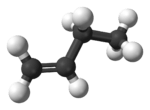
1-Butene
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
but-1-ene | |||
| Other names
ethylethylene, 1-butylene, α-butylene, but-1-ene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 106-98-9 | |||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:48362 | ||
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL117210 | ||
| ChemSpider | 7556 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image | ||
| PubChem | 7844 | ||
| |||
| UNII | LY001N554L | ||
| Properties | |||
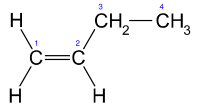
| Molecular formula |
C4H8 | ||
| Molar mass | 56.11 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless Gas | ||
| Odor | slightly aromatic | ||
| Density | 0.62 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −185.3 °C (−301.5 °F; 87.8 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −6.47 °C (20.35 °F; 266.68 K) | ||
| 0.221 g/100 mL | |||
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, ether, benzene | ||
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.3962 | ||
| Viscosity | 7.76 Pa | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.6-10% | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1-Butene is an organic chemical compound, linear alpha-olefin (alkene),[1] and one of the isomers of butene. The formula is C
4H
8.
Stability
1-Butene is stable in itself but polymerizes exothermically. It is highly flammable and readily forms explosive mixtures with air. It is, however, incompatible with metal salts, fluorine and other halogens, nitrogen oxides, boron trifluoride, hydrohalic acids, and strong oxidizing agents.
Manufacturing
1-Butene is produced either by separation from crude C4 refinery streams or from the dimerization of ethylene. It is distilled to give a very high-purity product. 1-butene is used to manufacture lots of other chemical products, such as linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), polypropylene resins, polybutene, butylene oxide, and butanone.[2]