1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC, consisting of the Arab members of the OPEC plus Egypt, Syria and Tunisia) proclaimed an oil embargo. By the end of the embargo in March 1974,[1] the price of oil had risen from $3 per barrel to nearly $12. The oil crisis, or "shock", had many short-term and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy.[2] It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock."
Summary
The embargo was a response to American involvement in the 1973 Yom Kippur War. Six days after Egypt and Syria launched a surprise military campaign against Israel to regain territories lost in the June 1967 Six-Day War, the US supplied Israel with arms. In response to this, OAPEC announced an oil embargo against Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the US.[3]
The crisis had a major impact on international relations and created a rift within NATO. Some European nations and Japan sought to disassociate themselves from United States foreign policy in the Middle East. Arab oil producers linked any future policy changes to peace between the belligerents. To address this, the Nixon Administration began multilateral negotiations with the combatants. They arranged for Israel to pull back from the Sinai Peninsula and the Golan Heights. By January 18, 1974, US Secretary of State Henry Kissinger had negotiated an Israeli troop withdrawal from parts of the Sinai Peninsula. The promise of a negotiated settlement between Israel and Syria was enough to convince Arab oil producers to lift the embargo in March 1974.[1]
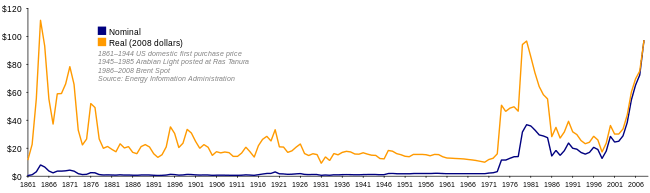
Independently, OAPEC members agreed to use their leverage over the world price-setting mechanism for oil to stabilize their incomes by raising world oil prices after the recent failure of negotiations with Western oil companies.
The embargo occurred at a time of rising petroleum consumption by industrialized countries and coincided with a sharp increase in oil imports by the world's largest oil consumer-the US. In the aftermath, targeted countries initiated a wide variety of policies to contain their future dependency.
The 1973 "oil price shock", with the accompanying 1973–74 stock market crash, were regarded as the first discrete event since the Great Depression to have a persistent economic effect.[4]
The embargo's success demonstrated Saudi Arabia's diplomatic and economic power. It was the largest oil exporter and a politically and religiously conservative kingdom. Thereafter, progressive Arab nationalism was swept aside by an Islamic revival. Throughout the Muslim world, in the coming years, the greatly increased wealth and international prestige of Saudi Arabia would help the puritanical, conservative "Wahhabi" interpretation of Islam it favored ("petro-Islam") to "attain a preeminent position of strength in the global expression of Islam."[5]
Background
US oil production decline
In 1970, US oil production started to decline, exacerbating the embargo's impact.[6] Following this, Nixon named James Akins as US Ambassador to Saudi Arabia to audit US production capacity. The confidential results were alarming—no spare capacity was available and production could only decrease.
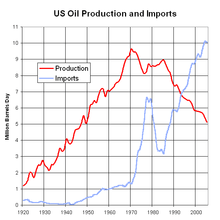
The oil embargo was not effective in limiting supply shortages, according to Akins.[7]
OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), which then comprised 12 countries, including Iran, seven Arab countries (Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates), plus Venezuela, Indonesia, Nigeria and Ecuador, was formed at a Baghdad conference on September 14, 1960. OPEC was organized to resist pressure by the "Seven Sisters" (seven large, Western oil companies) to reduce oil prices.
At first, OPEC operated as an informal bargaining unit for resource-rich third-world countries. OPEC confined its activities to gaining a larger share of the profits generated by oil companies and greater control over member production levels. In the early 1970s it began to exert economic and political strength; the oil companies and importing nations suddenly faced a unified exporter bloc.
End of the Bretton Woods accord
On August 15, 1971, the United States unilaterally pulled out of the Bretton Woods Accord. The US abandoned the Gold Exchange Standard whereby the value of the dollar had been pegged to the price of gold and all other currencies were pegged to the dollar, whose value was left to "float" (rise and fall according to market demand).[8] Shortly thereafter, Britain followed, floating the pound sterling. The other industrialized nations followed suit with their respective currencies. Anticipating that currency values would fluctuate unpredictably for a time, the industrialized nations increased their reserves (by expanding their money supplies) in amounts far greater than before. The result was a depreciation of the dollar and other industrialized nations' currencies. Because oil was priced in dollars, oil producers' real income decreased. In September 1971, OPEC issued a joint communiqué stating that, from then on, they would price oil in terms of a fixed amount of gold.[9]
This contributed to the "Oil Shock". After 1971, OPEC was slow to readjust prices to reflect this depreciation. From 1947 to 1967, the dollar price of oil had risen by less than two percent per year. Until the oil shock, the price had also remained fairly stable versus other currencies and commodities. OPEC ministers had not developed institutional mechanisms to update prices in sync with changing market conditions, so their real incomes lagged. The substantial price increases of 1973–74 largely returned their prices and corresponding incomes to Bretton Woods levels in terms of commodities such as gold.[10]
Yom Kippur War
On October 6, 1973, Syria and Egypt, with support from other Arab nations, launched a surprise attack on Israeli positions in the Israeli-occupied territories on Judaism's holiest day.[11] This renewal of hostilities in the Arab–Israeli conflict released the underlying economic pressure on oil prices. At the time, Iran was the world's second-largest oil exporter and a close US ally." In 1973, the Shah of Iran told the New York Times, "Of course [the world price of oil] is going to rise....Certainly! And how...; You [Western nations] increased the price of wheat you sell us by 300%, and the same for sugar and cement...; You buy our crude oil and sell it back to us, refined as petrochemicals, at a hundred times the price you've paid to us...; It's only fair that, from now on, you should pay more for oil. Let's say ten times more."[12]
On October 12, 1973, US president Richard Nixon authorized Operation Nickel Grass, a strategic airlift to deliver weapons and supplies to Israel, after the Soviet Union began sending arms to Syria and Egypt.
