1969 Atlantic hurricane season
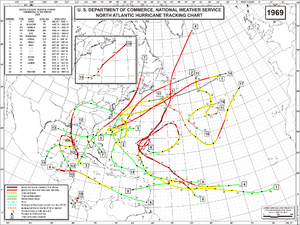 | |
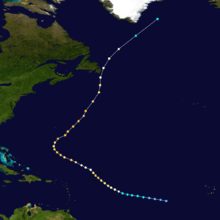
| Season summary map | |
| First system formed | June 7, 1969 |
|---|---|
| Last system dissipated | November 25, 1969 |
| Strongest storm | Camille – 900 mbar (hPa) (26.59 inHg), 175 mph (280 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| Total storms | 18 |
| Hurricanes | 12 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 5 |
| Total fatalities | 364 |
| Total damage | $1.7 billion (1969 USD) |
| Atlantic hurricane seasons 1967, 1968, 1969, 1970, 1971 | |
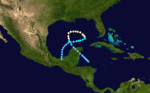
The 1969 Atlantic hurricane season had the highest number of systems reached hurricane status – twelve – in a single Atlantic hurricane season, until that record was surpassed in 2005. The hurricane season officially began on June 1, and lasted until November 30. It was the busiest Atlantic hurricane season since 1933. Activity began with a series of five tropical depressions, the first of which developed on May 29. The third system in that series, Tropical Depression Seven, caused extensive flooding in Cuba and Jamaica in early June. The final in the series formed on July 25, the same day that Tropical Storm Anna developed. Neither the former or latter caused significant impact on land. Later in the season, Tropical Depression Twenty-Nine caused severe local flooding in the Florida Panhandle and southwestern Georgia in September. Hurricane Blanche was a small and short-lived tropical cyclones in mid-August that resulted in minimal effects.
The most significant storm of the season was Hurricane Camille, a Category 5 hurricane that devastated the Gulf Coast of the United States by strong winds and storm surge heights, especially Mississippi and Louisiana. Later in its duration, the storm caused severe flooding Virginia and West Virginia. Camille alone was responsible for 261 deaths and $1.4 billion (1969 USD) in damage. It was the costliest United States hurricane at the time, until Hurricane Agnes in 1972. In early September, Hurricane Francelia caused deadly floods in Central America, with 100 people killed in Guatemala. Hurricane Inga had the third longest duration of an Atlantic tropical cyclone. The last storm, Hurricane Martha, was the only known tropical cyclone to make landfall in Panama. Martha caused minor flooding in the former and Costa Rica. Debbie, Gerda, Holly, Ten, Eleven, One, Kara, Laurie, Sixteen, and Seventeen had minimal impact on land. Overall, the systems of the season collectively caused 364 deaths and $1.7 billion in losses.
Season summary

The 1969 season once held the record for the most hurricanes (12 in all) to form than in any other year in the Atlantic basin. This record was broken in the 2005 season by Hurricane Wilma, with a season total of 15 hurricanes. Meteorologists were just beginning to understand the traits of tropical and subtropical storms; as a result, a large number of the eighteen cyclones that formed in 1969 went unnamed. In addition, many of the storms were dubbed hurricanes after the fact.
Storms
Tropical Depression Seven
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | June 7 – June 9 | ||
| Peak intensity | 30 mph (45 km/h) (1-min) 1006 mbar (hPa) | ||
Tropical Depression Seven developed near the Yucatan Peninsula on June 7. It moved north, reaching western Cuba by the following day.[1] As the depression moved towards Florida, small-craft warnings were issued for the southern coast.[2] The depression made landfall in Florida on June 9 and dissipated shortly thereafter. As a result of 2 to 3 in (51 to 76 mm) rain in Cuba, Radio Havana warned of a flash flood[2] and later reported that three rivers were overflowing in Camagüey. Flooding also forced 1,801 people from their homes.[3] Sustained winds of 15 to 25 mph (24 to 40 km/h) and gusts up to 40 mph (64 km/h) were observed on the island.[4] Impact from the depression in Florida is unknown.[5]
Damage was catastrophic in Jamaica with landslides, flooding, broken communication lines, cancellation of its railway service and evacuation of hundreds of people from their homes. The Jamaica Railway Corporation's trains were disrupted by landslides blocking the tracks from Spanish Town to Port Antonio and floodwaters inundating a bridge in Gregory Park. A train bound for Kingston was disrupted by the flooded bridge, as was a diesel tram, isolating both trains at Richmond. Furthermore, the former train did not reach its destination due to landslides. The Jamaica Telephone Company reported troubles due to waterlogged telephone lines. Schools and colleges in Kingston suspended classes and motorists in the area had difficulty traveling due to flooded roads. Correspondents from The Gleaner reported heavy rains, which inundated roads, washed away livestock and destroyed crops. On June 9, the Church Welfare Organization of the West Indies Junior Seventh Day Adventists set out food, money and blankets the victims.[6]
Tropical Storm Anna
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | July 25 – August 3 | ||
| Peak intensity | 65 mph (100 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 1002 mbar (hPa) | ||
