger (7918)
- Sarah (7919)
|
- Tip (7920)
- Vera (7921)
- Wayne (7922)
- Abby (7923)
- Ben (7924)
|
Philippines
The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) used its own naming scheme for tropical cyclones within its area of responsibility. Lists were recycled every four years. This was the list set for 1983.[2] This is the same list used for the 1975 season.
- Auring (7902)
- Bebeng (7903)
- Katring (7904)
- Diding (7905)
- Etang (7906)
|
- Gening (7907)
- Herming (7908)
- Ising (7909)
- Luding
- Mameng (7910)
|
- Neneng (7911)
- Oniang (7912)
- Pepang (7914)
- Rosing (7916)
- Sisang (7918)
|
|
- Barang (7923)
- Krising (7924)
-
Dadang (unused)
-
Erling (unused)
-
Goying (unused)
|
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1979 ATCR TABLE OF CONTENTS
- ↑ Michael Padua. "Old PAGASA Names". Retrieved 2007-04-14.
External links
| 1970–1979 Pacific typhoon seasons |
|---|
| |
|
|
|---|
| | | |
-
 Book Book
-
 Category Category
-
 Portal Portal
-
 WikiProject WikiProject
-
 Commons Commons
|
|