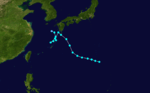
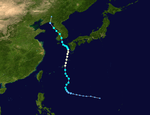
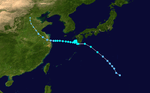
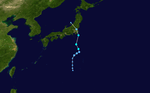
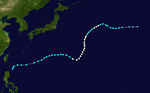
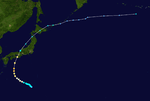
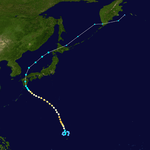
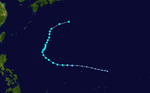
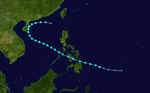
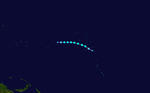
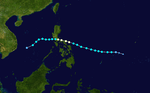
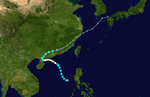
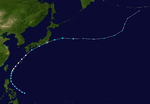
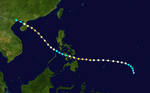
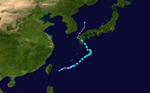
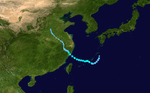
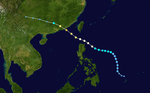
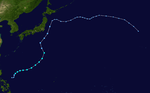
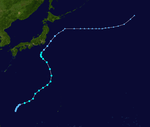
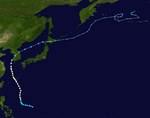
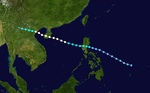
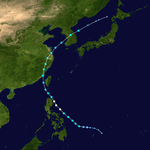
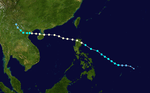
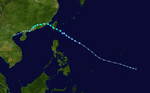
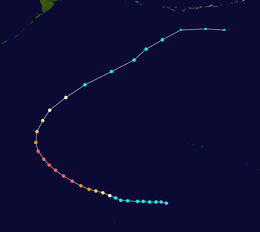
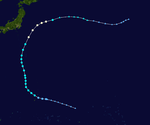
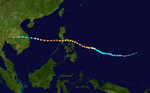
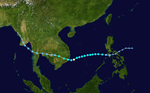
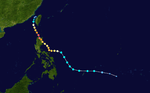
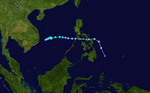
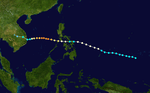
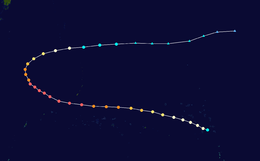
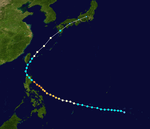
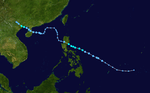
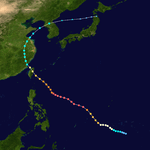
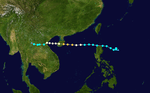
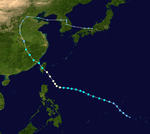
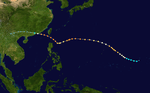
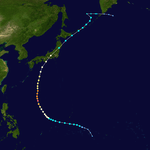
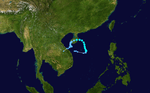
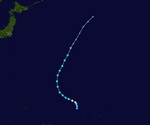
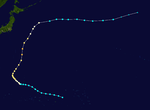
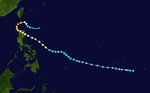
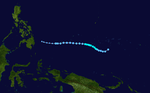
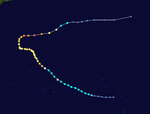
The 1950s featured the 1950–59 Pacific typhoon seasons. The seasons had no official bounds, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the international date line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1950-1959 Pacific hurricane seasons. Tropical storms formed in the entire west pacific basin were assigned a name by the North Pacific Typhoon Warning Service, Fleet Weather Center, or Joint Typhoon Warning Center.