On July 23, a tropical wave emerged into the Atlantic from the west coast of Africa.[7] By 0600 UTC on July 25, the system developed into Tropical Depression Twelve. Initially, the depression strengthened slowly while moving west-northwestward. Eventually, it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Anna on July 27. Intensification continued during the next 66 hours. On July 29, Anna peaked with maximum sustained winds of 70 mph (110 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 1,002 mbar (29.6 inHg). Thereafter, the storm began to weaken and moved in a more northwesterly direction. Late on July 31, Anna was downgraded to a tropical depression, while situated north of the Lesser Antilles.[5][8]
Anna briefly re-strengthened into a tropical storm late on August 1. The storm re-curved northeastward on July 2 and remained offshore of the East Coast of the United States. Ana once again reached tropical storm status by early on July 3. Further intensification occurred, with the storm reaching winds of 65 mph (100 km/h) later that day. However, Anna transitioned into an extratropical cyclone after merging with an extratropical low pressure area at 0000 UTC on August 4, while centered near Sable Island. The remnants continued rapidly east-northeastward across the Atlantic until becoming unidentifiable on August 5.[5][8]
Hurricane Blanche
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | August 11 – August 12 | ||
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min) 996 mbar (hPa) | ||
A tropical wave was initially tracked about 1,300 mi (2,100 km) east of the Lesser Antilles on August 6.[7] The system curved west-northward on August 6 and eventually moved around the western periphery of the Bermuda high. Late on August 10, a circulation developed and by 0000 UTC on August 11, the system became a tropical depression while located about 530 mi (850 km) east of Wabasso Beach, Florida. Under the influence of a trough, it headed rapidly north to north-northeastward. After ships reported winds up to 46 mph (74 km/h), the depression was upgraded to Tropical Storm Blanche later on August 11.[5]
Significant intensification then occurred. Later on August 11, Navy reconnaissance reports indicated that Blanche reached hurricane intensity. After winds peaked at 85 mph (140 km/h), the strong southwesterly current which Blanche was embedded in caused the storm to accelerate northeastward. On August 12, the storm began losing tropical characteristics near Sable Island; namely, the wind field was becoming asymmetrical. At Sable Island, a weather station reported sustained winds of 51 mph (82 km/h) and gusts up to 69 mph (111 km/h). While passing to the south of Newfoundland, Blanche was absorbed by a frontal zone at 0000 UTC on August 13.[5]
Hurricane Camille
| Category 5 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | August 14 – August 22 | ||
| Peak intensity | 175 mph (280 km/h) (1-min) 900 mbar (hPa) | ||
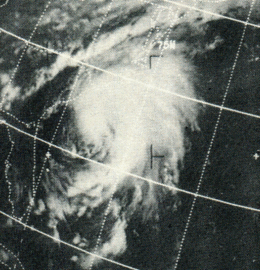
A tropical disturbance moved off the west coast of Africa on August 5, and developed into Tropical Storm Camille near Grand Cayman on August 14.[5][9] The storm strengthened quickly and was a Category 3 hurricane when it struck near the western tip of Cuba on August 15.[9] The storm damaged 100 homes on Isla de la Juventud,[10] while 20,000 residents were left homeless on the mainland;[11] Five fatalities were also reported.[12] Early on August 16, Camille emerged into the Gulf of Mexico. Between August 16 and August 17, the storm rapidly deepened, with a minimum barometric pressure of 905 mbar (26.7 inHg). Later on August 17, Camille peaked as a 175 mph (280 km/h) Category 5. It likely maintained this intensity until landfall near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi early on August 18;[9] Camille was one of only three tropical cyclones to strike the United States as a Category 5, the others were the 1935 Labor Day hurricane and Hurricane Andrew in 1992.[13] Mississippi bore the brunt of Hurricane Camille. A combination of strong winds and large storm surges caused adverse impact in the state. In Mississippi alone, 3,881 dwellings were destroyed and 41,848 were damaged. About 406 trailers were destroyed and an additional 325 suffered major losses. An estimated 645 farm buildings were destroyed and another 2,002 received major damage. In addition, 569 small businesses were impacted.[5]
In Mississippi's neighboring states of Alabama and Louisiana, 1,781 homes were destroyed and 6,000 others were inflicted losses. About 676 trailers were demolished and 296 were severely impacted. Additionally, 124 small businesses were either destroyed or incurred major damage.[5] Camille rapidly weakened after landfall on August 18 and was only a tropical depression about 24 hours later. However, the storm maintained intensity as it recurved to the east over the Ohio River Valley.[9] It dropped heavy rainfall while approaching the Atlantic Ocean, especially in Virginia.[5] Up to 27 in (690 mm) fell in west central Nelson County.