Embargo
In response to American aid to Israel, on October 16, 1973, OPEC raised the posted price of oil by 70%, to $5.11 a barrel.[13] The following day, oil ministers agreed to the embargo, a cut in production by five percent from September's output and to continue to cut production in five percent increments until their economic and political objectives were met.[14] On October 19, Nixon requested Congress to appropriate $2.2 billion in emergency aid to Israel, including $1.5 billion in outright grants. George Lenczowski notes, "Military supplies did not exhaust Nixon's eagerness to prevent Israel's collapse...This [$2.2 billion] decision triggered a collective OPEC response".[15] Libya immediately announced it would embargo oil shipments to the United States.[16] Saudi Arabia and the other Arab oil-producing states joined the embargo on October 20, 1973.[17] At their Kuwait meeting, OPEC proclaimed the embargo that curbed exports to various countries and blocked all oil deliveries to the US as a "principal hostile country".[15]
Price increases were also imposed. Since short-term oil demand is inelastic, immediate demand falls little when the price rises. Thus, market prices rose from $3 per barrel to $12 per barrel to reduce demand to the new, lower level of supply.[18] The world financial system, which was already under pressure from the Bretton Woods breakdown, was set on a path of recessions and inflation that persisted until the early 1980s, with oil prices continuing to rise until 1986.
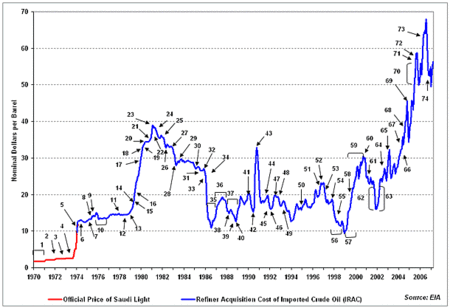
Over the long term, the oil embargo changed the nature of policy in the West towards increased exploration, alternative energy research, energy conservation and more restrictive monetary policy to better fight inflation.[19]
Chronology
- January 1973—The 1973–74 stock market crash commences as a result of inflation pressure and the collapsing monetary system.
- August 23, 1973—In preparation for the Yom Kippur War, Saudi king Faisal and Egyptian president Anwar Sadat meet in Riyadh and secretly negotiate an accord whereby the Arabs will use the "oil weapon" as part of the military conflict.[20]
- October 6—Egypt and Syria attack Israeli-occupied lands in the Sinai Peninsula and Golan Heights on Yom Kippur, starting the 1973 Arab–Israeli War.
- Night of October 8—Israel goes on full nuclear alert. Kissinger is notified on the morning of October 9. United States begins to resupply Israel.
- October 8–10—OPEC negotiations with major oil companies to revise the 1971 Tehran price agreement fail.
- October 12— The United States initiates Operation Nickel Grass, a strategic airlift to provide replacement weapons and supplies to Israel. This followed similar Soviet moves to supply the Arab side.
- October 16 – Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Abu Dhabi, Kuwait and Qatar raise posted prices by 17% to $3.65 per barrel and announce production cuts.[21]
- October 17—OAPEC oil ministers agree to use oil to influence the West's support of Israel. They recommended an embargo against non-complying states and mandated export cuts.
- October 19—Nixon requests Congress to appropriate $2.2 billion in emergency aid to Israel, which triggers a collective Arab response.[15] Libya immediately proclaims an embargo on oil exports to the US.[16] Saudi Arabia and other Arab oil-producing states follow the next day.[16]
- October 26—The Yom Kippur War ends in defeat for the attackers.
- November 5—Arab producers announce a 25% output cut. A further 5% cut is threatened.
- November 23—The Arab embargo is extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa.
- November 27—Nixon signs the Emergency Petroleum Allocation Act authorizing price, production, allocation and marketing controls.
- December 9—Arab oil ministers agree to another five percent production cut for non-friendly countries in January 1974.
- December 25—Arab oil ministers cancel the January output cut. Saudi oil minister Ahmed Zaki Yamani promises a ten percent OPEC production rise.
- January 7–9, 1974—OPEC decides to freeze prices until April 1.
- January 18—Israel signs a withdrawal agreement to pull back to the east side of the Suez Canal.
- February 11—Kissinger unveils the Project Independence plan for US energy independence.
- February 12–14—Progress in Arab-Israeli disengagement triggers discussion of oil strategy among the heads of state of Algeria, Egypt, Syria and Saudi Arabia.
- March 5—Israel withdraws the last of its troops from the west side of the Suez Canal.
- March 17—Arab oil ministers, with the exception of Libya, announce the end of the US embargo.
- May 31—Diplomacy by Kissinger produces a disengagement agreement on the Syrian front.