Seasons
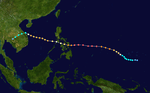
1950 Pacific typhoon season
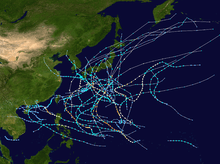
Season summary
Severe Tropical Storm 01W
| Severe tropical storm (CMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
April 12 – April 15 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 984 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Doris
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 6 – May 14 |
| Peak intensity |
240 km/h (150 mph) (1-min) 928 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 02W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 5 – June 9 |
| Peak intensity |
65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min) 997 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Elsie
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 23 – June 24 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 981 mbar (hPa) |
CMA Severe Tropical Storm 6
| Severe tropical storm (CMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 12 – July 15 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Flossie
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 15 – July 19 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 993 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Grace
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 16 – July 21 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (1-min) 981 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Helene
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 24 – August 3 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min) 991 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 13W
| Tropical storm (CMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 2 – August 4 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 992 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 15W
| Tropical storm (CMA) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 3 – August 4 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 998 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 16W
| Tropical storm (CMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 4 – August 6 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 996 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Ida
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 9 – August 21 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Storm 20W
| Severe tropical storm (CMA) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 10 – August 14 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Storm Twenty one
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 11 – August 14 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Storm 23W
| Severe tropical storm (CMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 14 – August 22 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Jane
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 29 – September 4 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 943 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Jane struck the island of Shikoku in Japan on the 3rd of September. Resulting flooding and landslides killed 539 people.
In late August, a depression formed and quickly intensified into a tropical storm and was given the name Jane. The storm drifted west-northwestward and intensified into a typhoon. Jane gradually curved to the north and intensified to a category 2 typhoon. Jane shortly reached category 3 status and peak intensity at 185 kph (115 mph). The typhoon accelerated to the north-northeast and weakened to a category 2 storm and made landfall in the modern-day Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto area. Jane crossed Kyoto Prefecture and weakened to a tropical storm and crossed the Noto Peninsula and reentered the Sea of Japan and passed just west of Sado Island. The storm struck eastern Aomori Prefecture and crossed the Tsugaru Straits and made a final landfall on the south coast of Hokkaido Prefecture. Jane crossed Hokkaido and dissipated south of the Kuril Islands.
Typhoon Kezia
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 4 – September 15 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 945 mbar (hPa) |
On September 13 Typhoon Kezia hit part of the fleet off Kyushu.
Severe Tropical Storm 26W
| Severe tropical storm (CMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 6 – September 8 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Lucretia
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 14 – September 19 |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (1-min) 987 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Missatha
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 13 – September 19 |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (1-min) 984 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Ossia
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 27 – October 6 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 966 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Petie
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 18 – October 24 |
| Peak intensity |
165 km/h (105 mph) (1-min) 978 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Storm 25W
| Severe tropical storm (CMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 26 – October 31 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Ruby
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 27 – October 31 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 918 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Billie
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 4 – November 9 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (1-min) 985 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Clara
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 4 – November 13 |
| Peak intensity |
230 km/h (145 mph) (1-min) 899 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Delilah
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 19 – November 25 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 989 mbar (hPa) |
Severe Tropical Storm Ellen
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 11 – December 13 |
| Peak intensity |
105 km/h (65 mph) (1-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Fran
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 26 – January 1 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (1-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Fran was a late season storm that struck the northern Philippines killing 5 people.[1]
1950 storm names
The names Delilah, Helene, Jane, Kezia, Lucretia, Missatha, Ossia, and Petie were retired after this year and replaced with Dot, Helen, June, Kathy, Lorna, Marie, Olga, and Pamela.
- Doris
- Elsie
- Flossie
- Grace
- Helene
- Ida
- Jane
- Kezia
- Lucretia
- Missatha
|
- Nancy
- Ossia
- Petie
- Ruby
- Anita
- Billie
- Clara
- Delilah
- Ellen
- Fran
|
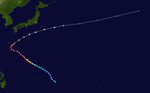
1951 Pacific typhoon season
1952 Pacific typhoon season
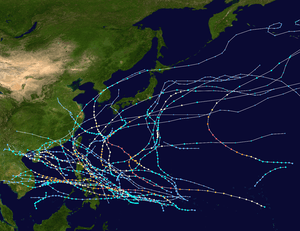
Season summary
Typhoon Charlotte
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 10 – June 15 |
| Peak intensity |
155 km/h (100 mph) (1-min) 960 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Dinah
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 19 – June 25 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 960 mbar (hPa) |
On June 23, Dinah struck to the west of the Kanto Region in Japan. 65 people were killed and 70 were missing.[2]
Typhoon Emma