[14] In Nelson County alone, 133 bridges washed out, while in some places entire communities were under water. Rivers crested at record heights, causing severe flooding. In the state of Virginia and West Virginia combined, an estimated 349 homes were destroyed and 2,587 received damage to some degree. Eighty-three trailers were demolished and 71 others received major losses. Reportedly, 730 farm buildings were destroyed and 535 were inflicted minor damage. Ninety-six small businesses were also severely damage or destroyed.[5] Along its path, rainfall was recorded in several other states, including Arkansas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Maryland, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, and Tennessee.[15] After reaching the Atlantic, Camille re-strengthened into a 70 mph (115 km/h) tropical storm,[9] but was absorbed by a cold front south of Newfoundland on August 22. With losses estimated at $1.4 billion, Camille was considered the costliest hurricane in United States history at the time. Additionally, there were 256 deaths in the United States.[5]
Hurricane Debbie
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | August 14 – August 25 | ||
| Peak intensity | 120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min) 951 mbar (hPa) | ||
On August 14, a tropical wave developed into a tropical depression while located about midway between the Lesser Antilles and the coast of Africa. The following day, the depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Debbie. By late on August 16, Debbie became a Category 1 hurricane.[5] Moving northwestward, it intensified further to a Category 3 hurricane with winds of 115 mph (185 km/h) on August 18. However, the storm then began oscillating between a Category 1 and a Category 3 hurricane for the next few days,[9] possibly due to being seeded by silver iodide as part of Project Stormfury.[5] On August 20, Debbie attained its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 120 mph (195 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 951 mbar (28.1 inHg).[9]
The storm curved northeastward as Hurricane Camille moved offshore the East Coast of the United States and briefly weakened to a Category 2 hurricane on August 21, before re-strengthened into a Category 3 hurricane hours later. Debbie accelerated and fell to Category 2 intensity by midday on August 23. The storm curved northward and weakened to a Category 1 hurricane on the following day, shortly before passing just offshore Newfoundland. Debbie turned northeastward and deteriorated to a tropical storm on August 25. Several hours later, the hurricane dissipated about 225 mi (360 km) east-northeast of Cape Farewell, Greenland.[9] In Newfoundland, wind gusts up to 85 mph (140 km/h) were observed in St. John's, while rainfall up to 0.98 in (25 mm) was recorded along the Avalon and Bonavista peninsulas.[16]
Tropical Storm Eve
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | August 25 – August 27 | ||
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) 996 mbar (hPa) | ||
In the wake of Hurricane Camille, a quasi-stationary front moved across the Southern United States and became situated over North Florida. A cut-off low pressure area developed along the system and acquired a low-level circulation.[5] By 0000 UTC on August 25, the system was classified as a tropical depression while located about 100 mi (160 km) east of Jacksonville, Florida.[9] Due to cold air in the region, the depression strengthened slowly while tracking nearly due east. Late on August 25, it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Eve.[5]
On August 26, the National Hurricane Center noted although conditions would prevent rapid deepening, further intensification was possible.[17] The storm threatened the Mid-Atlantic states and Bermuda,[18] but remained offshore and caused no impacts in either region. Eve strengthened slightly on August 26, reaching maximum sustained winds of 60 mph (95 km/h). Although the storm weakened later that day, Eve reached its minimum barometric pressure of 996 mbar (29.4 inHg). Early on August 2, Eve was downgraded to a tropical depression.[9] It began to succumb to the effects of cold air, which entrained the circulation of the storm.[5] At 0000 UTC on August 28,[9] Eve degenerated into a trough of low pressure while located about 70 mi (110 km) west-northwest of Bermuda.[5]
Hurricane Francelia
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | August 29 – September 4 | ||
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) | ||
A tropical wave developed into a tropical depression near the Windward Islands on August 29.[9][5] Initially, the depression slowly strengthened while moving west-northwestward and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Francelia until more than 24 hours later. While located north of Honduras, it curved west-southwestward and was upgraded to a hurricane on September 1. The storm briefly became a Category 3 hurricane on September 2, peaking with winds of 115 mph (185 km/h).[5] Late on September 3, Francelia made landfall near Punta Gorda, Belize with winds of 100 mph (155 km/h). The storm quickly weakened inland, and less than 24 hours later, it dissipated over northern Guatemala.[9] However, the remnants of Francelia later contributed to the development of Hurricane Glenda in the eastern Pacific Ocean.[5]