- December 1974—The 1973–74 stock market crash ends.
Effects
Immediate economic effects

The effects of the embargo were immediate. OPEC forced oil companies to increase payments drastically. The price of oil quadrupled by 1974 to nearly US$12 per barrel (75 US$/m3).[2]
This price increase had a dramatic effect on oil exporting nations, for the countries of the Middle East who had long been dominated by the industrial powers seen to have taken control of a vital commodity. The oil-exporting nations began to accumulate vast wealth.
Some of the income was dispensed in the form of aid to other underdeveloped nations whose economies had been caught between higher oil prices and lower prices for their own export commodities, amid shrinking Western demand. Much went for arms purchases that exacerbated political tensions, particularly in the Middle East.
Control of oil became known as the "oil weapon". It came in the form of an embargo and production cutbacks from the Arab states. The weapon was aimed at the United States, Great Britain, Canada, Japan and the Netherlands. These target governments perceived that the intent was to push them towards a more pro-Arab position.[22] Production was eventually cut by 25%.[23] However, the affected countries did not undertake dramatic policy changes.[24]
In the United States, scholars argue that there already existed a negotiated settlement based on equality between both parties prior to 1973. The possibility that the Middle East could become another superpower confrontation with the USSR was of more concern to the US than oil. Further, interest groups and government agencies more worried about energy were no match for Kissinger's dominance.[25] In the US production, distribution and price disruptions "have been held responsible for recessions, periods of excessive inflation, reduced productivity, and lower economic growth"[26]
The embargo had a negative influence on the US economy by causing immediate demands to address the threats to U.S. energy security.[27] On an international level, the price increases changed competitive positions in many industries, such as automobiles. Macroeconomic problems consisted of both inflationary and deflationary impacts.[28] The embargo left oil companies searching for new ways to increase oil supplies, even in rugged terrain such as the Arctic. Finding oil and developing new fields usually required five to ten years before significant production.[29]

OPEC-member states raised the prospect of nationalization of oil company holdings. Most notably, Saudi Arabia nationalized Aramco in 1980 under the leadership of Saudi oil minister Ahmed Zaki Yamani. As other OPEC nations followed suit, the cartel's income soared. Saudi Arabia undertook a series of ambitious five-year development plans. The biggest began in 1980, funded at $250 billion. Other cartel members also undertook major economic development programs.
US retail price gas prices rose from a national average of 38.5 cents in May 1973 to 55.1 cents in June 1974. State governments requested citizens not to put up Christmas lights. Oregon banned Christmas and commercial lighting altogether.[18] Politicians called for a national gas rationing program.[30] Nixon requested gasoline stations to voluntarily not sell gasoline on Saturday nights or Sundays; 90% of owners complied, which produced long queues.[18]
The embargo was not uniform across Europe. Of the nine members of the European Economic Community (EEC), the Netherlands faced a complete embargo, the UK and France received almost uninterrupted supplies (having refused to allow America to use their airfields and embargoed arms and supplies to both the Arabs and the Israelis), while the other six faced partial cutbacks. The UK had traditionally been an ally of Israel, and Harold Wilson's government supported the Israelis during the Six-Day War. His successor, Ted Heath, reversed this policy in 1970, calling for Israel to withdraw to its pre-1967 borders.
The EEC was unable to achieve a common policy during the first month of the War. It issued a statement on November 6, after the embargo and price rises had begun. It was widely viewed as pro-Arab supporting the Franco-British line on the war. OPEC duly lifted its embargo from all EEC members. The price rises had a much greater impact in Europe than the embargo.
The UK also faced strikes by coal miners and railroad workers over the winter of 1973–74, which became a major factor in the change of government.[31] Heath asked the British to heat only one room in their houses over the winter.[32] The UK, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and Norway banned flying, driving and boating on Sundays. Sweden rationed gasoline and heating oil. The Netherlands imposed prison sentences for those who used more than their ration of electricity.[18]
A few months later, the crisis eased. The embargo was lifted in March 1974 after negotiations at the Washington Oil Summit, but the effects lingered throughout the 1970s. The dollar price of energy increased again the following year, amid the weakening competitive position of the dollar in world markets.
Price controls and rationing
United States
Price controls exacerbated the crisis in the US. The system limited the price of "old oil" (that which had already been discovered) while allowing newly discovered oil to be sold at a higher price to encourage investment. Predictably, old oil was withdrawn from the market, creating greater scarcity. The rule also discouraged development of alternative energies.[30] The rule had been intended to promote oil exploration.[33] Scarcity was addressed by rationing (as in many countries). Motorists faced long lines at gas stations beginning in summer 1972 and increasing by summer 1973.[30]
In 1973, Nixon named William E. Simon as the first Administrator of the Federal Energy Office, a short-term organization created to coordinate the response to the embargo.[34] Simon allocated states the same amount of domestic oil for 1974 that each had consumed in 1972, which worked for states whose populations were not increasing.[35] In other states, lines at gasoline stations were common. The American Automobile Association reported that in the last week of February 1974, 20% of American gasoline stations had no fuel.[35]

Odd-even rationing allowed vehicles with license plates having an odd number as the last digit (or a vanity license plate) allowed to buy gas on odd-numbered days of the month, while others could buy only on even-numbered days.[36]
In some states, a three-color flag system was used to denote gasoline availability at service stations—green for unrationed availability, yellow for restricted/rationed sales and red for out of stock.[37]

Rationing led to violent incidents, when truck drivers chose to strike for two days in December 1973 over the limited supplies Simon had allocated for their industry. In Pennsylvania and Ohio, non-striking truckers were shot at by striking truckers, and in Arkansas, trucks of non-strikers were attacked with bombs.[35]
America had controlled the price of natural gas since the 1950s. With the inflation of the 1970s, the price was too low to encourage the search for new reserves.[38] America's natural gas reserves dwindled from 237 trillion in 1974 to 203 trillion in 1978. The price controls were not changed despite president Gerald Ford's repeated requests to Congress.[38]
United States
To help reduce consumption, in 1974 a national maximum speed limit of 55 mph (about 88 km/h) was imposed through the Emergency Highway Energy Conservation Act. Development of the Strategic Petroleum Reserve began in 1975, and in 1977 the cabinet-level Department of Energy was created, followed by the National Energy Act of 1978.