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 28 – July 6 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (1-min) 975 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Freda
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 11 – July 15 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Gilda
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 15 – July 20 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Harriet
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 26 – July 30 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Ivy
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 2 – August 8 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Jeanne
| Tropical Storm (JMA) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 4 – August 7 |
| Peak intensity |
Winds unknown 985 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Karen
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 10 – August 20 |
| Peak intensity |
155 km/h (100 mph) (1-min) 955 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Lois
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 22 – August 30 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 975 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Mary
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 29 – September 4 |
| Peak intensity |
120 km/h (75 mph) (1-min) 985 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Nona
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 2 – September 8 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (1-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 12W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 7 – September 14 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Olive
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 13 – September 21 |
| Peak intensity |
295 km/h (185 mph) (1-min) 940 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 14W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 16 – September 19 |
| Peak intensity |
65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min) 996 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Polly
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 26 – October 3 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (1-min) 975 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Rose
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 4 – October 10 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (1-min) 985 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Shirley
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 14 – October 15 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Trix
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 15 – October 26 |
| Peak intensity |
220 km/h (140 mph) (1-min) 965 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Trix struck the central Philippines with winds of 140 mph. Trix struck the Bicol region hard killing 995 people.[3]
Typhoon Vae
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 17 – October 20 |
| Peak intensity |
120 km/h (75 mph) (1-min) |
Super Typhoon Wilma
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 21 – October 31 |
| Peak intensity |
295 km/h (185 mph) (1-min) 930 mbar (hPa) |
On October 26, ten people were lost when a USAF WB-29 disappeared during a flight into Super Typhoon Wilma.[4]
Super Typhoon Agnes
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 28 – November 7 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 920 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Bess
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 9 – November 16 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 915 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Carmen
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 15 – November 22 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (1-min) 960 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Della
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 22 – November 27 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Elaine
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 4 – December 6 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Faye
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 16 – December 19 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Gloria
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 16 – December 25 |
| Peak intensity |
240 km/h (150 mph) (1-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Hester
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 27 – January 4 |
| Peak intensity |
295 km/h (185 mph) (1-min) 950 mbar (hPa) |
1952 storm names
The names Jeanne, Lois, Nona, Vae and Wilma were retired after this year.
- Charlotte
- Dinah
- Emma
- Freda
- Gilda
- Harriet
- Ivy
- Jeanne
- Karen
|
- Lois
- Mary
- Nona
- Olive
- Polly
- Rose
- Shirley
- Trix
- Vae
|
- Wilma
- Agnes
- Bess
- Carmen
- Della
- Elaine
- Faye
- Gloria
- Hester
|
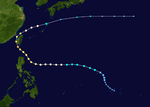
1953 Pacific typhoon season

Season summary
Typhoon Irma
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
February 18 – February 25 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Judy
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 28 – June 7 |
| Peak intensity |
220 km/h (140 mph) (1-min) 940 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Judy struck the Southern Japanese island of Kyūshū. 37 people were killed and 15 were missing.[2]
Tropical Storm 04W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 24 – June 26 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 1000 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Kit
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 25 – July 8 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 910 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Lola
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 23 – August 3 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (1-min) 970 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Mamie
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 30 – August 8 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 980 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Nina
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 8 – August 18 |
| Peak intensity |
295 km/h (185 mph) (1-min) 885 mbar (hPa) |
Nina was a major storm. It made landfall in China as a Category 4 tropical cyclone.
Tropical Storm 09W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 9 – August 11 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min) |
Typhoon Ophelia
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 12 – August 16 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 960 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Phyllis
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 15 – August 22 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 975 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Rita
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 23 – September 2 |
| Peak intensity |
230 km/h (145 mph) (1-min) 940 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 13W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 26 – August 29 |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (1-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Susan
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 15 – September 20 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (1-min) 970 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Tess
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 17 – September 27 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 900 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Tess struck the Central Honshū Island in Japan. 393 people were killed and 85 were missing.[2]