During its early stages, Francelia brought gusty winds and light rainfall to several islands in the Caribbean Sea.[19] While remaining nearly stationary offshore Central America, heavy precipitation fell in some countries, especially Guatemala where severe flooding killed 269 people and caused $15 million in damage. Throughout the country, approximately 10,200 people were left homeless. In neighboring Honduras, the hurricane caused damage in the northern portions of the country, with the offshore Bay Islands Department being particularly hard hit. There, the storm damaged or destroyed the majority of two towns. In El Salvador, flooding isolated towns for several days and caused crop damage.[20] Coastal areas of Belize lost electricity and telephone service, and high winds resulted in extensive damage to banana crops.[21] A number of rivers in the region flooded, including the Belize River, which reached 36 ft (11 m) above normal.[5] Francelia ranked as the deadliest tropical cyclone in Guatemala, until Hurricane Mitch in 1998.[22] Overall damage was estimated at $35.6 million, and there were 271 deaths.[20]
Hurricane Gerda
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | September 6 – September 10 | ||
| Peak intensity | 125 mph (205 km/h) (1-min) 979 mbar (hPa) | ||
A tropical wave located over the central Bahamas developed into a tropical depression on September 6.[5] The depression moved northwestward and initially remained disorganized. By early on September 7, the depression made landfall near West Palm Beach, Florida.[9] Impact in the state was minimal, limited mostly to light rainfall. Later on September 7, the depression reemerged into the Atlantic Ocean just south of Cape Canaveral. It began to strengthen on the following day and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Gerda at 0600 UTC. By late on September 8, Gerda intensified into a hurricane. The storm deepened significantly further, peaking with winds of 125 mph (205 km/h) on September 9. Early on September 10, Gerda weakened slightly while approaching New England and Atlantic Canada.[9]
It made landfall near Eastport, Maine on September 10 and was one of the strongest tropical cyclones to strike the state.[9] Despite landfall as a Category 2 hurricane, the strongest sustained wind speed recorded was 60 mph (95 km/h) in Washington County, Maine. Twenty-four hour rainfall amounts exceeding 4 in (100 mm) were observed in some areas of New England,[23] with a precipitation peak of 5.67 in (144 mm) in Wellfleet, Massachusetts.[24] Due to the winds and rainfall, portions of Maine, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire reported power outages and localized flooding.[23] By 0600 UTC on September 10, Gerda became extratropical over southeastern Quebec.[9] In Atlantic Canada, winds left many without electricity in New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, and left about $3.5 million in losses to apple crops.[25]
Hurricane Holly
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | September 14 – September 21 | ||
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min) 984 mbar (hPa) | ||
A tropical wave emerged into the Atlantic Ocean from the west coast of Africa on September 8.[5] Moving westward to west-northwestward, it developed into a tropical depression at 1200 UTC on September 14, while located about 1,250 mi (2,315 km) southeast of Puerto Rico,[9] based on Hurricane Hunter observations of an organized circulation.[26] It quickly organized and was soon upgraded to Tropical Storm Holly.[27] Continuing northwestward, it steadily intensified, and the Hurricane Hunters reported that Holly attained hurricane status on September 16,[28] with peak winds of 85 mph (140 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 984 mbar (29.1 inHg).[9]
On September 16, Holly weakened slightly while turning westward toward the Lesser Antilles.[29] Due to the lack of good upper-level outflow, as well as unfavorable water, Holly quickly weakened to tropical storm status on September 18, as confirmed by the Hurricane Hunters.[30] By the next day, it weakened to tropical depression status and later moved through the Lesser Antilles. Holly dissipated on September 21 in the Caribbean Sea, while situated between the Los Roques archipelago of Venezuela and Puerto Rico.[9]
Tropical Depression Twenty-Nine
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | September 19 – September 21 | ||
| Peak intensity | 30 mph (45 km/h) (1-min) 1008 mbar (hPa) | ||
Ship reports on September 19 indicated the presence of low pressure area in the Gulf of Mexico, centered about 300 mi (480 km) west-northwest of Key West, Florida.[31] It is estimated that a tropical depression developed at 1200 UTC on that day. The depression headed north-northwestward and did not strengthen.[9] By early on September 21, the depression made landfall between Panama City, Florida and Port St. Joe.[31] It degenerated into a remnant low pressure area only a few hours later.[9] A high-pressure ridge blocked the system's movement, moving it to the east. By September 23, the system became a low pressure trough. Upper-level wind shear moved the circulation to the east-northeast and moved into the Atlantic Ocean the next day.[5]