Year-round daylight saving time was implemented from January 6, 1974, to February 23, 1975. The move spawned significant criticism because it forced many children to travel to school before sunrise. The prior rules were restored in 1976.

The crisis prompted a call to conserve energy, most notably a campaign by the Advertising Council using the tagline "Don't Be Fuelish".[39] Many newspapers carried advertisements featuring cut-outs that could be attached to light switches, reading "Last Out, Lights Out: Don't Be Fuelish."
By 1980, domestic luxury cars with a 130-inch (3.3 m) wheelbase and gross weights averaging 4,500 pounds (2,041 kg) were no longer made. The automakers had begun phasing out the traditional front engine/rear wheel drive layout in compact cars in favor of lighter front engine/front wheel drive designs. A higher percentage of cars offered more efficient 4-cylinder engines.
Though not regulated by the new legislation, auto racing groups voluntarily began conserving. In 1974, the 24 Hours of Daytona was cancelled and NASCAR reduced all race distances by 10%; the 12 Hours of Sebring race was cancelled.
In 1976, Congress created the Weatherization Assistance Program to help low-income homeowners and renters reduce their demand for heating and cooling through better insulation.
Alternative energy
The energy crisis led to greater interest in renewable energy and spurred research in solar power and wind power.[40] It also led to greater pressure to exploit North American oil sources and increased the West's dependence on coal and nuclear power.
Interest in mass transit increased.
In Australia, heating oil lost favor as an appropriate winter heating fuel. Many oil-fired room heaters that were popular from the late-1950s to the early 1970s were considered outdated. Kits that let the heaters burn natural gas or propane were introduced.
The Brazilian government implemented its "Proálcool" (pro-alcohol) project in 1975 that mixed ethanol with gasoline for automotive fuel.[41]
Israel was one of the few countries unaffected by the embargo, since it could extract sufficient oil from the Sinai. But to supplement Israel's over-taxed power grid, Harry Zvi Tabor, the father of Israel's solar industry, developed the prototype for a solar water heater now used in over 90% of Israeli homes.[42]
Macroeconomy
The crisis was a major factor in shifting Japan's economy away from oil-intensive industries. Investment shifted to industries such as electronics. Japanese auto makers also benefited from the crisis. Increased fuel costs allowed their small, fuel-efficient models to gain market share from the "gas-guzzling" American competition. This triggered a drop in American auto sales that lasted into the 1980s.
Western central banks decided to sharply cut interest rates to encourage growth, deciding that inflation was a secondary concern. Although this was the orthodox macroeconomic prescription at the time, the resulting stagflation surprised economists and central bankers. The policy is now considered by some to have deepened and lengthened the adverse effects of the embargo. Recent research claims that in the period after 1985 the economy became more resilient to energy price increases.[43]
The price shock created large current account deficits in oil-importing economies. A petrodollar recycling mechanism was created, through which OPEC surplus funds were channeled through the capital markets to the West to finance the current account deficits. The functioning of this mechanism required the relaxation of capital controls in oil-importing economies.It marked the beginning of an exponential growth of Western capital markets.[44]
Many in the public remain suspicious of oil companies, believing they profiteered, or even colluded with OPEC. In 1974, seven of the fifteen top Fortune 500 companies were oil companies, falling to four in 2014.[45]
International relations
United States
America's Cold War policies suffered a major blow from the embargo. They had focused on China and the Soviet Union, but the latent challenge to US hegemony coming from the third world became evident.
NATO
Western Europe began switching from pro-Israel to more pro-Arab policies.[46][47][48] This change strained the Western alliance. The US, which imported only 12% of its oil from the Middle East (compared with 80% for the Europeans and over 90% for Japan), remained staunchly committed to Israel. The percentage of U.S. oil which comes from the nations bordering the Persian Gulf remained steady over the decades, with a figure of a little more than 10% in 2008.[49]
With the embargo in place, many developed countries altered their policies regarding the Arab-Israeli conflict. These included the UK, which refused to allow the United States to use British bases and Cyprus to airlift resupplies to Israel along with the rest of the members of the European Community.[50]
Canada shifted towards a more pro-Arab position after displeasure was expressed towards Canada's mostly neutral position. "On the other hand, after the embargo the Canadian government moved quickly indeed toward the Arab position, despite its low dependence on Middle Eastern oil".[51]
Japan
Although lacking historical connections to the Middle East, Japan was the country most dependent on Arab oil. 71% of its imported oil came from the Middle East in 1970. On November 7, 1973, the Saudi and Kuwaiti governments declared Japan a "nonfriendly" country to encourage it to change its noninvolvement policy. It received a 5% production cut in December, causing a panic. On November 22, Japan issued a statement "asserting that Israel should withdraw from all of the 1967 territories, advocating Palestinian self-determination, and threatening to reconsider its policy toward Israel if Israel refused to accept these preconditions".[51] By December 25, Japan was considered an Arab-friendly state.