Tropical Storm 16W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 25 – September 28 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 1000 mbar (hPa) |
JMA Tropical Storm 15
| Tropical Storm (JMA) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 1 – October 3 |
| Peak intensity |
Winds unknown 999 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Viola
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 3 – October 8 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 965 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Winnie
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 6 – October 9 |
| Peak intensity |
120 km/h (75 mph) (1-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Alice
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 11 – October 23 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 915 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Betty
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 25 – November 2 |
| Peak intensity |
240 km/h (150 mph) (1-min) 965 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Cora
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 8 – November 20 |
| Peak intensity |
220 km/h (140 mph) (1-min) 960 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 22W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 25 – November 29 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 1000 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 23W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 28 – December 3 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 1000 mbar (hPa) |
Super Typhoon Doris
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 9 – December 22 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 935 mbar (hPa) |
1953 storm names
- Irma
- Judy
- Kit
- Lola
- Mamie
- Nina
- Ophelia
- Phyllis
- Rita
|
- Susan
- Tess
- Viola
- Winnie
- Alice
- Betty
- Cora
- Doris
|
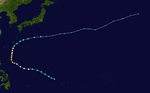
1954 Pacific typhoon season

Season summary
Tropical Storm 01W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
March 1 – March 4 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min) 990 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Elsie
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 5 – May 12 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 945 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Flossie
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 4 – July 10 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 985 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Grace
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 11 – August 19 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 940 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Grace struck the Southern Japanese islands of Kyūshū and Shikoku. 28 people were killed and 33 were missing.[2]
Typhoon Helen
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 11 – August 17 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (1-min) 965 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Ida
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 18 – August 31 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 890 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 07W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 20 – August 26 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 998 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 08W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 28 – August 31 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Kathy
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 28 – September 8 |
| Peak intensity |
165 km/h (105 mph) (1-min) 940 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon June
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 4 – September 15 |
| Peak intensity |
240 km/h (150 mph) (1-min) 910 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon June struck the Southern Japanese hitting the area west of Kanto especially hard. 107 people were killed and 39 were missing.[2]
Typhoon Lorna
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 11 – September 19 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 950 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Lorna brushed the southern coast of the Japanese island of Shikoku. 34 people were killed and 20 were missing.[2]
Typhoon Marie
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 19 – September 28 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 956 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Marie had a minimum pressure of 956 mb and a maximum windspeeds of 85 mph. Marie crossed the southern islands of Kyūshū and Shikoku before turning northeast and striking Hokkaidō island. Marie caused the ship Toya Maru to sink in the Hokkaidō Strait. 1,361 people were killed and 400 were left missing.[2]
Typhoon Nancy
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 30 – October 13 |
| Peak intensity |
155 km/h (100 mph) (1-min) 965 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Olga
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 12 – October 19 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 935 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm 15W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 24 – October 26 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 1004 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Pamela
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 27 – November 8 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 900 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Ruby
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 2 – November 11 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 940 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Sally
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 10 – November 20 |
| Peak intensity |
280 km/h (175 mph) (1-min) 925 mbar (hPa) |
Typhoon Tilda
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 22 – December 1 |
| Peak intensity |
230 km/h (145 mph) (1-min) 940 mbar (hPa) |
1954 storm names
- Elsie
- Flossie
- Grace
- Helen
- Ida
- June
- Kathy
- Lorna
|
- Marie
- Nancy
- Olga
- Pamela
- Ruby
- Sally
- Tilda
|
1955 Pacific typhoon season
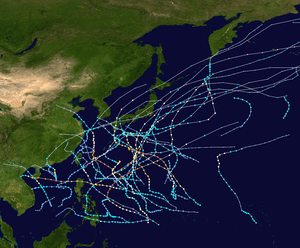
Season summary
Typhoon Louise struck the western Kyūshū Island in southern Japan. 54 people were killed and 14 were missing.[2]
- Violet
- Wilda
- Anita
- Billie
- Clara
- Dot
- Ellen
- Fran
- Georgia
- Hope
|
- Iris
- Joan
- Kate
- Louise
- Marge
- Nora
- Opal
- Patsy
- Ruth
|
1956 Pacific typhoon season
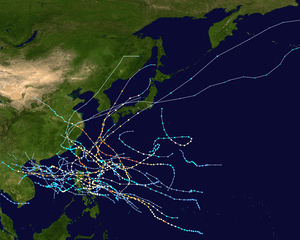
Season summary
Typhoon Sarah formed at a low latitude on March 21, 1956 and took a generally Northwest heading. On the 31st as it approached the Philippine Islands, it slowed then reversed its direction dissipating on April 4th.
On April 16, 1956, Typhoon Thelma formed near the formation place of Typhoon Sarah. Thelma struck the Philippine Islands in the 21st and passed close to Formosa on the 23rd then struck Japan. The U.S. Navy Fleet Weather Central in Guam stopped following Thelma on April 25th.
Typhoon Babs struck the western Kyūshū Island in southern Japan. 33 people were killed and 3 were missing.[2]
Emma was a powerful mid-season typhoon that struck the U.S. held island of Okinawa and South Korea. The typhoon killed 64 people with 35 missing and down millions in damage.