Rainfall in peaked at 23.4 in (590 mm) in Havana, with and exceeding 15 in (380 mm) in most of the central Panhandle.[31] Many bridges and roads were washed out or inundated by water, including portions of U.S. Route 98 and State Road 20 between Tallahassee and Panama City.[32] In addition, a tornado spawned by the depression destroyed a trailer, damaged 30 homes, and toppled ballpark bleachers, fences, lights, and electrical poles. Damage in Florida reached almost $3.78 million, including $1.65 million to crops and $2.135 million to property. In southwest Georgia, precipitation totals exceeding 5 in (130 mm) were common, while rainfall peaked at 14 in (360 mm) in southern Decatur County. Severe local flooding ensued, causing damage to property and crops, mostly to peanuts that were not threshed.[23] Up to 7 in (180 mm) of rainfall fell in Alabama, while precipitation totals reached 3 in (76 mm) in Tennessee, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Virginia.[31]
Hurricane Inga
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | September 20 – October 15 | ||
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 964 mbar (hPa) | ||
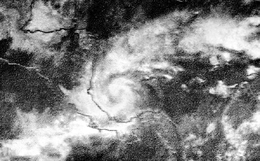
A tropical disturbance developed into a tropical depression on September 20. By the following day, it strengthened into Tropical Storm Inga while centered about 930 mi (1,500 km) east-southeast of San Juan, Puerto Rico. At the time, the storm was moving westward at 14 mph (23 km/h). However, by September 23, the storm weakened to a tropical depression. The depression continued west-northwestward, passing north of the Leeward Islands, before drifting northwestward. Inga became a tropical storm again on September 29. It continued to intensify, and achieved hurricane status on September 30, while curving northeastward. The storm then turned towards the south, and ultimately completed a cyclonic loop as it bent back westward. Late on October 3, Inga turned to the northwest.[9]
Early on October 5, the hurricane produced wind gusts up to 80 mph (130 km/h) on Bermuda, though minimal impact occurred other than power outages.[33] Thereafter, Inga curved northeastward and continued deepen. Later on October 5, it peaked as a Category 3 with maximum sustained winds of 115 mph (185 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 964 mbar (28.5 inHg).[9] While moving into an environment of colder sea surface temperatures,[34] the storm began to weaken. As cold air became entrained into its circulation, the storm began to lose tropical characteristics.[35] Inga briefly re-strengthened while beginning to drift generally eastward. However, storm turned southward and began to weaken, deteriorating to a tropical storm on October 10.[9] Heading westward, Inga was downgraded to a tropical depression,[36] before dissipating fully on October 15,[9] while located about 290 mi (470 km) from where it initially attained hurricane status.[5]
Subtropical Storm One
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | September 29 – October 1 | ||
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) 996 mbar (hPa) | ||
An upper-level low pressure area in the southeastern Gulf of Mexico spawned a subtropical depression at 1200 UTC on September 29.[37][9] Operationally, it was classified as Tropical Depression Thirty-Two.[37] Six hours later, the strengthened into a subtropical storm. Early on the following day, the storm peaked with maximum sustained winds of 60 mph (95 km/h).[9] It maintained that intensity for about 24 hours, before cool air and wind shear began weakening the storm early on October 1.[37] Shortly thereafter, the storm weakened back to a subtropical depression, a few hours prior to landfall near Fort Walton Beach, Florida. The subtropical depression rapidly dissipated inland.[9]
Rainfall was relatively light and the heaviest amounts were displaced far east of the track, with precipitation peaking at 6.74 inches (171 mm) in Saint Augustine, Florida.[37] Closer to the location of landfall, rainfall reached nearly 4 inches (100 mm) in Pensacola. Several waterspouts were reported in the Panama City area,[38] while a tornado in Carabelle and unroofed a home in the St. James community.[39] United States Coast Guard planes searched for three people in a light aircraft that went missing as it traveled from DeFuniak Springs to Sebring.[38] The storm brought rainfall to several others states, reaching as far north as Maine.[37]
Tropical Storm Jenny
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | October 1 – October 6 | ||
| Peak intensity | 65 mph (100 km/h) (1-min) 998 mbar (hPa) | ||
Tropical Storm Jenny formed from the same cutoff low that formed Subtropical Storm One. Jenny began as a tropical depression in the northwest Caribbean Sea, and after moving across Cuba, became a Tropical storm just before its landfall between Fort Myers and Naples, Florida on October 2, bringing heavy rains. Jenny made it to the western Atlantic as a tropical depression, but increased ridging forced the storm over the already soaked Florida peninsula. It was unable to strengthen further, and Jenny dissipated on October 6 south of Louisiana.[5] Rainfall peaked at 6.61 inches in Deland, FL causing flooding. It also had a minor impact on Cuba and the Gulf coast. Damage was significant from a system like this one, $95 million (1969 USD) $120 million (2014 USD).