Nonaligned nations
The oil embargo was announced roughly one month after a right-wing military coup in Chile led by General Augusto Pinochet toppled socialist president Salvador Allende on September 11, 1973. The response of the Nixon administration was to propose doubling arms sales. As a consequence, an opposing Latin American bloc was organized and financed in part by Venezuelan oil revenues, which quadrupled between 1970 and 1975.
A year after the start of the embargo, the UN's nonaligned bloc passed a resolution demanding the creation of a "New International Economic Order" under which nations within the global South would receive a greater share of benefits derived from the exploitation of southern resources and greater control over their self-development.
Arab states
Prior to the embargo, the geo-political competition between the Soviet Union and the United States, in combination with low oil prices that hindered the necessity and feasibility of alternative energy sources, presented the Arab States with financial security, moderate economic growth, and disproportionate international bargaining power.[52]
The oil shock disrupted the status quo relationships between Arab countries and the US and USSR. At the time, Egypt, Syria and Iraq were allied with the USSR, while Saudi Arabia, Turkey and Iran (plus Israel) aligned with the US. Vacillations in alignment often resulted in greater support from the respective superpowers.
When Anwar Sadat became president of Egypt in 1970, he dismissed Soviet specialists in Egypt and reoriented towards the US. Concerns over economic domination from increased Soviet oil production turned into fears of military aggression after the 1979 Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, turning the Persian Gulf states towards the US for security guarantees against Soviet military action.
The USSR's invasion of Afghanistan was only one sign of insecurity in the region, also marked by increased American weapons sales, technology, and outright military presence. Saudi Arabia and Iran became increasingly dependent on American security assurances to manage both external and internal threats, including increased military competition between them over increased oil revenues. Both states were competing for preeminence in the Persian Gulf and using increased revenues to fund expanded militaries. By 1979, Saudi arms purchases from the US exceeded five times Israel's.[53] Another motive for the large scale purchase of arms from the US by Saudi Arabia was the failure of the Shah during January 1979 to maintain control of Iran, a non-Arabic but largely Shiite Muslim nation, which fell to a theocratic Islamist government under the Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini in the wake of the 1979 Iranian Revolution. Saudi Arabia, on the other hand, is an Arab, largely Sunni Muslim nation headed by a near absolutist monarchy. In the wake of the Iranian revolution the Saudis were forced to deal with the prospect of internal destabilization via the radicalism of Islamism, a reality which would quickly be revealed in the seizure of the Grand Mosque in Mecca by Wahhabi extremists during November 1979 and a Shiite revolt in the oil rich Al-Hasa region of Saudi Arabia in December of the same year.[54] In November 2010, Wikileaks leaked confidential diplomatic cables pertaining to the United States and its allies which revealed that the late Saudi King Abdullah urged the United States to attack Iran in order to destroy its potential nuclear weapons program, describing Iran as "a snake whose head should be cut off without any procrastination."[55]
Automobile industry
The oil crisis sent a signal to the auto industry globally, which changed many aspects of production and usage for decades to come.
Western Europe
After World War II, most West European countries taxed motor fuel to limit imports, and as a result most cars made in Europe were smaller and economical than their American counterparts. By the late 1960s increasing incomes supported rising car sizes.
The oil crisis pushed West European car buyers away from larger, less economical cars.[56] The most notable result of this transition was the rise in popularity of compact hatchbacks. The only notable small hatchbacks built in Western Europe before the oil crisis were the Peugeot 104, Renault 5 and Fiat 127. By the end of the decade, the market had expanded with the introduction of the Ford Fiesta, Opel Kadett (sold as the Vauxhall Astra in Great Britain), Chrysler Sunbeam and Citroën Visa.
Buyers looking for larger cars were increasingly drawn to medium-sized hatchbacks. Virtually unknown in Europe in 1973, by the end of the decade they were gradually replacing saloons as the mainstay of this sector. Between 1973 and 1980, medium-sized hatchbacks were launched across Europe: the Chrysler/Simca Horizon, Fiat Ritmo (Strada in the UK), Ford Escort MK3, Renault 14, Volvo 340 / 360, Opel Kadett, and Volkswagen Golf.
These cars were considerably more economical than the traditional saloons they were replacing, and attracted buyers who traditionally bought larger vehicles. Some 15 years after the oil crisis, hatchbacks dominated most European small and medium car markets, and had gained a substantial share of the large family car market.
United States
Before the energy crisis, large, heavy, and powerful cars were popular. By 1971, the standard engine in a Chevrolet Caprice was a 400-cubic inch (6.5 liter) V8. The wheelbase of this car was 121.5 inches (3,090 mm), and Motor Trend's 1972 road test of the similar Chevrolet Impala achieved no more than 15 highway miles per gallon.
