1972–73 South Pacific cyclone season
1972–73 South Pacific cyclone season
| |
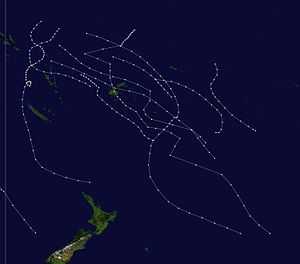
| Season summary map |
| First system formed |
October 19, 1972 |
| Last system dissipated |
April 6, 1973 |
| Strongest storm |
Bebe – 945 hPa (mbar), 160 km/h (100 mph) (11-minute sustained) |
| Total disturbances |
9 |
| Tropical cyclones |
9 |
| Severe tropical cyclones |
2 |
| Total fatalities |
Unknown |
| Total damage |
Unknown |
South Pacific tropical cyclone seasons
1970–71, 1971–72, 1972–73, 1973–74, 1974–75 |
| Related articles |
|
|
Storms
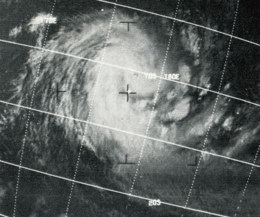
Severe Tropical Cyclone Bebe
Main article:
Cyclone Bebe
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 19 – October 29 |
| Peak intensity |
155 km/h (100 mph) (10-min) 945 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Bebe was a pre-season storm that impacted the Gilbert, Ellice, and Fiji island groups.[1] First spotted on October 20, the system intensified and grew in size through October 22. Its course began along a south-southwest trajectory before recurving near the 14th parallel south, which resulted in a south-southeast motion through the western portion of the Fiji island group.[1] It became the first cyclone to impact Fiji since 1952. On October 24, winds of 150 knots (280 km/h) or more were reported on Rotuma and Viti Levu. Cyclone Bebe passed through Funafuti on Saturday 21st and Sunday 22 October 1972. At about 4 p.m. on the 21st, sea water was bubbling through the coral on the airfield with the water reaching a height of about 4 –5 feet high. The Ellice Islands Colony's ship Moanaraoi was in the lagoon and survived, however 3 tuna boats were wrecked. Waves broke over the atoll. Five people died, two adults and a 3 month old child were swept away by waves, and two sailors from the tuna boats were drowned.[2] Cyclone Bebe knocked down 90% of the houses and trees. The storm surge created a wall of coral rubble along the ocean side of Funafuti and Funafala that was about ten to twelve miles long, and about ten to twenty feet thick at the bottom.[2] The cyclone submerged Funafuti and sources of drinking water were contaminated as a result of the system's storm surge and fresh water flooding. After passing by the archipelago, Bebe transitioned into an extratropical cyclone, with the remnants last noted on October 28.[1] A total of 28 people died and thousands were left homeless. Damages totaled $20 million (1972 USD).[3][4]
Tropical Cyclone Collette
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 2 – November 3 |
| Peak intensity |
65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Diana
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 6 – December 18 |
| Peak intensity |
135 km/h (85 mph) (10-min) 965 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Felicity
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
January 14 – January 18 |
| Peak intensity |
70 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Elenore
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
January 31 – February 7 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Glenda
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
January 31 – February 1 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Kirsty
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
March 1 – March 2 |
| Peak intensity |
105 km/h (65 mph) (10-min) ≥ 990 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Henrietta
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
February 28 – March 7 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Cyclone Juliette
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
April 2 – April 6 |
| Peak intensity |
80 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Bureau of Meteorology (1975) Tropical Cyclones in the Northern Australian Regions 1971-1972 Australian Government Publishing Service
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Resture, Jane (5 October 2009). Hurricane Bebe 1972. Tuvalu and the Hurricanes: ‘The Hurricane in Funafuti, Tuvalu’ by Pasefika Falani (Pacific Frank).
- ↑ Elwyn E. Wilson (January 1973). "October Hurricane Clobbers Fiji". Mariners Weather Log (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) 17 (1): 19–20.
- ↑ RSMC Nadi – Tropical Cyclone Centre, TCWC Brisbane, TCWC Wellington (May 22, 2009). "TCWC Wellington Best Track Data 1967–2006". Fiji Meteorological Service, Meteorological Service of New Zealand Limited, Australian Bureau of Meteorology. United States: International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship.
External links