Hurricane Kara
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | October 7 – October 18 | ||
| Peak intensity | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 978 mbar (hPa) | ||
A cold core trough of low pressure over the western Atlantic Ocean warmed on the eastern end, becoming a tropical depression on October 7. The trough brought it northeastward, strengthening it to a tropical storm on October 9. An upper level low formed to Kara's west, and when the two merged on October 11, their motions became erratic. At this time it was not very tropical, but as it moved southward towards warm waters, it became more tropical, and became a hurricane on the October 15. Upper level westerlies forced it northeastward, and after reaching a peak of 105 mph (165 km/h), Kara became extratropical on October 19.[5]
Hurricane Laurie
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | October 17 – October 27 | ||
| Peak intensity | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) | ||
A low pressure area developed into a tropical depression while located about 75 mi (120 km). Although conditions were favorable for rapid deepening, the depression failed to do so possibly because it was not vertically stacked and struck the Yucatan Peninsula late on October 18. After emerging into the Gulf of Mexico on the following day, the system strengthened into Tropical Storm Laurie. Later on October 19, Laurie curved northward and continued intensifying. At 12:00 UTC on October 20, the storm became a hurricane. It then curved eastward over the central Gulf of Mexico and continued to deepen, peaking with sustained winds of 105 mph (165 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 973 mbar (28.7 inHg) early the next day. Thereafter, drier air began weakening Laurie on October 22. Laurie curved southeastward and then southward, allowing it to remain well offshore the Gulf Coast of the United States. Early on October 23, the cyclone weakened to a tropical storm while curving west-southwestward. Late the following day, Laurie deteriorated into a tropical depression. After moving southwestward and then southward, the storm made landfall near Paraíso, Tabasco, Mexico, early on October 27. Laurie promptly dissipated.[5]
Hurricane Martha
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Duration | November 21 – November 25 | ||
| Peak intensity | 90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min) 979 mbar (hPa) | ||
Tropical Storm Martha developed in the southwestern Caribbean Sea on November 21. Initially, the storm developed with sustained winds of 50 mph (85 km/h), skipping tropical depression status. It remained stationary and quickly intensified into a hurricane. Martha attained maximum sustained winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) on November 22. Subsequently, Martha weakened and drifted southward. On November 24, Martha made landfall in Veraguas Province, Panama, as a strong tropical storm.[9] Martha was the only tropical cyclone on record to make landfall in Panama.[5][40] The system weakened to a tropical depression and dissipated over land on November 25.[9]
Because the storm weakened prior to landfall, strong winds were not expected or reported in the impacted countries.[41] In Panama, more than 13 inches (330 mm) of precipitation may have fallen in some areas. Agricultural land was flooded in Almirante, Bocas del Toro and streets became inundated in low-lying areas of Puerto Armuelles, Chiriquí.[42] The storm also brought significant rains to Costa Rica. Flooding and mudslides isolated most of the capital city of San José.[5] Numerous streets were inundated in Golfito.[42] Damage in Costa Rica reached $30 million and 5 deaths were reported.[5]
Other storms
In addition to the 20 other tropical cyclones of the season, there were three minor tropical depressions. The first tropical depression (numbered five), developed on May 29 about 85 mi (137 km) southeast of Cutler Bay, Florida. The depression tracked northeastward, and passed through the Bahamas on the Abaco Islands later that day. After crossing the Bahamas, the depression continued northeastward, and eventually dissipated 430 mi (690 km) southwest of Bermuda on May 30. No impact was reported in the Bahamas.[8] Also on May 29, Tropical Depression Six developed while centered 38 mi (61 km) south-southwest of San Andrés Island, Colombia. The depression headed west-northwestward toward the coast of Nicaragua, however, it quickly veered away to the northeast. For the rest of its duration, the depression mainly headed north or north-northeastward across the Caribbean Sea. On June 1, the day that the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season officially began, Tropical Depression Six made landfall on the Zapata Peninsula in Cuba. The depression dissipated early on June 2. No impact was reported in Cuba or Nicaragua.[8]