The crisis reduced the demand for large cars.[38] Japanese imports, primarily the Toyota Corona, the Toyota Corolla, the Datsun B210, the Datsun 510, the Honda Civic, the Mitsubishi Galant (a captive import from Chrysler sold as the Dodge Colt), the Subaru DL, and later the Honda Accord all had four cylinder engines that were more fuel efficient than the typical American V8 and six cylinder engines. Honda and Subaru imports became mass market leaders with front-wheel drive—which became the de facto standard.
From Europe, the Volkswagen Beetle, the Volkswagen Fastback, the Renault 8, the Renault LeCar, and the Fiat Brava were successful. Detroit responded with the Ford Pinto, the Ford Maverick, the Chevrolet Vega, the Chevrolet Nova, the Plymouth Valiant and the Plymouth Volaré. American Motors sold its homegrown Gremlin, Hornet and Pacer models.
Some buyers lamented the small size of the first Japanese compacts, and both Toyota and Nissan (then known as Datsun) introduced larger cars such as the Toyota Corona Mark II, the Toyota Cressida, the Mazda 616 and Datsun 810, which added passenger space and amenities such as air conditioning, power steering, AM-FM radios, and even power windows and central locking without increasing the price of the vehicle. A decade after the 1973 oil crisis, Honda, Toyota and Nissan, affected by the 1981 voluntary export restraints that limited the imports of their mass market automobiles, opened US assembly plants and luxury divisions (Acura, Lexus and Infiniti, respectively.
Compact trucks were introduced, such as the Toyota Hilux and the Datsun Truck, followed by the Mazda Truck (sold as the Ford Courier), and the Isuzu-built Chevrolet LUV. Mitsubishi rebranded its Forte as the Dodge D-50 a few years after the oil crisis. Mazda, Mitsubishi and Isuzu had joint partnerships with Ford, Chrysler, and GM, respectively. Later the American makers introduced their domestic replacements (Ford Ranger, Dodge Dakota and the Chevrolet S10/GMC S-15, ending their captive import policy.
An increase in imported cars into North America forced General Motors, Ford and Chrysler) to introduce smaller and fuel-efficient models for domestic sales. The Dodge Omni / Plymouth Horizon from Chrysler, the Ford Fiesta and the Chevrolet Chevette all had four-cylinder engines and room for at least four passengers by the late 1970s. By 1985, the average American vehicle moved 17.4 miles per gallon, compared to 13.5 in 1970. The improvements stayed even though the price of a barrel of oil remained constant at $12 from 1974 to 1979.[38] Sales of large sedans for most makes (except Chrysler products) recovered within two model years of the 1973 crisis. The Cadillac DeVille, Buick Electra, Oldsmobile 98, Lincoln Continental, Mercury Marquis, and various other luxury oriented sedans became popular again in the mid-1970s. The only full-size models that did not recover were lower price models such as the Chevrolet Bel Air, and Ford Galaxie 500. Slightly smaller, mid-size models such as the Oldsmobile Cutlass, Chevrolet Monte Carlo, Ford Thunderbird and various other models sold well.
Economical imports succeeded alongside heavy, expensive vehicles. In 1976 Toyota sold 346,920 cars (average weight around 2,100 lbs), while Cadillac sold 309,139 cars (average weight around 5,000 lbs).
Federal safety standards, such as NHTSA Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 215 (pertaining to safety bumpers), and compacts like the 1974 Mustang I were a prelude to the DOT "downsize" revision of vehicle categories.[57] By 1977, GM's full-sized cars reflected the crisis.[58] By 1979, virtually all "full-size" American cars had shrunk, featuring smaller engines and smaller outside dimensions. Chrysler ended production of their full-sized luxury sedans at the end of the 1981 model year, moving instead to a full front-wheel drive lineup for 1982 (except for the M-body Dodge Diplomat/Plymouth Gran Fury and Chrysler New Yorker Fifth Avenue sedans).
Decline of OPEC
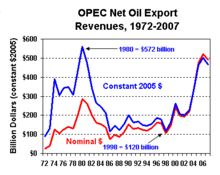
OPEC soon lost its preeminent position, and in 1981, its production was surpassed by that of other countries. Additionally, its own member nations were divided. Saudi Arabia, trying to recover market share, increased production, pushing prices down, shrinking or eliminating profits for high-cost producers. The world price, which had peaked during the 1979 energy crisis, at more than $80 per barrel, decreased during the early 1980s to $38 per barrel (239 US$/m3). In real prices, oil briefly fell back to pre-1973 levels. This "sale" price was a windfall for oil-consuming nations—both developing and developed.
The embargo opened new avenues for energy exploration including Alaska, the North Sea, the Caspian Sea, and Caucasus.[60] Exploration in the Caspian Basin and Siberia became profitable. Cooperation changed into a far more adversarial relationship as the USSR increased its production. By 1980 the Soviet Union had become the world's largest producer.[61][62]
Part of the decline in prices and economic and geopolitical power of OPEC came from the move to alternate energy sources. OPEC had relied on price inelasticity[63] to maintain high consumption but had underestimated the extent to which conservation and other sources of supply would eventually reduce demand. Electricity generation from nuclear power and natural gas, home heating from natural gas and ethanol-blended gasoline all reduced the demand for oil.