On August 1, Typhoon Wanda made landfall along the coast of Zhejiang, China, killing over 5700 people. This was the second strongest typhoon to hit China since 1949, after Typhoon Saomai, as well as the second deadliest since 1949, after Typhoon Nina (1975).
A moderately powerful typhoon, Harriet brought heavy rains and 110 mph winds to Japan. The typhoon destroyed 600 buildings and killed 38 people. Harriet then crossed the Sea of Japan before making a second landfall in South Korea. There, the storm brought heavy rains and gusty winds before dissipating. Harriet killed 53 people and left $50 million (1956) dollars in damage.
A weak December typhoon, Polly brought 100 mph winds and 11 inch rains to the Philippines on December 13. The typhoon killed 79 people and left $2.5 million (1956) dollars in damage.
1956 storm names
- Sarah
- Thelma
- Vera
- Wanda
- Amy
- Babs
- Charlotte
|
- Dinah
- Emma
- Freda
- Gilda
- Harriet
- Ivy
- Jean
|
- Karen
- Lucille
- Mary
- Nadine
- Olive
- Polly
|
1957 Pacific typhoon season
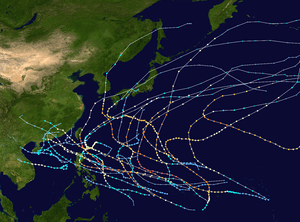
Season summary
The 1957 season was fairly active, with 17 typhoons, of which six reached supertyphoon status. Typhoon Virginia in June killed 86 people and caused $80 million in damage when it struck Taiwan and southern Japan. Typhoon Faye in September resulted in heavy damage and killed over 50 people on Okinawa.
1958 Pacific typhoon season

Season summary
The 1958 season included 23 named storms. The first storm of the season, Ophelia, crashed a recon flight into the storm on January 15.[4] In May, Typhoon Phyllis attained a peak of 185 mph, the strongest typhoon ever in the month of May.[5] Typhoon Alice caused 41 deaths and heavy damage after hitting southeastern Japan on July 22.[6] Later, Typhoon Ida reached peak winds of 200 mph on September 24 with a record low pressure (at the time) of 877 mbar.[7] It caused extensive mudslides in Japan, killed 888 people, and left 500,000 people homeless.[2][8]
1959 Pacific typhoon season
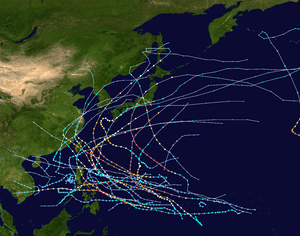
Season summary
The 1959 Pacific typhoon season featured 24 tropical cyclones, though operationally 59 total areas of investigation were classified by the
Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC);
[9] three systems were handled by the responsibility of FWB at Pearl Harbor and the USWB at Honolulu. Three systems were questionable due to lack of reconnaissance aircraft use. In total, the season featured 65 tropical cyclones and areas of investigation operationally, including central Pacific Hurricane Patsy, which was operationally believed to have crossed the International Date Line into the western Pacific.
[9] The first annual tropical cyclone report for the western North Pacific Ocean was issued by the agency.
[9]
Of the 23 tropical cyclones and 65 total areas of investigation, 17 storms attained typhoon status, which was below the yearly average of 19.
[9] At least nine other tropical systems never exceeded tropical storm intensity operationally. Most of the systems were noted to have developed within the typical spawning grounds for typhoons originating from easterly waves within the Intertropical Convergence Zone; the exceptions were Ellen and Georgia which developed from cold-core troughs extending southward into the tropical latitudes.
[9] Of the 17 typhoons that formed, five were first detected within 300 miles (500 km) of the island of Guam. Three of the typhoons developed at a slow rate, while three others rapidly intensified to typhoon status within hours. Only four typhoons were small in diameter, while at least three typhoons developed to large sizes and became the dominant tropical features during the season.
[9] Two of the typhoons — Joan and Vera — featured sea-level pressures below 900 millibars and were the most intense tropical cyclones during the season, each featuring winds of 190 mph (305 km/h) or greater.
[9]
[10]
Of the total number of typhoons, 215 reconnaissance missions were flown into the storms, including 3,799 observations and 391 total fixes. The average track error for each advisory for storms during the season was 63.9 miles (102.8 km) for 12-hour forecasts and 301.6 miles (485.4 km) for 48-hour forecasts.
[9]
See also
- List of Pacific typhoon seasons
References
External links
| 1950–1959 Pacific typhoon seasons |
|---|
| |
|