Between June 7 and June 9, the notable Tropical Depression Seven existed. At 0000 UTC on June 12, Tropical Depression Eight formed about 55 miles (89 km) east of Cozumel, Quintana Roo. It moved west-northwestward without strengthening and made landfall between Playa del Carmen and Puerto Morelos, Quitana Roo, later that day with winds of 30 mph (45 km/h). The depression moved slowly across the Yucatán Peninsula until emerging into the Gulf of Mexico along the north coast of Yucatán on June 14. No intensification occurred in the Gulf of Mexico occurred, and by 0000 UTC on June 15, the depression dissipated while located about 50 miles (80 km) north-northeast of Progreso, Yucatán.[8] A tropical wave situated about 400 miles (640 km) east of Trinidad developed into Tropical Depression Thirteen on July 25.[43] The depression moved northwestward toward the Lesser Antilles and later that day crossed Barbados with winds of 35 mph (55 km/h). It continued to the northwest and may have struck Martinique on June 26. At 0000 UTC on the following day, the depression dissipated about 30 miles (48 km) west-southwest of Basseterre, Guadeloupe.[8]

In addition to the tropical depressions, four additional unnamed storms existed during the season. A subtropical depression formed offshore North Carolina on September 21. It reached subtropical storm strength that day. A few days later, it reached hurricane strength while moving to the northeast. The storm dissipated on September 26 while located about 200 mi (320 km) south of Newfoundland. Another storm developed from a subtropical depression southwest of the Azores on September 24. After drifting west-southwest, it moved westward and strengthened into a subtropical storm on September 25, and later a tropical storm. The cyclone reached its 70 mph (110 km/h) peak on September 27 while moving northward. On September 29, it dissipated east of Newfoundland. A subtropical depression formed west-southwest of the Azores on October 28. Moving northwestward, it reached tropical storm status on October 29 and soon peaked with winds of 70 mph (110 km/h). The storm became extratropical to the west of the Azores on October 31. A large extratropical storm over the North Atlantic formed a subtropical storm on October 31 south of Newfoundland. It moved southeast, gaining tropical characteristics and strength on the way. It reached hurricane strength on November 4, peaking as a minimal Category 1 storm while approaching the Azores, but weakened prior to passing through the islands. The system dissipated on November 7.[9]
Storm names
The following names were used for named storms that formed in the Atlantic basin in 1969. Storms were named Blanche, Camille, Eve, Francelia, Holly, Kara, Laurie and Martha for the first time in 1969. Names that were not assigned are marked in gray. At some point between June 1 and August 14, 1969, the name Carol (originally the C name on this year's list) was replaced with Camille. After the season, the name Camille was retired.[44][45]
|
See also
- 1969 Pacific hurricane season
- List of Atlantic hurricanes
- List of Atlantic hurricane seasons
References
- ↑ Frank, Neil (April 1970). "Atlantic Tropical Systems of 1969" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved February 1, 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Tropical Depression Heading For Florida". St. Petersburg Times. June 9, 1969. Retrieved December 8, 2012.
- ↑ "Flood Rout Cubans From Homes on Island". Fort Scott Tribune. Associated Press. June 9, 1969. Retrieved December 8, 2012.
- ↑ "'Depression' Strengthens". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. Associated Press. June 9, 1969. Retrieved December 8, 2012.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 5.14 5.15 5.16 5.17 5.18 5.19 5.20 5.21 5.22 5.23 5.24 5.25 5.26 5.27 5.28 5.29 5.30 Arnold, Sugg (April 1970). "The Atlantic hurricane season of 1969" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 January 2011. Retrieved February 1, 2011.
- ↑ "Spawned by a Tropical Depression In the Caribbean...". The Gleaner. 1969.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Richard M. DeAngelis (January 1970). "North Atlantic Tropical Cyclones, 1969". Mariners Weather Log (Environmental Science Services Agency) 14 (1): 2.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 David Roth (February 14, 2011). "Extended Best Track Database for CLIQR program". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved August 12, 2011.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 9.8 9.9 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 9.15 9.16 9.17 9.18 9.19 9.20 9.21 9.22 9.23 9.24 9.25 9.26 9.27 9.28 9.29 9.30 9.31 National Hurricane Center; Hurricane Research Division (March 2, 2015). "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved April 23, 2015.
- ↑ "Cuba Faces Big Problem From Storm". The Progress-Index. Associated Press. August 17, 1969.
- ↑ "Florida Braces for Big Blow". The Kingston Gleaner. Associated Press. August 16, 1969.
- ↑ Roger A. Pielke Jr. et al. (August 2003). Hurricane Vulnerability in Latin America and The Caribbean: Normalized Damage and Loss Potentials (PDF). National Hazards Review (Report). Retrieved February 24, 2013.
