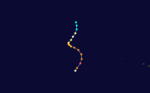1959 Pacific hurricane season
| |
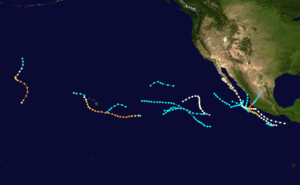
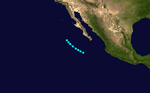
| Season summary map |
| First system formed |
June 8, 1959 |
| Last system dissipated |
October 29, 1959 |
| Strongest storm |
Patsy - 170 mph (270 km/h) – |
| Total depressions |
15 |
| Total storms |
15 |
| Hurricanes |
5 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) |
3 |
| Total fatalities |
Unknown |
| Total damage |
~ $280 million (1959 USD) |
Pacific hurricane seasons
1957, 1958, 1959, 1960, 1961 |
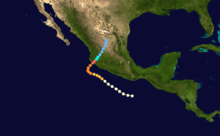
The 1959 Pacific hurricane season featured the first two Category 5 hurricanes ever recorded in the Eastern and Central Pacific basins.
During the season, 15 storms developed, 5 of those became hurricanes, and 3 of those became major hurricanes. The strongest of the storms was Hurricane Patsy, which was a Category 5 but which stayed out to sea. Patsy reached 170 miles per hour (270 km/h) winds. The deadliest storm of the season was Hurricane Fifteen, which made landfall in Mexico at Category 5 and killed 1,800 people.
Storms
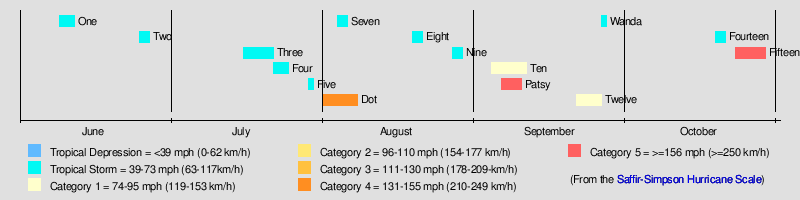
Tropical Storm One
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 9 – June 12 |
| Peak intensity |
45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 1003 mbar (hPa) |
A 55 mph (75 km/h) tropical storm was first located on June 9 while west of Mexico.[1] It did not strengthen any further as it paralleled the Mexican coast.[1] It made landfall near Los Mochis, Mexico on June 12 and dissipated shortly afterward.[1] There are no reports of damages or deaths due to the storm.
Tropical Storm Two
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 25 – June 27 |
| Peak intensity |
50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) 1006 mbar (hPa) |
On June 25, a small tropical storm developed off the coast of Mexico. It attained winds of 50 mph at its peak. It later dissipated on June 27.[2]
Tropical Storm Clara
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 16 – July 22 |
| Peak intensity |
50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) 977 mbar (hPa) |
After a month of inactivity, a tropical storm formed several thousands of miles south-west of the southern tip of Baja California. This tropical storm began moving north-westwards while keeping its intensity. Winds peaked at 50 mph (85 km/h). On July 19, this tropical storm began moving west and finally dissipated 3 days later.
The name Clara was assigned from the North Pacific Typhoon name list.
[3]
Tropical Storm Four
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 22 – July 25 |
| Peak intensity |
50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) 1004 mbar (hPa) |
Soon after Tropical Storm Three dissipated, a new tropical storm formed in the open Pacific. Tropical Storm Four moved west, then west-north-west. Like the previous 2 tropical storms, it did not affect land. It dissipated on July 25.[4]
Tropical Storm Five
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 29 – July 30 |
| Peak intensity |
45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) |
Tropical Storm Five was a short-lived tropical storm, only lasting a day. It peaked at a relatively weak 45 mph (75 km/h). It moved parallel to the Mexican coast. [5]
Hurricane Dot
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 1 – August 8 |
| Peak intensity |
150 mph (240 km/h) (1-min) 952 mbar (hPa) |
On August 1, Tropical Storm Dot was first seen southeast of Hawaii. It moved westward, strengthening to a 150 mph (240 km/h) Category 4 hurricane before turning to the northwest. It crossed over the northwestern Hawaiian islands as a minimal hurricane, and dissipated on the 8th. Dot caused around $5.5 million in damage.
The name Dot was assigned from the North Pacific Typhoon name list.