The drop in prices presented a serious problem for oil-producing countries in northern Europe and the Persian Gulf. Heavily populated, impoverished countries, whose economies were largely dependent on oil—including Mexico, Nigeria, Algeria, and Libya—did not prepare for a market reversal that left them in sometimes desperate situations.
When reduced demand and increased production glutted the world market in the mid-1980s, oil prices plummeted and the cartel lost its unity. Mexico, Nigeria, and Venezuela, whose economies had expanded in the 1970s, faced near-bankruptcy, and even Saudi Arabian economic power was significantly weakened. The divisions within OPEC made concerted action more difficult. As of 2015, OPEC had never approached its earlier dominance.
See also
- 1967 Oil Embargo
- 1970s energy crisis
- 1990 oil price shock
- 2000s energy crisis
- Hubbert peak theory
- Supply shock
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "OPEC Oil Embargo 1973–1974". U.S. Department of State, Office of the Historian. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "The price of oil – in context". CBC News. Archived from the original on June 9, 2007. Retrieved May 29, 2007.
- ↑ "CHE | Responding to Crisis". Envhist.wisc.edu. April 26, 2010. Retrieved August 7, 2012.
- ↑ Perron, P.; University, Princeton; Program, Econometric Research (1988). "The Great Crash, the Oil Price Shock and the Unit Root Hypothesis" (PDF). Econometric Research Program, Princeton University Princeton, New Jersey. Retrieved February 3, 2012.
- ↑ Kepel, Gilles (2006). "Building Petro-Islam on the Ruins of Arab Nationalism". Jihad: The Trail of Political Islam. I.B. Tauris. p. 51.
had been amply demonstrated during the oil embargo against the United States, following the Arab-Israeli war of 1973. This show of international power, along with the nation's astronomical increase in wealth, allowed Saudi Arabia's puritanical, conservative Wahhabite faction to attain a preeminent position of strength in the global expression of Islam. Saudi Arabia's impact on Muslims throughout the world was less visible than that of Khomeini's Iran, but the effect was deeper and more enduring. The kingdom seized the initiative from progressive nationalism, which had dominated the 1960s, it reorganized the religious landscape by promoting those associations and ulemas who followed its lead, and then, by injecting substantial amounts of money into Islamic interests of all sorts, it won over many more converts. Above all, the Saudis raised a new standard -- the virtuous Islamic civilization -- as a foil for the corrupting influence of the West, while still managing to remain a staunch ally of the United Sates and the West against the Soviet bloc.
- ↑ "The hidden face of oil" (in French).
- ↑ "The hidden face of oil" (in French).
during the interview at 24:10 in the documentary La face cachée du pétrole part 2
- ↑ Masouros 2013, pp. 55–57.
- ↑ Taghizadegan, Rahim; Stöferle, Ronald; Stöferle, Mark (13 Jun 2014). Österreichische Schule für Anleger: Austrian Investing zwischen Inflation und Deflation (in German). FinanzBuch Verlag. p. 87. ISBN 9783862485949.
Unsere Mitgliedslander werden alle notwendigen Schritte unternehmen und/oder Verhandlungen mit den Olfirmen fuhren, am Mittel und Wege zu finden, um nachteiligen Auswirkungen auf das Realeinkommen der Mitgliedslander, die sich aus den internationalen monetaren Entwicklungen per August 15, 1971 ergeben, entgegenzuwirken.
- ↑ Hammes, David. and Douglas Wills. "Black Gold: The End of Bretton Woods and the Oil-Price Shocks of the 1970s," The Independent Review, v. IX, n. 4, Spring 2005. pp. 501–511.
- ↑ Energy Insights: News: Oil price – speculation and international politics at play Archived July 23, 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Smith, William. D. "Price Quadruples for Iranian Crude Oil at Auction", New York Times December 12, 1973.
- ↑ Yergin 2008, p. 587.
- ↑ Yergin 2008, p. 589.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Lenczowski 1990, p. 130.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 "Significant Events in U.S.-Libyan Relations". 2001-2009.state.gov. Retrieved August 7, 2012.
- ↑ Yergin 2008, p. 590.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 Frum 2000, p. 318.
- ↑ http://www.history.com/topics/energy-crisis
- ↑ Yergin 2008, p. 597.
- ↑ Editorial Note: this conflicts somewhat with the 70% price increase to $5.11, noted by a cited reference, in the paragraph above.
- ↑ Licklider 1988, p. 205-226.
- ↑ Paust, Jordan J. & Blaustein, Albert P. (1974). "The Arab Oil Weapon—A Threat to International Peace". The American Journal of International Law (The American Journal of International Law, Vol. 68, No. 3) 68 (3): 410–439 [p. 411]. doi:10.2307/2200513. JSTOR 2200513.
- ↑ Licklider 1988, p. 217.
- ↑ Licklider 1988.
- ↑ Barsky, Robert B. & Kilian, Lutz (2004). "Oil and the Macroeconomy since the 1970s". The Journal of Economic Perspectives 18 (4): 115–134 [p. 115]. doi:10.1257/0895330042632708.
- ↑ Ikenberry 1986, p. 107.
- ↑ Ikenberry 1986, p. 109.
- ↑ Hirsch, Robert L. (1987). "Impending United States Energy Crisis". Science 235 (4795): 1467–1473 [p. 1467]. doi:10.1126/science.235.4795.1467. PMID 17775008.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 Frum 2000, p. 313.