- ↑ Eric S. Blake, Jerry D. Jarrell, B. Max Mayfield, and Edward N. Rappaport (July 25, 2005). The Most Intense Hurricanes in the United States 1851-2004 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 17, 2014.
- ↑ Roth, David M; Hydrometeorological Prediction Center (November 16, 2012). "Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Point Maxima". Tropical Cyclone Point Maxima. United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service. Retrieved December 7, 2012.
- ↑ David M. Roth (October 31, 2007). Hurricane Camille - August 16-21, 1969. Weather Prediction Center]] (Report) (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved February 24, 2013.
- ↑ 1969-Debbie (Report). Moncton, New Brunswick: Environment Canada. November 6, 2009. Retrieved July 17, 2014.
- ↑ Tropical Cyclone Discussion Storm Eve (JPG). National Hurricane Center (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). August 26, 1969. Retrieved July 17, 2014.
- ↑ "Eve churns ocean, near 'cane force". The Miami News. August 26, 1969. Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ Caribbean1 (JPG) (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. 1969. Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Foreign Disaster Emergency Relief Tenth Report (PDF) (Report). Washington, D.C.: United States Agency for International Development. 1970. pp. 115–128. Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ "Hurricane Slams Honduran Coast". The News and Courier. United Press International. September 3, 1969.
- ↑ Mitch: The Deadliest Atlantic Hurricane Since 1780. National Climatic Data Center (Report) (Asheville, North Carolina: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). January 23, 2009. Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 Storm Data and Unusual Weather Phenomena: September 1969 (PDF). National Climatic Data Center (Report) (Asheville, North Carolina: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration): 132 and 133. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 18, 2014. Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ David M. Roth (March 15, 2007). Hurricane Gerda – September 5-10, 1969. Weather Prediction Center (Report) (College Park, Maryland: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ 1969-Gerda (Report). Moncton, New Brunswick: Environment Canada. September 14, 2010. Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ Robert H. Simpson (September 14, 1969). National Hurricane Center Special Bulletin. National Hurricane Center (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ Robert H. Simpson (September 14, 1969). Tropical Storm Advisory Number 1 Holly. National Hurricane Center (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ Neil L. Frank (September 15, 1969). Hurricane Advisory Number 4 Holly. National Hurricane Center (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ Gilbert B. Clark (September 16, 1969). Hurricane Advisory Number 7 Holly. National Hurricane Center (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ Tropical Storm Advisory Number 13 Holly. National Hurricane Center (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). September 17, 1969. Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 David M. Roth (August 28, 2008). Tropical Depression – September 20-25, 1969. Weather Prediction Center (Report) (College Park, Maryland: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ Special Weather Statement. Weather Bureau Office Tallahassee, Florida (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). September 21, 1969. Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ "Hurricane Inga Hammers Bermuda". The Milwaukee Sentinel (Hamilton, Bermuda). October 6, 1969. Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ Paul J. Hebert (October 6, 1969). Hurricane Advisory Number 46 Inga. National Hurricane Center (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ John R. Hope (October 6, 1969). Hurricane Advisory Number 49 Inga. National Hurricane Center (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ John R. Hope (October 12, 1969). Hurricane Advisory Number 72 Inga. National Hurricane Center (Report) (Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 37.2 37.3 37.4 David M. Roth (April 8, 2010). Subtropical Storm/T. D. #32 - September 30-October 3, 1969 (Report). Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Retrieved February 23, 2013.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "Squalls Hit Panhandle". The Palm Beach Post. October 2, 1969. p. 33. Retrieved February 23, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Data and Unusual Weather Phenomena: October 1969 (PDF) (Report). National Climatic Data Center. p. 142. Retrieved February 23, 2013.
- ↑ Jeff Masters (November 16, 2009). "The Atlantic hurricane season is effectively over; heavy rains in the Northwest". Weather Underground. Retrieved February 24, 2013.
- ↑ Neil L. Frank (November 23, 1969). National Hurricane Center Tropical Storm Advisory Number 7 Martha (Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 1, 2013.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 I. V. Chapman, Jr. (May 28, 1970). 1969 (JPG) (Report). United Fruit Company. Retrieved January 1, 2013.
- ↑ "NSS 270000". National Hurricane Center. June 27, 1969. Retrieved December 30, 2012.
- ↑ Reuters (1969). It's time (June) to match for Anna... The Daily Gleaner. Retrieved on January 4, 2009.
- ↑ Dave Baity. Hurricanes Get Women's Names For Expediency. Retrieved on January 2, 2009.
External links
| |||||||||||||