Tropical Storm Seven
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 4 – August 6 |
| Peak intensity |
45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 1010 mbar (hPa) |
On August 4, a tropical storm formed at about 26°N, quite a long way north for tropical cyclone formation. This system gradually moved west and then turned to the west-south-west late on August 5. It dissipated a couple of hours later.
Tropical Storm Eight
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 19 – August 21 |
| Peak intensity |
45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 1007 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Eight formed on August 19, a several hundred miles west of Mexico. This system did not affect land so no deaths or damages were contributed to this tropical storm. [6]
Tropical Storm Nine
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 27 – August 29 |
| Peak intensity |
45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 996 mbar (hPa) |
Just days after Tropical Storm Eight dissipated, meteorologists noticed a new tropical system that, once again, was out at sea. Although the storm reached 45 mph winds, it only lasted 2 days. [7]
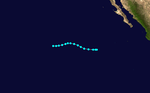
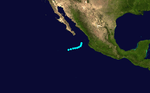
Hurricane Ten
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 4 – September 11 |
| Peak intensity |
85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min) 987 mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Ten formed off the coast of Guatemala as a Category 1 hurricane. It nearly made landfall on September 6. The system turned to the north, then NNW on September 7. It made landfall in Baja California Sur and continued along the state before weakening to a tropical storm, then a tropical depression. It dissipated near the USA-Mexico border. [8]
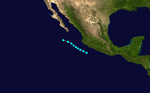
Hurricane Patsy
| Category 5 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 6 – September 10 |
| Peak intensity |
170 mph (275 km/h) (1-min) 960 mbar (hPa) |
On September 6, reports from aircraft indicated the existence of a tropical storm near the international dateline. Earlier stages were missed because of a lack of data in the isolated area. A trough moved Patsy northeast. A second trough then developed, dominated over the first, and recurved Patsy northeast. It then slowly headed northwards and gradually weakened. It dissipated on September 10. Patsy's erratic path near the dateline was unusual and no known tropical cyclone had taken such a path over the previous ten years,[9] although that of Typhoon June of 1958 was somewhat similar.[10]
The National Hurricane Center's "best track" data set has Patsy exclusively east of the dateline from detection to dissipation.[11] The Japan Meteorological Agency's "best track" does not give windspeeds, only indicating that Patsy was a typhoon.[12] The Joint Typhoon Warning Center's report disagrees on location but also has Patsy's maximum windspeed east of the dateline;[9] the JMA's data does not indicate windspeeds.[12] By reaching Category 5 intensity on September 6, 1959 it is the earliest known Pacific hurricane to reach that intensity on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale.[11] Also, its maximum reported windspeed of 150 knots (280 km/h) makes it the central Pacific hurricane with the highest sustained winds; Hurricane John tied this record in 1994. In addition, Patsy is an uncommon west-to-east crosser of the dateline. Including only systems recognized by the Central Pacific Hurricane Center, that has only happened six times since.[13]
Hurricane Twelve
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 21 – September 26 |
| Peak intensity |
85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min) 967 mbar (hPa) |
Twelve stayed to sea and was a hurricane for its life.
Tropical Storm Wanda
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 26 – September 27 |
| Peak intensity |
70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) |
Tropical Storm Wanda existed from September 26 to September 27. The name Wanda was assigned from the North Pacific Typhoon name list.
Tropical Storm Fourteen
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 19 – October 21 |
| Peak intensity |
50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) 1003 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Fourteen existed from October 19 to October 21.
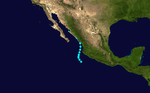
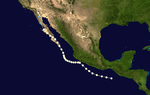
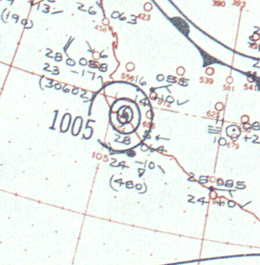
Hurricane Fifteen
| Category 5 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 23 – October 29 |
| Peak intensity |
160 mph (260 km/h) (1-min) 958 mbar (hPa) |
The most notable storm this year was the 1959 Mexico Hurricane. It made landfall as a Category 5 and killed at least 1800 people.
See also
References
|
|---|
| | <div title="{{{strength}}} "Mexico"" > | |
-
 Book Book
-
 Category Category
-
 Portal Portal
-
 WikiProject WikiProject
-
 Commons Commons
|
|