- ↑ Slavin, Barbara; Freudenheim, Milt; Rhoden, William C. (January 24, 1982). "The World; British Miners Settle for Less". New York Times. Retrieved April 20, 2010.
- ↑ Frum 2000, p. 319.
- ↑ "Oil Price Controls: A Counterproductive Effort" (PDF). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Review. November 1975. Retrieved June 7, 2010.
- ↑ Frum 2000, p. 312.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 Frum 2000, p. 320.
- ↑ "Gas Fever: Happiness Is a Full Tank". Time Magazine. February 18, 1974. Retrieved June 7, 2010.
- ↑ "Spotty Local Starts". Time Magazine. February 25, 1974. Retrieved June 7, 2010.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 38.2 38.3 Frum 2000, p. 321.
- ↑ Ad Council – Don't be Fuelish. January 1975. Retrieved August 23, 2009.
- ↑ The 1970s Energy Crisis
- ↑ Milton Briquet Bastos (June 20, 2007). "Brazil’s Ethanol Program – An Insider’s View". Energy Tribune. Retrieved August 14, 2008.
- ↑ At the Zenith of Solar Energy, Neal Sandler,BusinessWeek, March 26, 2008.
- ↑ Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, How Resilient Is the Modern Economy to Energy Price Shocks?, 2006
- ↑ Masouros 2013, pp. 60–62.
- ↑ "2014 Fortune 500". April 2014. Retrieved January 2015.
- ↑ America, Russia, and the Cold War, 1945–1975, p. 280, Walter LaFeber, Wiley, 1975
- ↑ Far Eastern Economic Review, v.84, Apr–Jun 1974, p. 8, Review Publishing, 1974
- ↑ The New Tensions in Japan, Martin Collick, Richard Storry, p. 16, Institute for the Study of Conflict, 1974
- ↑ Afshin Molavi, "Obama, Gulf Oil and the Myth of America's Addiction", New America Foundation, The National (United Arab Emirates), January 21, 2009, . Retrieved August 16, 2009. Archived August 21, 2009.
- ↑ Licklider 1988, p. 216.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 Licklider 1988, p. 214.
- ↑ Ritchie Ovendale, The Origins of the Arab-Israeli Wars (New York: Pearson Longman, 2004), p. 184-191 and 197
- ↑ George C. Wilson "U.S. Military Sales To Saudis 5 Times Total For Israelis", Washington Post October 11, 1979 pg. A24
- ↑ Daniel Yergin, The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money, and Power (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1991). p.609.
- ↑ Wikileaks and Iran.(http://articles.chicagotribune.com/2010-11-29/news/ct-edit-wiki-20101129_1_iran-s-amb-nuclear-program-diplomats). Chicago Tribune. November 29, 2010.
- ↑ 10 Ways the 1973 Oil Embargo Changed the Industry
- ↑ "Designing Cars of the 1970s: Freedoms Lost". Collectible Automobile. February 2008.
- ↑ "GM's full-sized cars". Collectible Automobile. March 2008.
- ↑ "EIA – 1000 Independence Avenue, SW, Washington, DC 20585". Eia.doe.gov. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ↑ Yergin 2008, pp. 619-625.
- ↑ "World: Saudis Edge U.S. on Oil" in Washington Post January 3, 1980 pg. D2
- ↑ Dusko Doder "Soviet Production of Gas, Oil Set Records Over 6 Months" in Washington Post August 14, 1980 pg. A24
- ↑ Anderson, Patrick L. (November 13, 1997). "Approx. PED of Various Products (U.S.)". Mackinac.org. Archived from the original on July 21, 2011. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
Sources
- Frum, David (2000). How We Got Here: The '70s. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-04195-4.
- Ikenberry, G. John (1986). "The Irony of State Strength: Comparative Responses to the Oil Shocks in the 1970s". International Organization 40 (1): 105–137. doi:10.1017/S0020818300004495.
- Lenczowski, George (1990). American Presidents and the Middle East. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-0972-7.
- Licklider, Roy (1988). "The Power of Oil: The Arab Oil Weapon and the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Canada, Japan, and the United States". International Studies Quarterly (International Studies Quarterly) 32 (2): 205–226. doi:10.2307/2600627. JSTOR 2600627.
- Masouros, Pavlos E. (2013). Corporate Law and Economic Stagnation: How Shareholder Value and Short-termism Contribute to the Decline of the Western Economies. Eleven International Publishing.
- Yergin, Daniel (2008). The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money, and Power. New York: Simon and Schuster.
- Ammann, Daniel (2009). The King of Oil: The Secret Lives of Marc Rich. New York: St. Martin‘s Press. ISBN 978-0-312-57074-3.
- Alan S. Blinder, Economic Policy and the Great Stagflation (New York: Academic Press, 1979)
- Otto Eckstein, The Great Recession (Amsterdam: North-Holland, 1979)
- Mark E. Rupert and David P. Rapkin, "The Erosion of U.S. Leadership Capabilities"
- Paul M. Johnson and William R. Thompson, eds., Rhythms in Politics and Economics (New York: Praeger, 1985)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1973 oil crisis. |
- Saudi dove in the oil slick – Sheikh Ahmed Zaki Yamani, former oil minister of Saudi Arabia gives his personal account of the 1973 energy crisis.
- EIA presentation: 25th Anniversary of the 1973 Oil Embargo
- 35 Years After the Arab Oil Embargo
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||